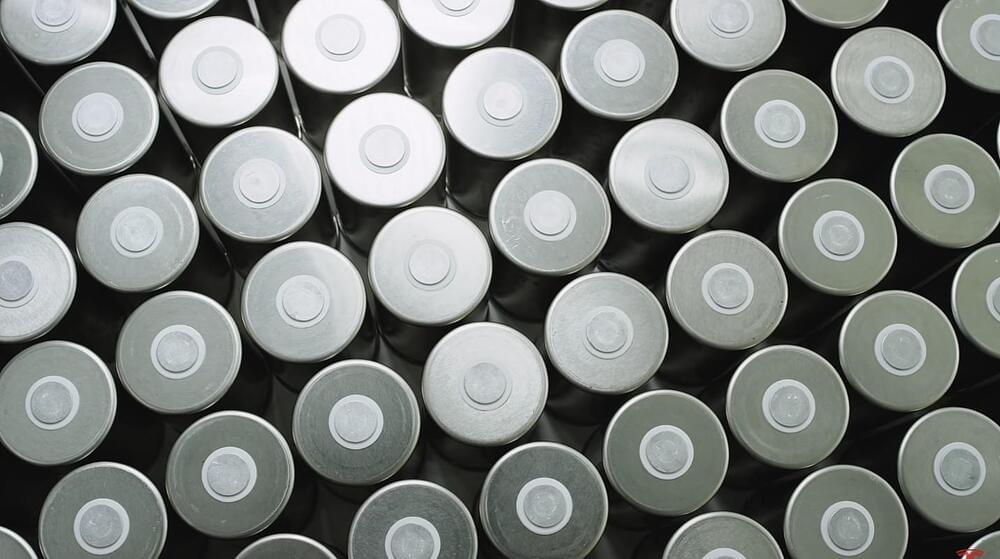
Tesla announced major progress in 4,680 battery cell production with a new milestone at Giga Texas.
“… living systems evolve to exploit any aspect of physics that enables exploration of all possible ‘fitness landscapes’.”
Indeed!
In 1990, within the intellectual haven of Haverford College, I embarked on a transformative academic journey into biophysics – the captivating intersection of physics and biology.
It was during this time that I delved into the tantalising notion of quantum mechanics operating within living organisms.
Unbeknownst to me, this exploration would etch an enduring imprint on my scientific voyage, kindling a lifelong fascination with biophysics. Ultimately, I charted my research course in quantum cosmology, but the echoes of biophysics persisted.
Scientists harnessed a new method to precisely measure the amount of information the brain can store, and it could help advance our understanding of learning.
Many fear future technologies may doom our civilization, but could the pursuit of technology, and civilization itself, be what dooms humanity?
Watch my exclusive video ISRU: https://nebula.tv/videos/isaacarthur–…
Get Nebula using my link for 40% off an annual subscription: https://go.nebula.tv/isaacarthur.
Get a Lifetime Membership to Nebula for only $300: https://go.nebula.tv/lifetime?ref=isa…
Join this channel to get access to perks:
/ @isaacarthursfia.
Visit our Website: http://www.isaacarthur.net.
Join Nebula: https://go.nebula.tv/isaacarthur.
Support us on Patreon: / isaacarthur.
Support us on Subscribestar: https://www.subscribestar.com/isaac-a…
Facebook Group: / 1583992725237264
Reddit: / isaacarthur.
Twitter: / isaac_a_arthur on Twitter and RT our future content.
SFIA Discord Server: / discord.
Credits:
The Fermi Paradox: Timebombs.
Episode 450; June 6, 2024
Written, Produced \& Narrated by: Isaac Arthur.
Sound Music Courtesy of:
Epidemic Sound Epidemic Sound http://epidemicsound.com/creator.
Stellardrone, \
GSK announced a major breakthrough concerning cancer therapy. A drug called Jemperli (dostarlimab) showed impressive results in a phase 2 trial at the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSK). The study included 42 patients suffering from mismatch repair deficient (dMMR) locally advanced rectal cancer, a type of bowel cancer.
