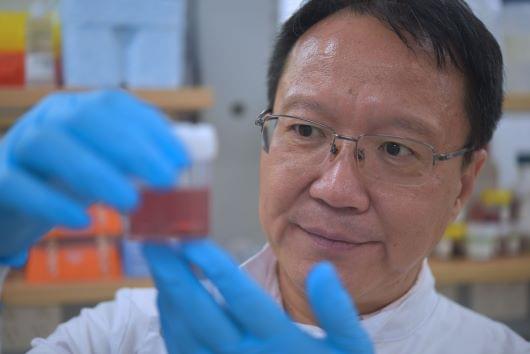
University of Queensland researchers are designing nanotechnology they believe could improve how we treat the most aggressive form of breast cancer.
Professor Chengzhong (Michael) Yu and his team are developing novel nanoparticles that could dramatically increase the effectiveness of immunotherapies when treating triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC).
TNBC is aggressive, fast-growing and accounts for 30 per cent of all breast cancer deaths in Australia each year, despite making up only 10 to 15 per cent of new cases.
Professor Yu, from UQ’s Australian Institute for Bioengineering and Nanotechnology (AIBN), said a new solution was needed because TNBC cancer cells lacked the proteins targeted by some of the treatments used against other cancers.
UQ researchers are designing nanotechnology they believe could improve how we treat the most aggressive form of breast cancer.