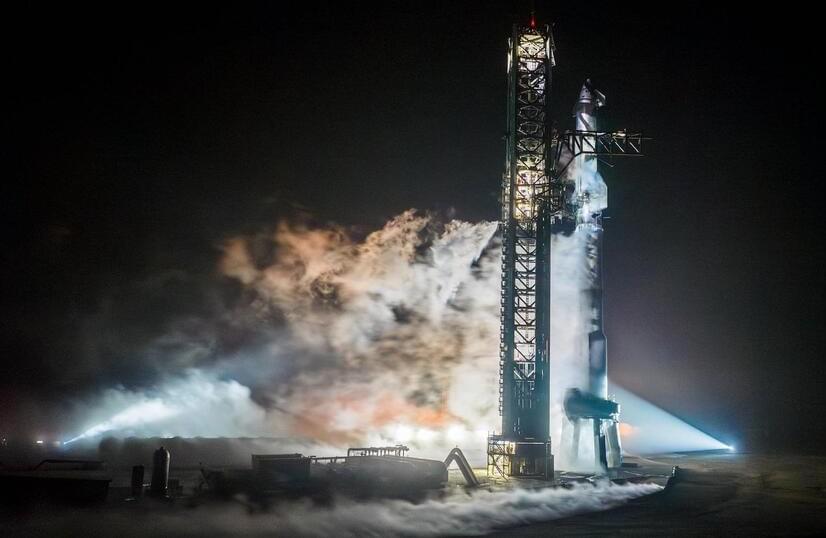
Starship will attempt a controlled reentry as well as the first re-light of a Raptor engine. It could fly again next week.
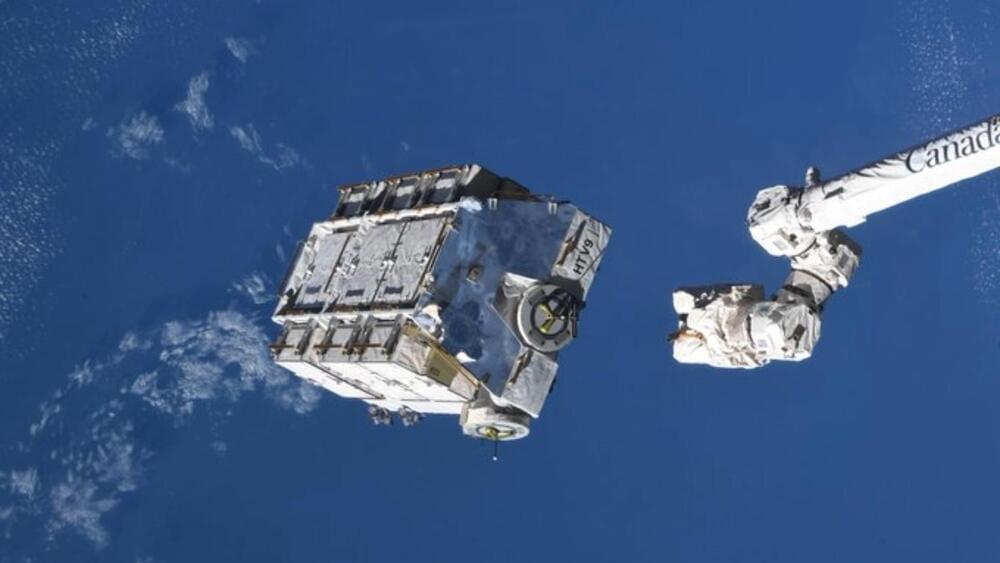
This 2.6-metric-ton cargo pallet is now slated to naturally reach the Earth’s atmosphere between March 8 and 9, 2024.
Very small solar panels placed on the eye can send electric signals directly to the brain and restore vision.
“The goal is to make all these parts work together effectively on a single platform, which would greatly reduce the loss of signals and remove the need for extra technology,” said Quinlan. “Phase one of this project was to show that all these individual pieces work together. Phase two is putting them together on the chip,” he added.
A team of researchers from several prestigious institutions helped NIST with this amazing achievement. These included the University of Colorado Boulder, the NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory, the California Institute of Technology, the University of California Santa Barbara, the University of Virginia, and Yale University.
“I like to compare our research to a construction project. There are a lot of moving parts, and you need to make sure everyone is coordinated so the plumber and electrician show up at the right time in the project,” said Quinlan. We all work together really well to keep things moving forward,” he added.
“But in the process, we also made a major finding: that hydrovoltaic devices can operate over a wide range of salinities, contradicting prior understanding that highly purified water was required for best performance.”
The process can generate power around the clock since evaporation occurs at various temperatures and even at night. The process also occurs across humidities, making it suitable for use across the planet, irrespective of location.
India has the lowest number of women in R&D jobs in the world, with less than 16.6% being women in 2018.
Learn about the exciting career shift of Remi Cadene, from Tesla to Hugging Face, and their new open robotics project.
As it stands, the draft policy would undermine the long-standing Bayh-Dole Act, with unintended consequences for innovation.
OpenAI has announced new additions to its board of directors, including CEO Sam Altman, who lost his seat in a power struggle months ago.
The film industry, always at the forefront of technological innovation, is increasingly embracing artificial intelligence (AI) to revolutionize movie production, distribution, and marketing. From script analysis to post-production, Already AI is reshaping how movies are made and consumed. Let’s explore the current applications of AI in movie studios and speculates on future uses, highlighting real examples and the transformative impact of these technologies.
AI’s infiltration into the movie industry begins at the scriptwriting stage. Tools like ScriptBook use natural language processing to analyze scripts, predict box office success, and offer insights into plot and character development. For instance, 20th Century Fox employed AI to analyze the script of Logan, which helped in making informed decisions about the movie’s plot and themes. Consider, in pre-production, AI has also aided in casting and location scouting. Warner Bros. partnered with Cinelytic to use AI for casting decisions, evaluating an actor’s market value to predict a film’s financial success. For example, let’s look at location scouting. AI algorithms can sift through thousands of hours of footage to identify suitable filming locations, streamlining what was once a time-consuming process.
During filmmaking, AI plays a crucial role in visual effects (VFX). Disney’s FaceDirector software can generate composite expressions from multiple takes, enabling directors to adjust an actor’s performance in post-production. This technology was notably used in Avengers: Infinity War to perfect emotional expressions in complex CGI scenes. Conversely, AI-driven software like deepfake technology, though controversial, has been used to create realistic face swaps in movies. For instance, it was used in The Irishman to de-age actors, offering a cost-effective alternative to traditional CGI. Additionally, AI is used in color grading and editing. IBM Watson was used to create the movie trailer for Morgan, analyzing visuals, sounds, and compositions from other movie trailers to determine what would be most appealing to audiences.