Used as a first-line treatment and an alternative to chemotherapy and surgery, Jemperli cured cancer in all patients, showing “an unprecedented 100% clinical complete response rate.” Tests that followed showed no evidence of remaining tumors. Moreover, the first 24 of the 42 patients were observed after an average time of 26.3 months, and they showed no signs of cancer resurfacing.
GSK will test the drug in additional studies involving certain types of colorectal cancers.
Welcome to episode 2 of our behind-the-scenes series as we document space exploration. In this episode, join our team as we capture slow-motion footage of SpaceX’s Starship at Starbase, record powerful liftoff audio, share stereoscopic VR from up close, and journey to the top of NASA’s Vehicle Assembly Building for an exciting astronaut launch. Thank you for watching!
Want to support the work we do? Get access to our exclusive Discord server and collect member-only perks. Support the team on Patreon: / cosmicperspective.
or join on Youtube: / @cosmicperspective.
Early access to the full 100x slowmo: / starship-engines-105298825
Explore the Beta release of our IFT-3 Stereoscopic 3D film on Oculus headsets https://www.meta.com/experiences/4722…
(Apple Vision Pro Sideload video files available for patrons)
Music by @annu__music (MaryLiz)
Launch Audio by Andrew Keating, Cosmic Perspective.
The Cosmic Perspective team: Ryan and MaryLiz Chylinski, Andrew Keating, Nick Jakubik, Kelly Rodriguez, John Pisani, J. Trent Adams, and an extra special thanks to the Everyday Astronaut crew and our friends and volunteers!
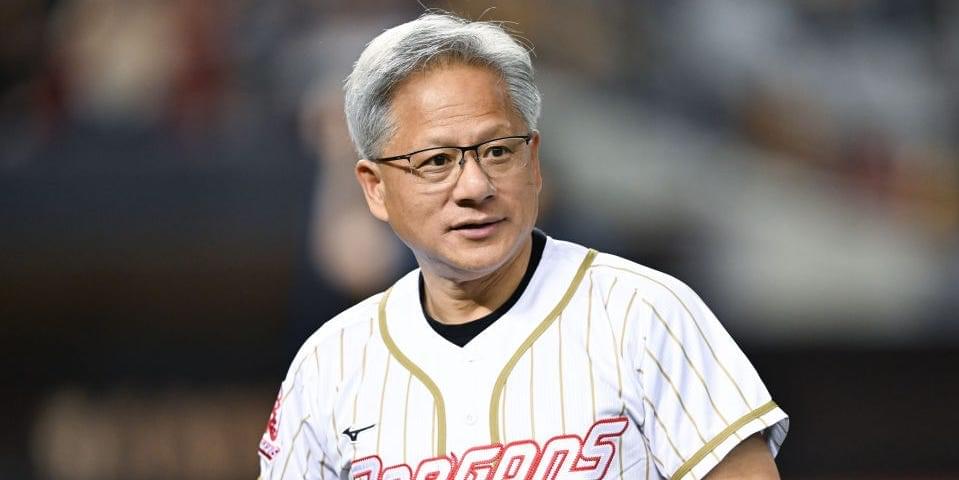
Nvidia stock has surged by more than 700% since the start of last year, boosting CEO Jensen Huang’s wealth by about $93 billion.
Starship Flight Test 4 (unofficially IFT-4) will be the 4th flight of Starship. The current launch date is set for NET June 6, 2024. [1] Ship 29 (S29) and Booster 11 (B11) will be used for this mission. Both vehicles have received upgrades since Flight 3. The fourth flight test of Starship is currently planned for the 6th of June, 2024 at 7 am CDT, pending regulatory approval. The test profile of this mission is almost identical to the one on Flight 3, but there are some changes. The most notable of these changes are the jettison of the hot stage ring from B11 and a soft, engine powered landing for S29. The goals for the fourth flight per SpaceX: \.