An experiment 180 years ago first demonstrated a connection between light and electromagnetism – but the link is deeper than we thought


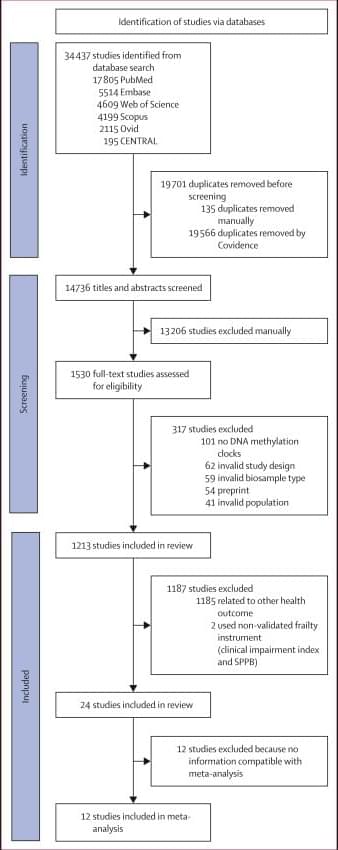
Higher GrimAge EAA is consistently associated with higher frailty. Future research should focus on developing and validating DNA methylation clocks that integrate molecular surrogates of health risk and are specifically trained to predict frailty in large, harmonised, longitudinal cohorts, enabling their translation into clinical practice.

A researcher who completed numerous brain scans found that her cerebral cortex volume was 1% smaller while using hormonal contraceptives.
Read this article at.
A researcher who underwent dozens of brain scans discovered that the volume of her cerebral cortex was 1 per cent lower when she took hormonal contraceptives.
By Grace Wade

Physicists from Oxford and Lisbon have run a full 3D, time-resolved simulation showing that empty space can act like a nonlinear medium. Their model finds that three intense laser pulses make photons rebound and forge a fourth beam, echoing a long-standing prediction from quantum electrodynamics.
Classical physics treats vacuum as an absence. Quantum theory disagrees. The vacuum teems with flickering pairs of virtual electrons and positrons that borrow energy briefly and vanish. Strong electromagnetic fields can polarize those pairs. That tiny response turns “nothing” into a medium with a faint optical nonlinearity.
When three high-power laser pulses cross at the right angles and frequencies, quantum electrodynamics (QED) predicts four-wave mixing in vacuum. The combined fields nudge virtual pairs, which then mediate photon‑photon scattering. A new, phase‑matched beam should appear with a frequency and direction dictated by the input pulses.

There’s always a touch of melancholy when a chapter that has absorbed years of work comes to an end. In the case of the Atacama Cosmology Telescope (ACT), those years amount to nearly 20—and now the telescope has completed its mission. Yet some endings are also important beginnings, opening new paths for the entire scientific community.
The three papers published in the Journal of Cosmology and Astroparticle Physics by the ACT Collaboration describe and contextualize in detail the sixth and final major ACT data release—perhaps the most important one—marking significant advances in our understanding of the universe’s evolution and its current state.
ACT’s data clarify several key points: the measurement of the Hubble constant (the number that indicates the current rate of cosmic expansion—the universe’s “speedometer”) obtained from observations at very large cosmological distances is confirmed, and it remains markedly different from the value derived from the nearby universe. This is both a problem and a remarkable discovery: it confirms the so-called “Hubble tension,” which challenges the model we use to describe the cosmos.
The bone marrow usually works quietly in the background. It only comes into focus when something goes wrong, such as in blood cancers. In these cases, understanding exactly how blood production in our body works, and how this process fails, becomes critical.
Typically, bone marrow research relies heavily on animal models and oversimplified cell cultures in the laboratory. Now, researchers from the Department of Biomedicine at the University of Basel and University Hospital Basel have developed a realistic model of the bone marrow engineered entirely from human cells. This model may become a valuable tool not only for blood cancer research, but also for drug testing and potentially for personalized therapies, as reported by a team of researchers led by Professor Ivan Martin and Dr Andrés García García in the journal Cell Stem Cell.
Researchers are realistically recreating human bone marrow in the laboratory using artificial bone structures and human cells.

