Scientists control atomically thin semiconductors using ultrashort pulses of terahertz light.
Discover how ultrashort terahertz light pulses can control semiconductors, leading to faster electronic components.
Scientists control atomically thin semiconductors using ultrashort pulses of terahertz light.
Discover how ultrashort terahertz light pulses can control semiconductors, leading to faster electronic components.
A team of researchers in Finland has set a new world record for how long a quantum bit, known as a qubit, can hold onto its information.
They have pushed the coherence time of a superconducting transmon qubit to a full millisecond at best, with a median time of half a millisecond. That might sound brief, but in the world of quantum computing, it’s a massive improvement that could change the game.
Longer coherence times mean qubits can run more operations and quantum computers can perform more calculations before errors start to appear.
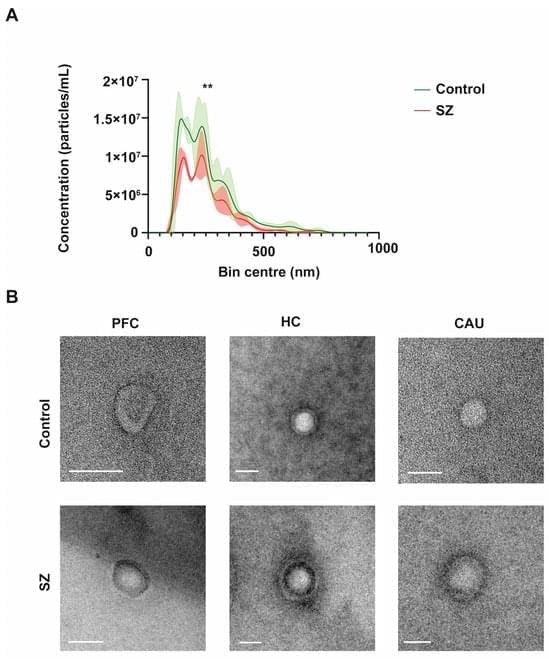
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are tiny membranous structures that mediate intercellular communication. The role(s) of these vesicles have been widely investigated in the context of neurological diseases; however, their potential implications in the neuropathology subjacent to human psychiatric disorders remain mostly unknown. Here, by using next-generation discovery-driven proteomics, we investigate the potential role(s) of brain EVs (bEVs) in schizophrenia (SZ) by analyzing these vesicles from the three post-mortem anatomical brain regions: the prefrontal cortex (PFC), hippocampus (HC), and caudate (CAU). The results obtained indicate that bEVs from SZ-affected brains contain region-specific proteins that are associated with abnormal GABAergic and glutamatergic transmission.


Join us on Patreon! https://www.patreon.com/MichaelLustgartenPhD
Discount Links/Affiliates:
Blood testing (where I get the majority of my labs): https://www.ultalabtests.com/partners/michaellustgarten.
At-Home Metabolomics: https://www.iollo.com?ref=michael-lustgarten.
Use Code: CONQUERAGING At Checkout.
Clearly Filtered Water Filter: https://get.aspr.app/SHoPY
Epigenetic, Telomere Testing: https://trudiagnostic.com/?irclickid=U-s3Ii2r7xyIU-LSYLyQdQ6…M0&irgwc=1
Use Code: CONQUERAGING
NAD+ Quantification: https://www.jinfiniti.com/intracellular-nad-test/

