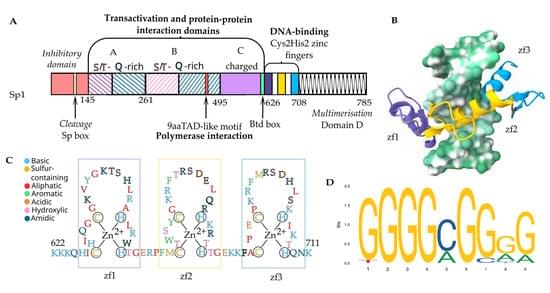
Specificity protein 1 (Sp1) is a highly ubiquitous transcription factor and one employed by numerous viruses to complete their life cycles. In this review, we start by summarizing the relationships between Sp1 function, DNA binding, and structural motifs. We then describe the role Sp1 plays in transcriptional activation of seven viral families, composed of human retro- and DNA viruses, with a focus on key promoter regions. Additionally, we discuss pathways in common across multiple viruses, highlighting the importance of the cell regulatory role of Sp1. We also describe Sp1-related epigenetic and protein post-translational modifications during viral infection and how they relate to Sp1 binding. Finally, with these insights in mind, we comment on the potential for Sp1-targeting therapies, such as repurposing drugs currently in use in the anti-cancer realm, and what limitations such agents would have as antivirals.