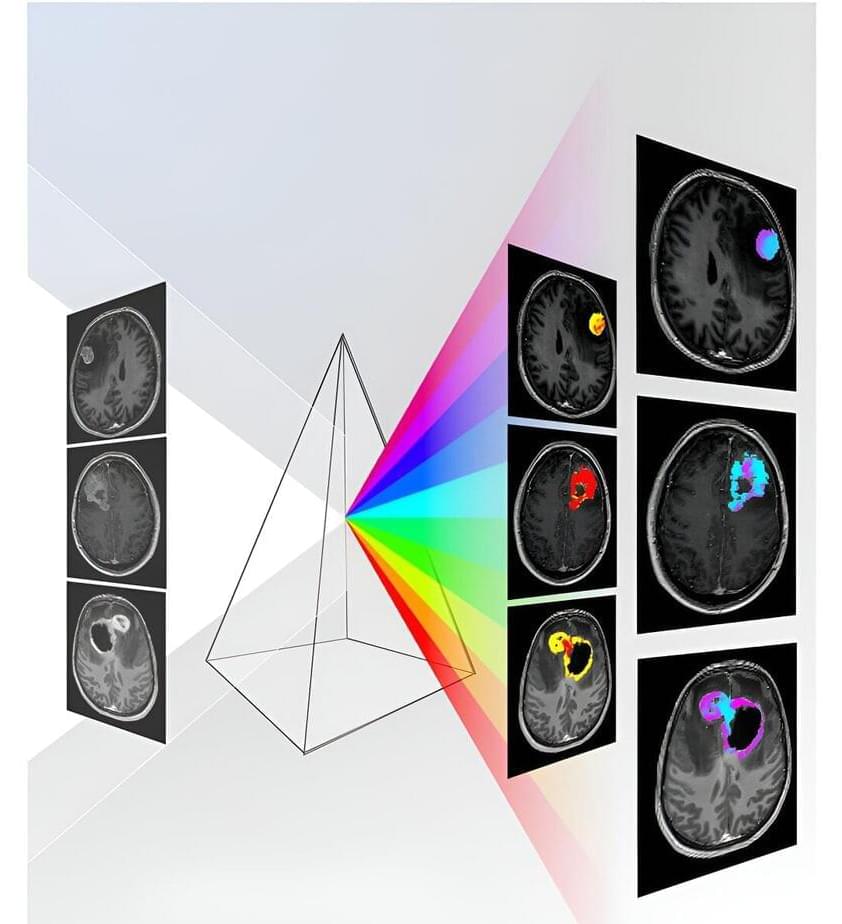
Jointly developed by investigators of the Vall d’Hebron Institute of Oncology’s (VHIO) Radiomics Group and the Bellvitge University Hospital’s Neuroradiology Unit, the Diagnosis in Susceptibility Contrast Enhancing Regions for Neuroncology (DISCERN) is an open-access deep learning tool based on the training of patterns using artificial intelligence models from information of standard magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
More than a dozen state attorneys general (AGs) are accusing banking titan Wells Fargo of abruptly terminating customers’ accounts without warning.
In a letter addressed to Wells Fargo CEO Charles Scharf, 16 Republican AGs across the country accuse the trillion-dollar lender of debanking customers in a political and discriminatory manner.
The AGs say Wells Fargo has started a new trend that looks at clients’ political views as a basis for retaining banking access.
Lt solution for ht problem.
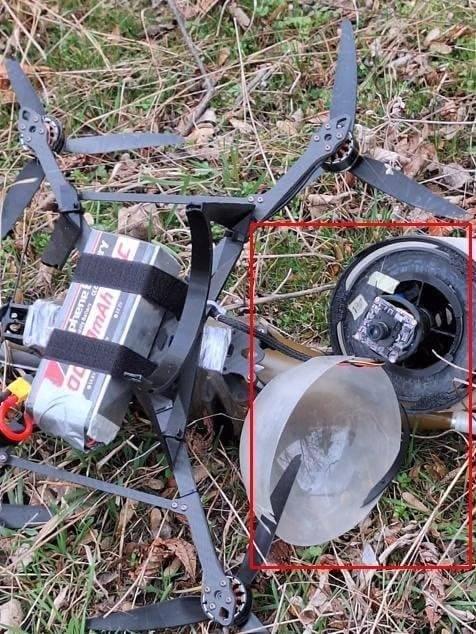
The Ukrainians recently captured a Russian drone which communicates via a fiber-optic link, making it jam-proof. This looks like a big headache and not just for Ukraine.
