Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
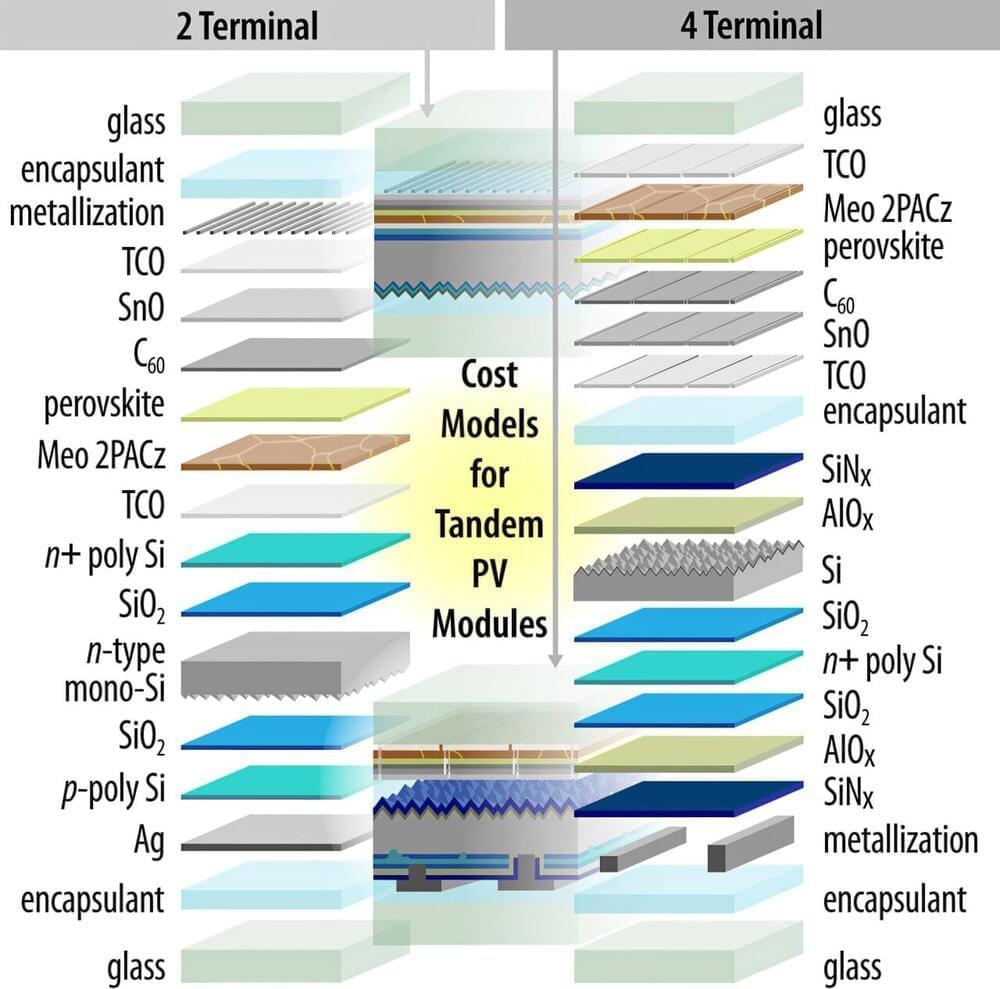
Enhanced tandem solar modules promise lower costs and higher efficiency
Increasing module efficiency and expanding manufacturing capacity play complementary roles in reducing costs of metal halide perovskite/silicon tandem solar modules, according to researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL). Each cost lever can play a similar role depending on a manufacturer’s ability to scale up and improve module performance.
Most photovoltaic (PV) modules manufactured today are based on single-junction silicon solar cells. By pairing silicon with another solar cell material such as metal halide perovskites (MHPs), thus creating a tandem, manufacturers can create a solar module that can convert more sunlight to electricity than using silicon alone.
This tandem technology is still in the early stages, and there are multiple options being pursued to integrate MHPs and silicon, with a lot of unknowns in terms of cost and performance. To address this gap, the researchers built a manufacturing cost model that combines laboratory processes with existing equipment and supply chains to compare different possible approaches at scale.
