An exploration of new findings regarding the last universe common ancestor of life, or LUCA, and abiogenesis in general.
My Patreon Page:
/ johnmichaelgodier.
My Event Horizon Channel:
/ eventhorizonshow.
Papers:
An exploration of new findings regarding the last universe common ancestor of life, or LUCA, and abiogenesis in general.
My Patreon Page:
/ johnmichaelgodier.
My Event Horizon Channel:
/ eventhorizonshow.
Papers:

From the article:
I’m also worried that being on A.I.’s bad side could have dire consequences.
Today’s chatbots mostly seem like harmless assistants and homework helpers.
When I set out to improve my tainted reputation with chatbots, I discovered a new world of A.I. manipulation.
Enjoy the videos and music you love, upload original content, and share it all with friends, family, and the world on YouTube.
Image: Prof Thomas Hartung.
Over just a few decades, computers shrunk from massive installations to slick devices that fit in our pockets. But this dizzying trend might end soon, because we simply can’t produce small enough components. To keep driving computing forward, scientists are looking for alternative approaches. An article published in Frontiers in Science presents a revolutionary strategy, called organoid intelligence.

Metamaterials have recently garnered substantial research interest as they can be engineered to achieve materials properties not found in nature, thus presenting unique opportunities across various fields. In order to facilitate the rational design of metamaterials, computational methods have been widely employed, but not without numerous challenges yet to be addressed. This Focus highlights recent advancements, challenges, and opportunities in computational models for metamaterials design and manufacturing, as well as explores their potential promises in emerging information processors and computing technologies.
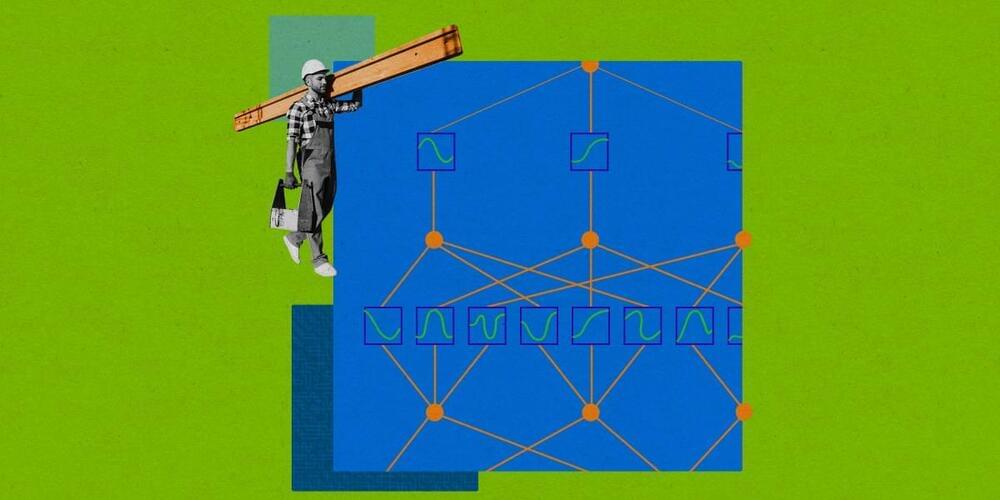
The simplified approach makes it easier to see how neural networks produce the outputs they do.