Through the actuation of vibronic modes in cell-membrane-associated aminocyanines, using near-infrared light, a distinct type of molecular mechanical action can be exploited to rapidly kill cells by necrosis. Vibronic-driven action (VDA) is distinct from both photodynamic therapy and photothermal therapy as its mechanical effect on the cell membrane is not abrogated by inhibitors of reactive oxygen species and it does not induce thermal killing. Subpicosecond concerted whole-molecule vibrations of VDA-induced mechanical disruption can be achieved using very low concentrations (500 nM) of aminocyanines or low doses of light (12 J cm-2, 80 mW cm-2 for 2.5 min), resulting in complete eradication of human melanoma cells in vitro. Also, 50% tumour-free efficacy in mouse models for melanoma was achieved. The molecules that destroy cell membranes through VDA have been termed molecular jackhammers because they undergo concerted whole-molecule vibrations. Given that a cell is unlikely to develop resistance to such molecular mechanical forces, molecular jackhammers present an alternative modality for inducing cancer cell death.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
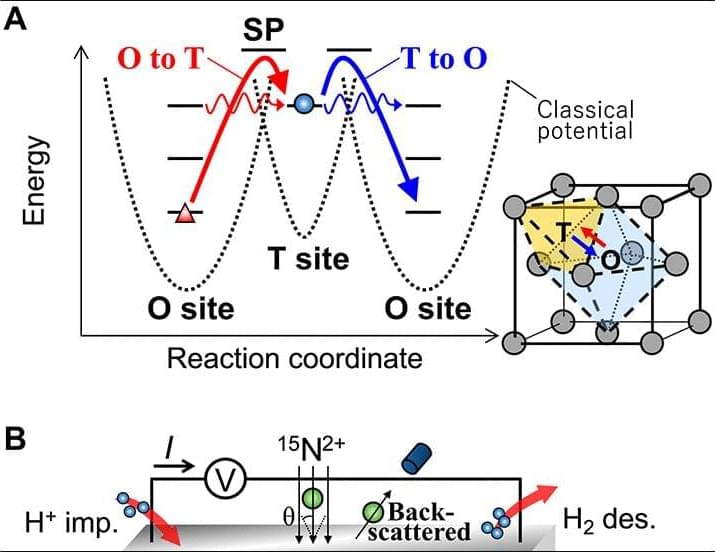
Hydrogen in materials finds various applications such as hydrogen storage and heterogeneous catalysis (1–3). Hydrogen diffusion is an elementary step for hydrogen storage and reactions and has long been studied to date. Hydrogen, as the lightest and smallest atom, manifests nuclear quantum effects including the zero-point vibration, discrete vibrational energy levels, and quantum tunneling (4). These quantum effects are believed to have a substantial impact on diffusion at low temperatures.
The interaction of hydrogen with surroundings such as phonons and electrons of host materials can be crucial for the hydrogen tunneling. It has been theoretically suggested that whereas phonon effects associated with lattice deformation bring about a positive temperature dependence in the tunneling rate, the effect of nonadiabatic electron-hole pair excitation due to the presence of the Fermi surface causes a slightly negative temperature dependence in metals (5–10). From an experimental viewpoint, however, such temperature-dependent tunneling was rarely observed except for some cases of H on metal surfaces (11–19). As for three-dimensional systems, the tunneling was only mimicked by muon, a light isotope with about one-ninth the mass of H, in the spin relaxation experiments in simple metals (20–23). Detailed experimental data of the temperature-dependent hydrogen hopping rate at low temperatures in materials are still lacking to comprehensively elucidate the quantum nature of hydrogen.
Absorbed hydrogen in metals occupies interstitial lattice locations. Figure 1A illustrates the face-centered cubic (fcc) lattice structure, where tetrahedral (T) and/or octahedral (O) sites are preferred by hydrogen. Hydrogen atoms are known to thermally diffuse between stable sites via a metastable site at elevated temperatures. At low temperature, the quantum nature appears, and the tunneling between them might also play a decisive role. Although it is recognized that the potential shape is crucial for the tunneling rate (24), the influence of the interaction with surroundings on the tunneling in an asymmetric potential between inequivalent sites such as the stable and metastable sites has hardly been considered even theoretically (25). In this regard, experimental identification of the hopping pathway is also important to address the quantum nature of hydrogen.