Photoacoustic spectroscopy approach achieves real-time detection of low gas concentrations
Researchers have developed a new method for quickly detecting and identifying very low concentrations of gases. The new approach, called coherently controlled quartz-enhanced photoacoustic spectroscopy, could form the basis for highly sensitive real-time sensors for applications such as environmental monitoring, breath analysis and chemical process control.
“Most gases are present in small amounts, so detecting gases at low concentrations is important in a wide variety of industries and applications,” said research team leader Simon Angstenberger from the University of Stuttgart in Germany. “Unlike other trace gas detection methods that rely on photoacoustics, ours is not limited to specific gases and does not require prior knowledge of the gas that might be present.”
In Optica, the researchers report the acquisition of a complete methane spectrum spanning 3,050 to 3,450 nanometers in just three seconds, a feat that would typically take around 30 minutes.
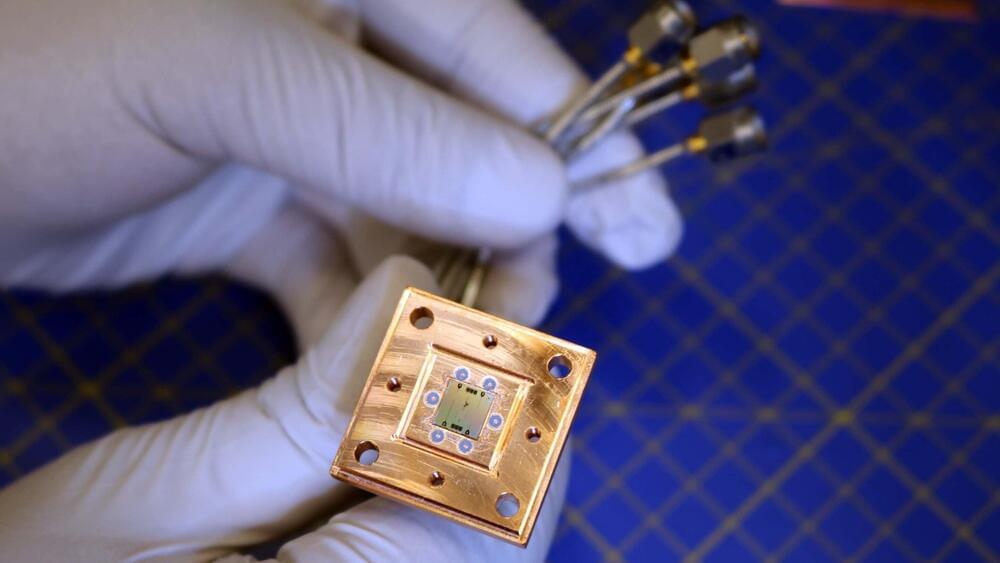
Record cold quantum refrigerator paves way for reliable quantum computers
Quantum computers require extreme cooling to perform reliable calculations. One of the challenges preventing quantum computers from entering society is the difficulty of freezing the qubits to temperatures close to absolute zero.
Now, researchers at Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, and the University of Maryland, U.S., have engineered a new type of refrigerator that can autonomously cool superconducting qubits to record low temperatures, paving the way for more reliable quantum computation.
Quantum computers have the potential to revolutionize fundamental technologies in various sectors of society, with applications in medicine, energy, encryption, AI, and logistics. While the building blocks of a classical computer—bits—can take a value of either 0 or 1, the most common building blocks in quantum computers—qubits—can have a value of 0 and 1 simultaneously.