Models Large Language Model Agents and swarms thereof as computational graphs reflecting the hierarchical nature of intelligence.
Graph optimization automatically improves nodes and edges.
V/ @SchmidhuberAI #AI #LLM
How LLM #AI can make a patient-friendly— more understandable, more concise— hospital discharge summary for patients.
Generative artificial intelligence to transform inpatient discharge summaries to patient-friendly language and format.
This cross-sectional study, as part of a larger project to improve care delivery in our health system, was deemed exempt from institutional review board review based on the NYU Langone Health self-certification protocol. The study followed the Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) reporting guideline.
This was a cross-sectional review of 50 inpatient discharge summaries. The number 50 was chosen a priori based on feasibility. We used Epic Systems reporting workbench to export a dataset containing metadata for all notes of the Discharge Summary Note type across NYU Langone Health Systems from June 1 to 30, 2023, totaling 5,025 summaries. We used the Excel 2016 rand() function (Microsoft Corporation) to generate a random number corresponding to each note and selected the 200 notes with the lowest random number. A single reviewer confirmed the identified notes were actual discharge summaries written by the General Internal Medicine service and that the patients were not discharged as dead. For final inclusion in the study, we selected 50 of the remaining notes with the lowest random numbers. Our sample included discharges from all of NYU Langone’s hospital campuses and did not include more than 1 discharge from any single patient.
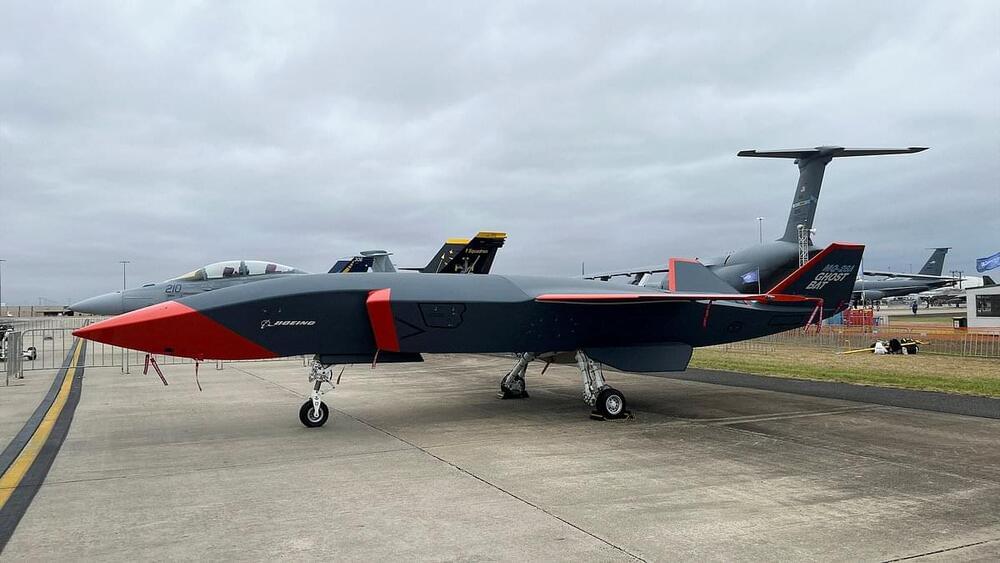
Five aerospace companies are bidding for the $6 billion contract to produce new unmanned aircraft for the Air Force. The planes will be AI-piloted and will be able to perform dangerous maneuvers.