A team of researchers, led by Raúl Jiménez, an ICREA scientist at the University of Barcelona’s Institute of Cosmos Sciences (ICCUB), and working in partnership with the University of Padua (Italy), has introduced a groundbreaking new theory about how the Universe began.
Published in Physical Review Research, their study offers a major shift in how scientists understand the earliest moments following the Big Bang.
The Big Bang is the leading cosmological model explaining how the universe as we know it began approximately 13.8 billion years ago.
Detroit has become a hotbed for robot startups whose machines can mow lawns, remove snow, and pick up trash on city beaches.
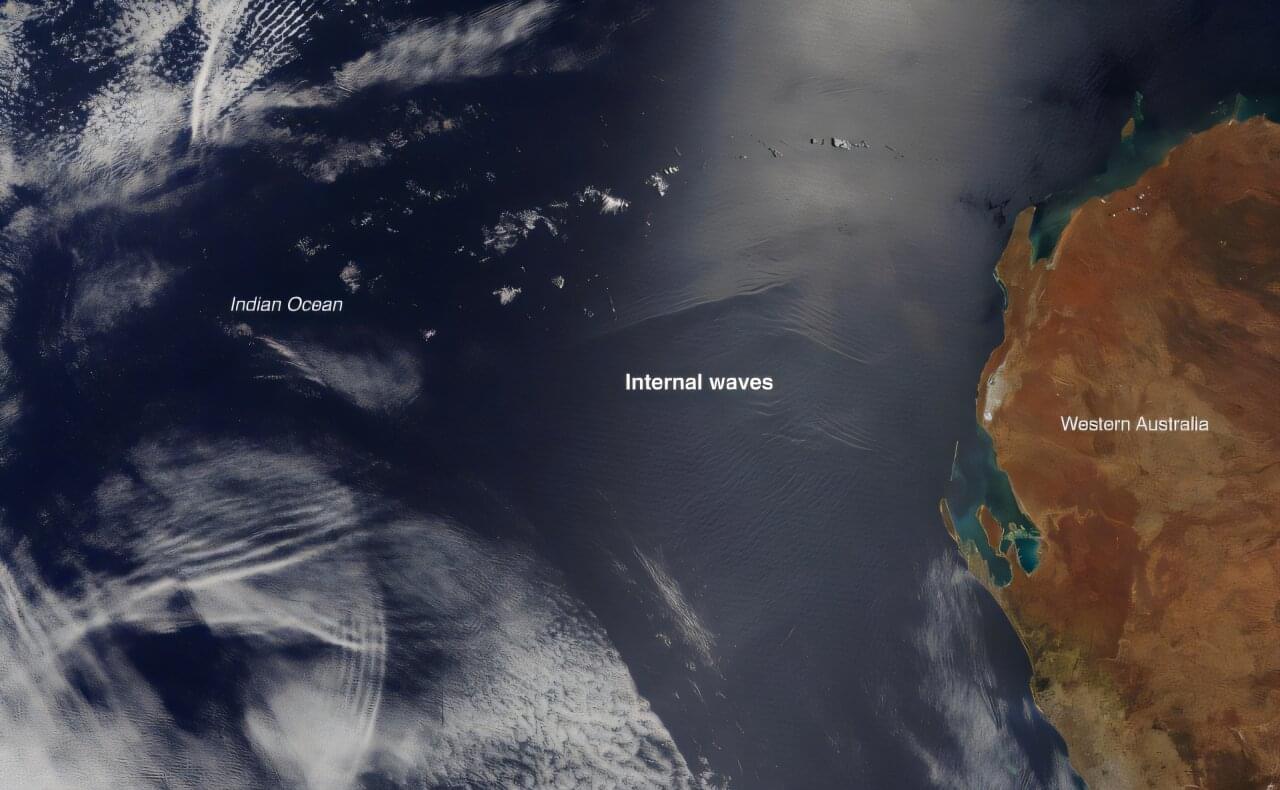

Deep below the surface of the ocean, unseen waves roil and churn the water. These internal waves, traveling between water layers of different temperatures and densities, draw cold, nutrient-rich water up from the depths and play a major role in oceanic circulation. Understanding and modeling their behavior is critical for developing more accurate simulations of an increasingly unpredictable climate.
In a Nature Communications paper, Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute (RPI) Math Professor Yuri V. Lvov, Ph.D. and a team of oceanographers develop a first-of-its-kind model of internal wave dynamics that lays the foundation for new, more reliable models of ocean circulation.
“Internal, wave-driven, vertical mixing is believed to be a main driver of oceanic circulation,” Lvov said. “It shapes Earth’s climate by influencing sea level rise, nutrient fluxes, marine ecosystems, and anthropogenic heat and carbon uptake.”