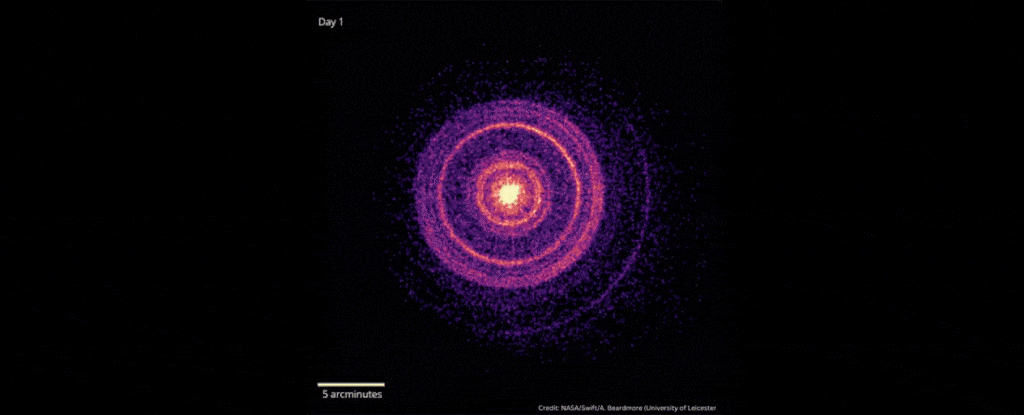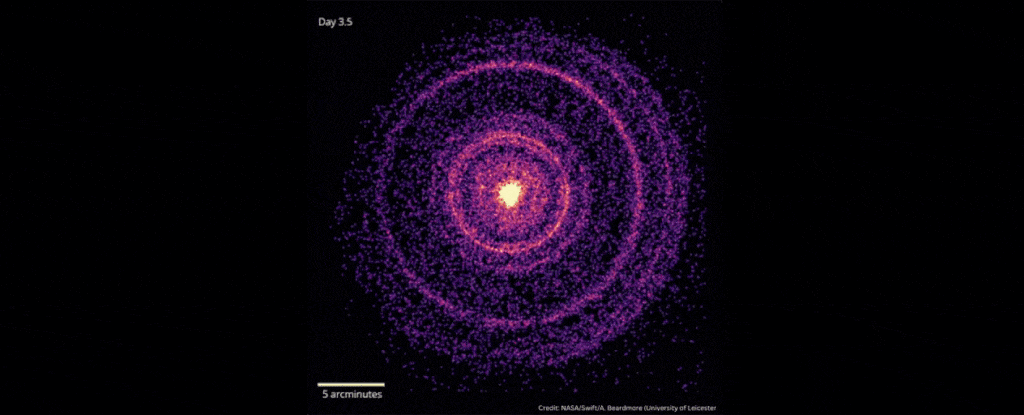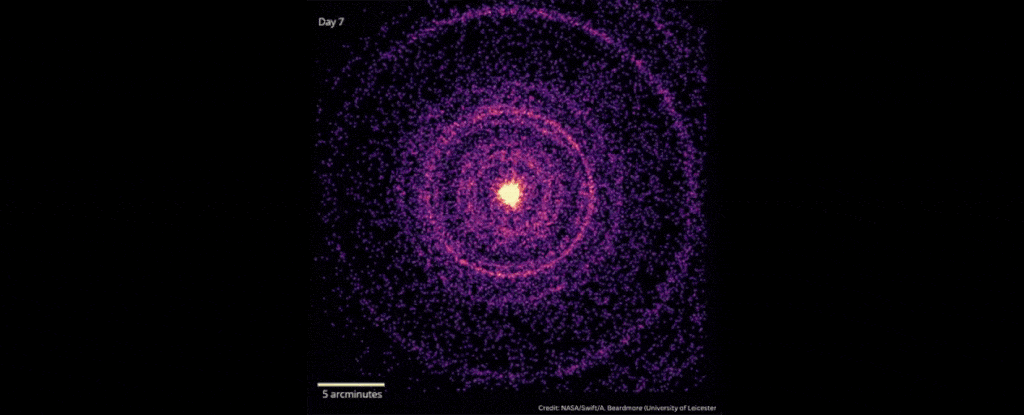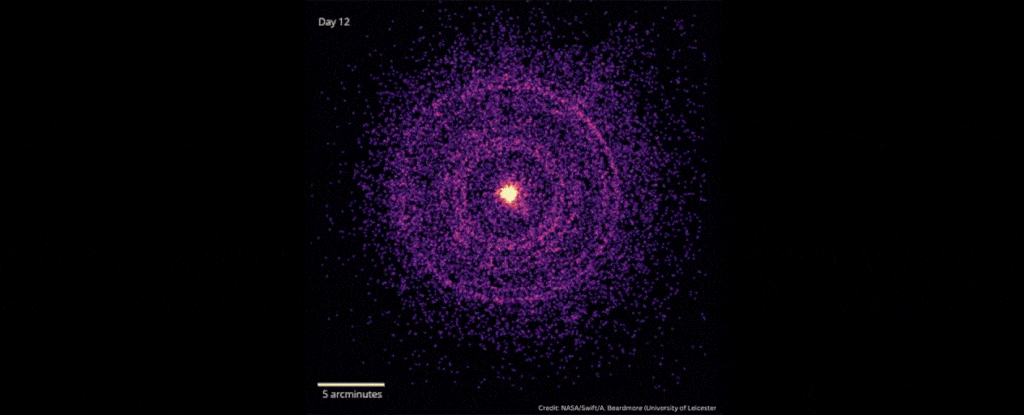
Brightest Space Explosion Ever May Hide an Elusive Dark Matter Particle
In October 2022, scientists detected the explosive death of a star 2.4 billion light-years away that was brighter than any ever recorded.
As the star’s core collapsed down into a black hole, the gamma-ray burst emitted by the star – an event named GRB 221009A – erupted with energies of up to 18 teraelectronvolts. Gamma-ray bursts are already the brightest explosions our Universe can produce; but GRB 221009A was an absolute record-smasher, earning it the moniker “the BOAT” – Brightest Of All Time.
There is, however, something wrong with the picture, according to a team of astrophysicists led by Giorgio Galanti of the National Institute for Astrophysics (INAF) in Italy. Based on cutting-edge models of the Universe, we shouldn’t be able to see photons more powerful than 10 teraelectronvolts in data from the Large High Altitude Air Shower Observatory (LHAASO) that made the detection.