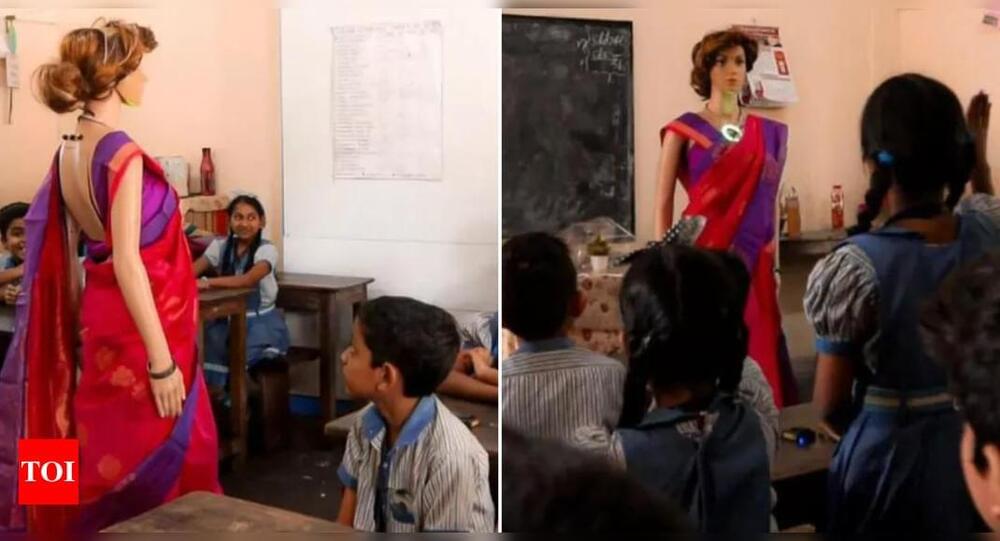
Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala: A school in Kerala is taking what may be called a revolutionary step towards revamping education with the introduction of Iris, claimed to be the first-ever AI teacher robot in the state.
The KTCT Higher Secondary School, a venture of the Kaduvayil Thangal Charitable Trust, unveiled Iris last month in collaboration with Makerlabs Edutech Private Limited. The Iris robot is designed to be more than just a robot. Built as part of the Atal Tinkering Lab (ATL) project by NITI Aayog, Iris is equipped to answer complex questions across various subjects in three different languages. It can also provide personalized voice assistance and facilitate interactive learning experiences.
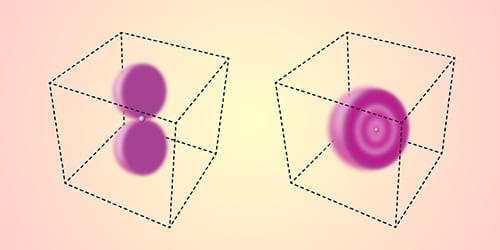
Physicists used to think they had a good idea of the size of the proton. Values derived from measurements of hydrogen’s emission spectrum and from electron-scattering experiments agreed with a proton radius of around 0.88 femtometers (fm). Then, in 2010, confidence was shaken by a spectral measurement that indicated a proton radius of approximately 0.84 fm [1]. In the years since, this “proton radius puzzle” has become even more of a head-scratcher, with some experiments supporting the original estimate and others finding an even greater discrepancy. Simon Scheidegger and Frédéric Merkt at the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (ETH), Zurich, have now made precise new measurements of the transition energies between one of hydrogen’s metastable low-energy states and several of its highly excited states [2] (Fig. 1). These measurements allow the researchers to derive some of the atom’s properties, such as its ionization energy, with greater confidence, which should help clear up some of the confusion.
