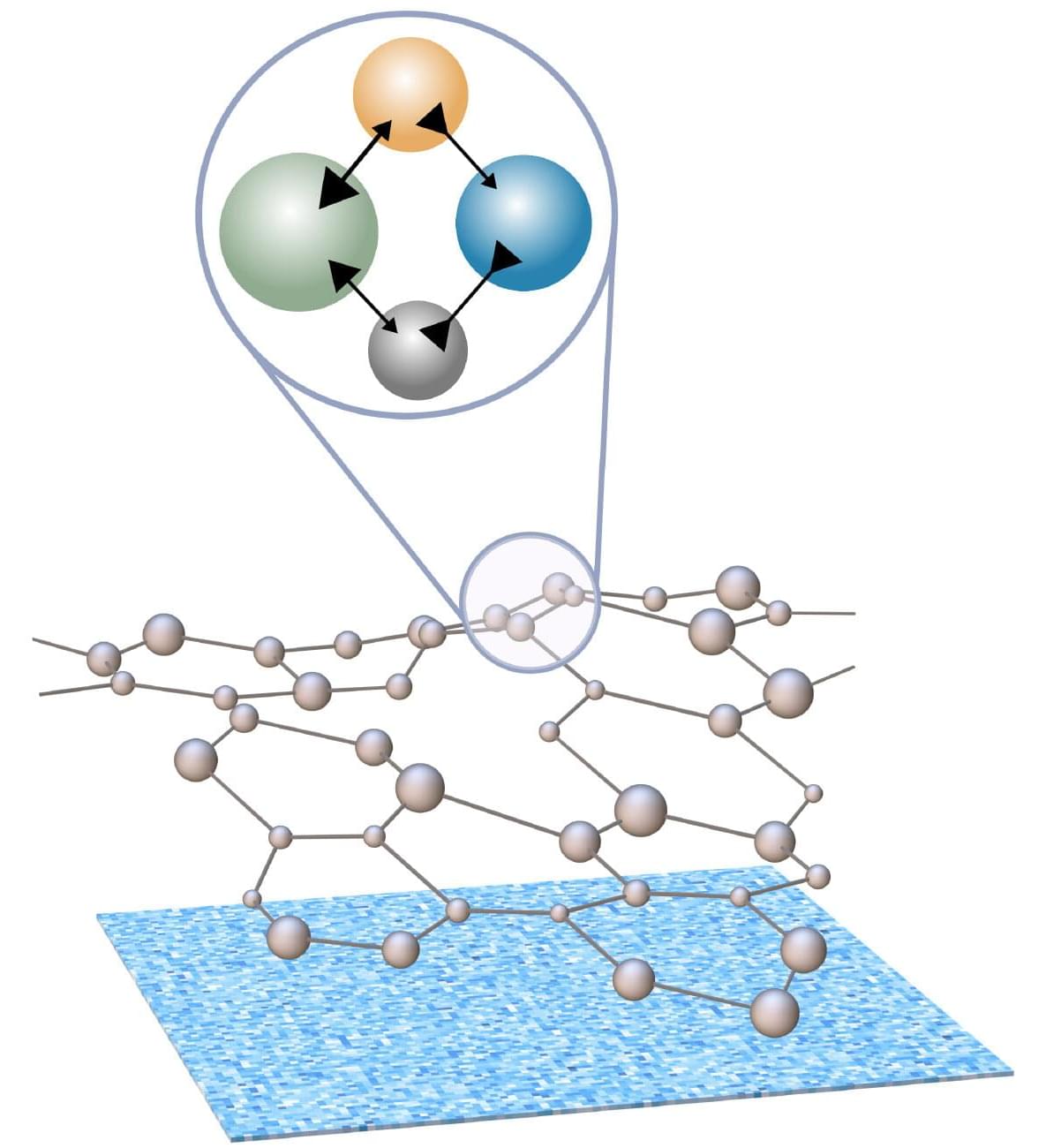
Asymmetric interactions between molecules may serve as a stabilizing factor for biological systems. A new model by researchers in the Department of Living Matter Physics at the Max Planck Institute for Dynamics and Self-Organization (MPI-DS) reveals the regulatory role of non-reciprocity.
The scientists aim to understand the physical principles based on which particles and molecules are able to form living beings, and eventually, organisms. The work is published in the journal Physical Review Letters.
Most organizations, including companies, societies, or nations, function best when each member carries out their assigned role. Moreover, this efficiency often relies on spatial organization, which arose due to rules or emerged naturally via learning and self-organization. At the microscopic level, cells operate in a similar way, with different components handling specific tasks.