Researchers at the University of Toronto have found that using virtual and augmented reality (VR and AR) can temporarily change the way people perceive and interact with the real world—with potential implications for the growing number of industries that use these technologies for training purposes.
The study, published recently in the journal Scientific Reports, not only found that people moved differently in VR and AR, but that these changes led to temporary errors in movement in the real world. In particular, participants who used VR tended to undershoot their targets by not reaching far enough, while those who used AR tended to overshoot their targets by reaching too far.
This effect was noticeable immediately after using VR or AR, but gradually disappeared as participants readjusted to real-world conditions.
The standard model of the universe relies on just six numbers. Using a new approach powered by artificial intelligence, researchers at the Flatiron Institute and their colleagues extracted information hidden in the distribution of galaxies to estimate the values of five of these so-called cosmological parameters with incredible precision.
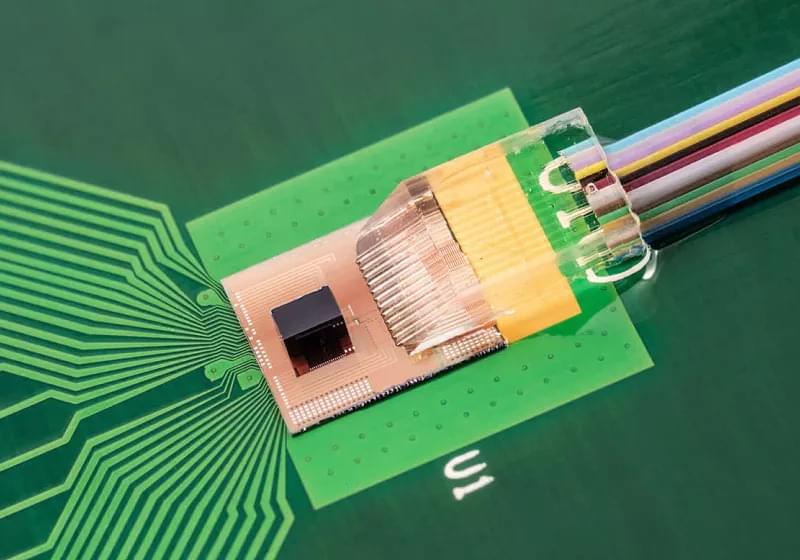
Forward-looking: We’re approaching a point where traditional copper interconnections won’t be able to carry enough data to keep GPUs and other specialized chips fully utilized. The AI market is urgently demanding a next-generation solution to this interconnection bottleneck, and Broadcom appears to be working on an optics-based solution that is closer to the chip itself.
Broadcom is developing new silicon photonics technology aimed at significantly increasing the bandwidth available to GPUs and other AI accelerators. By utilizing co-packaged optics (CPOs), the fabless chip manufacturer aims to integrate optical connectivity components directly into GPUs, enabling higher data rates while simultaneously reducing power requirements.
The company has been working on CPO solutions for several years and showcased its latest advancements at the recent Hot Chips convention. Broadcom’s “optical engine” reportedly delivers a total interconnect bandwidth of 1.6 TB/sec, equivalent to 6.4 Tbit/sec or 800 GB/sec in each direction.
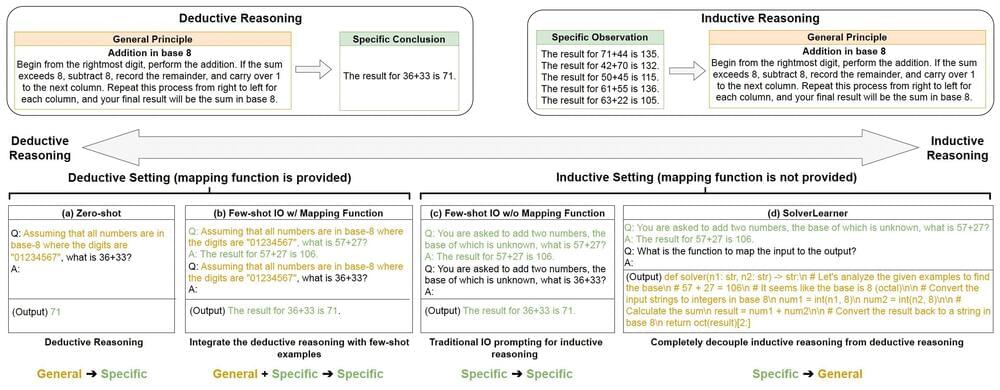
Reasoning, the process through which human beings mentally process information to draw specific conclusions or solve problems, can be divided into two main categories. The first type of reasoning, known as deductive reasoning, entails starting from a general rule or premise and then using this rule to draw conclusions about specific cases.
This could mean, for instance, building on the premise that “all dogs have ears” and “Chihuahuas are dogs,” to conclude that “chihuahuas have ears.”
The second widely used form of reasoning is inductive reasoning, which instead consists of generalizing (i.e., formulating general rules) based on specific observations. This could mean, for instance, assuming that all swans are white because all the swans we encountered during our lifetime were white.