The 2010 study that “shrank the proton” (as the title of the editorial summary in Nature jokingly stated) concerned the 2 S –2 P1/2 Lamb shift [1]. According to Dirac’s predictions, the 2 S and 2 P1/2 levels of atomic hydrogen should be degenerate. The Lamb shift refers to the lifting of this degeneracy by quantum electrodynamic (QED) effects, the largest contribution being the electron “self-energy” due to interactions with virtual photons. Once this and other QED effects are accounted for, a tiny shift of the bound-state energy levels remains, which can be attributed to the proton’s finite size. By measuring this residual energy shift, one can determine the proton radius directly. The authors of the 2010 study did so using hydrogen atoms in which the electron was replaced by its heavier cousin, the muon, since the finite-size effect is stronger in this system.
Ever since that surprise result, researchers have tried to pin down the proton radius both directly, via the finite-size effect, and indirectly, via the Rydberg constant. The Rydberg constant relates an atom’s energy levels to other physical constants and is one of the key inputs used in calculations of the proton radius. Determining its value requires painstaking measurements of the transition energies between hydrogen’s various states. Several groups have made monumental efforts in this regard, but the values they derive for the proton radius have been all over the place. A 2018 measurement of the 1 S –3 S transition by a group in France gave a value of about 0.88 fm [3], a 2019 measurement of the classic Lamb shift (this time in regular hydrogen) by a group in Canada came up with a value of about 0.833 fm [4], and a 2017 measurement of the 2 S –4 P transition by a group in Germany suggested a similarly low value of about 0.834 fm [5]. In 2020, the group in Germany arrived at a slightly higher value of 0.848 fm [6]. In 2022, finally, from measurements of the 2 S –8 D transition, a group at Colorado State University proposed a “compromise value” of about 0.86 fm [7].
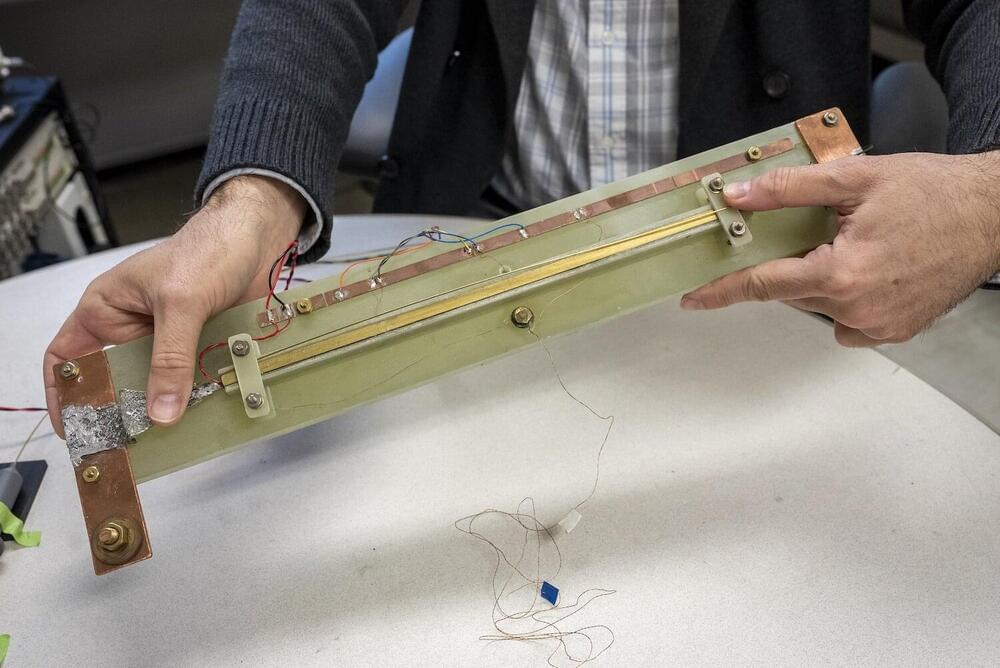
The particle accelerators that enable high-energy physics and serve many fields of science, such as materials, medical, and fusion research, are driven by superconducting magnets that are, to put it simply, quite finicky.
When we recycle electronic devices we can no longer use, we expect to make the most out of the precious natural resources that went into building them. But electronic waste is notoriously difficult to recycle because it’s hard to separate the different metals in the waste from each other.