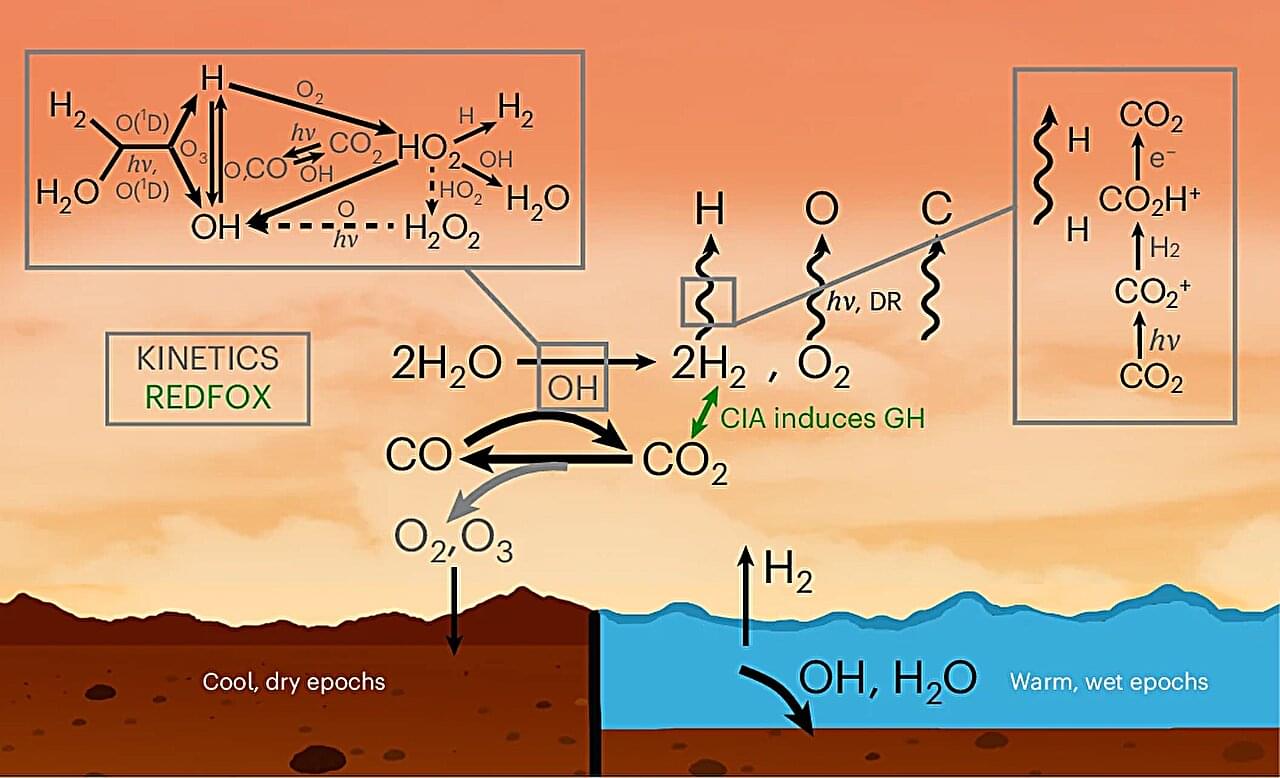
The fact that the cold, dry Mars of today had flowing rivers and lakes several billion years ago has puzzled scientists for decades. Now, Harvard researchers think they have a good explanation for a warmer, wetter ancient Mars.
Building on prior theories describing the Mars of yore as a hot again, cold again place, a team led by researchers at the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) have determined the chemical mechanisms by which ancient Mars was able to sustain enough warmth in its early days to host water, and possibly life.
“It’s been such a puzzle that there was liquid water on Mars, because Mars is further from the sun, and also, the sun was fainter early on,” said Danica Adams, NASA Sagan Postdoctoral Fellow and lead author of the new paper in Nature Geoscience.