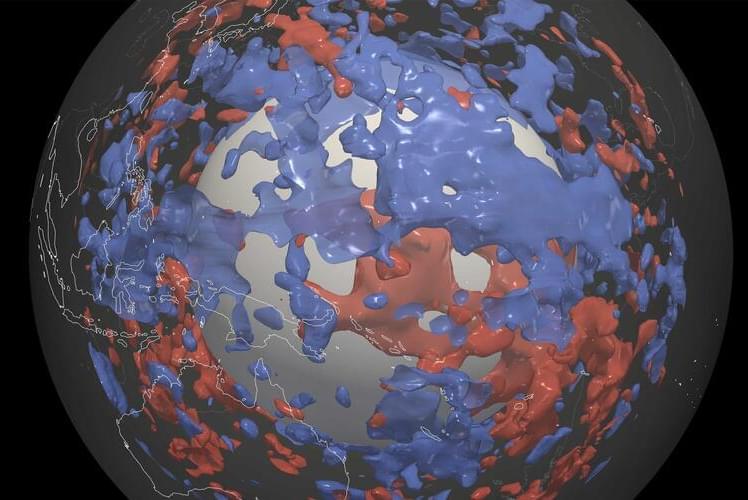
Sunken worlds under the Pacific?
Geophysicists at ETH Zurich are using models of the lower mantle to identify areas where earthquake waves behave differently than previously assumed. This indicates the presence of zones of rocks that are colder, or have a different composition, than the surrounding rocks. This finding challenges our current understanding of the Earth’s plate tectonics – and presents the researchers with a major mystery.

Smartest man in the world shares what he thinks happens after we die
CTMU https://ctmucommunity.org/wiki/Cognitive-Theoretic_Model_of_the_Universe
‘What happens after we die?’ is the most existential question humans face.
But a man with one of the highest IQs in history claims to know the answer.
Chris Langan, 72, is an American horse rancher who is alleged to have an IQ between 190 and 210. That ‘genius’ score is 30 to 50 points higher than Albert Einstein’s.