The term is everywhere this week, but its meaning is as vague as ever. Working on a definition matters.


Inside the body, a 24-hour rhythm, known as the circadian rhythm, quietly coordinates when we sleep, wake, eat, and recover. This internal timing system helps keep organs and hormones working in sync.
When it becomes disrupted, the effects may extend well beyond poor sleep, with growing evidence suggesting consequences for long-term brain health.
A large 2025 study of more than 2,000 people with an average age of 79 found that those with a strong circadian rhythm had an almost halved risk of developing dementia. Circadian rhythms regulate daily processes, including sleep timing, hormone release, heart rate, and body temperature.
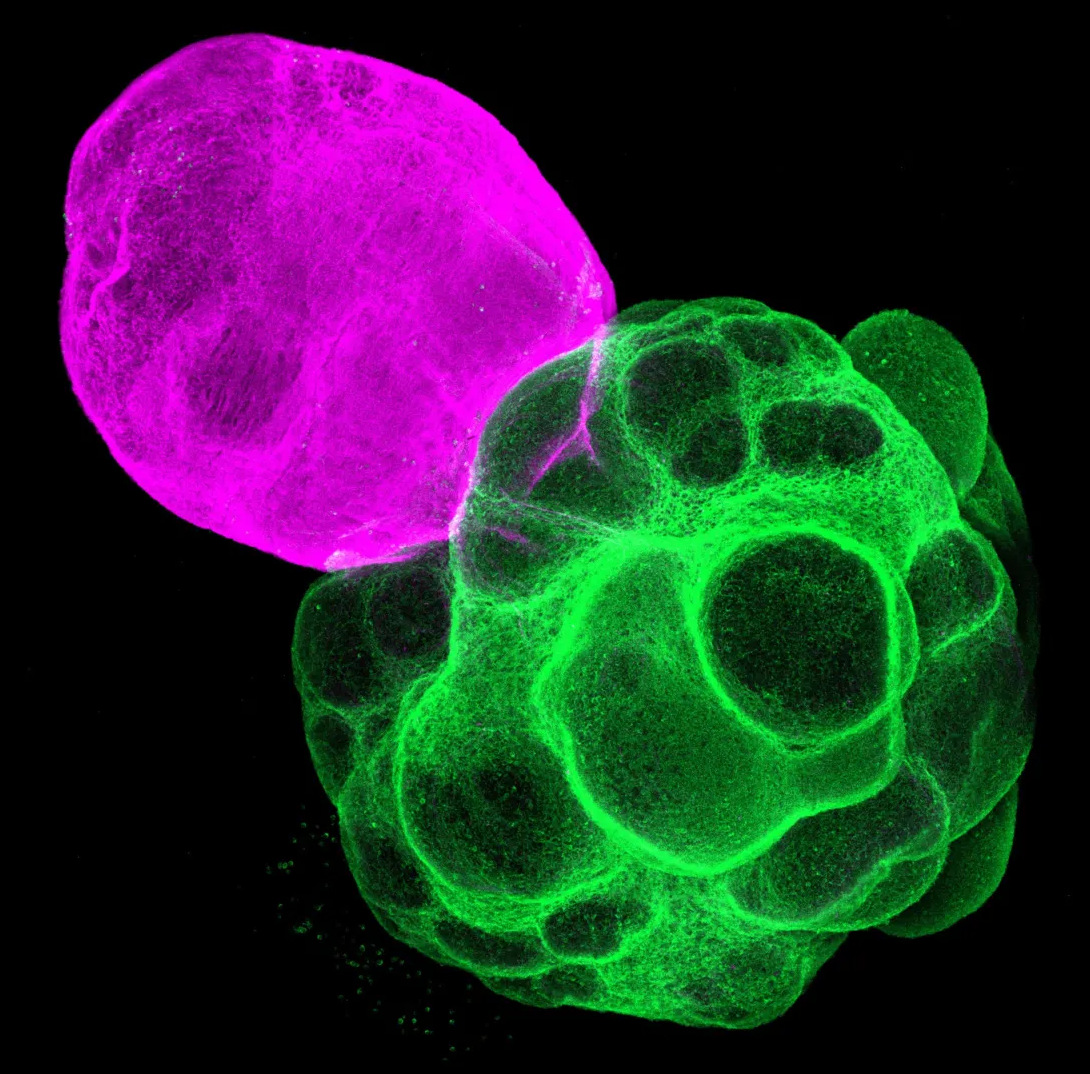
To assess how this interaction affected development, the team compared gene expression in the cortical region of the assembloid with that of a standalone cortical organoid. The cortical tissue connected to the thalamus showed signs of greater maturity, indicating that thalamus cortex communication promotes cortical growth and development.
Thalamic Signals Drive Neural Synchrony
The scientists also examined how signals traveled through the assembloid. They found that neural activity spread from the thalamus into the cortex in wave like patterns, creating synchronized activity across cortical networks.
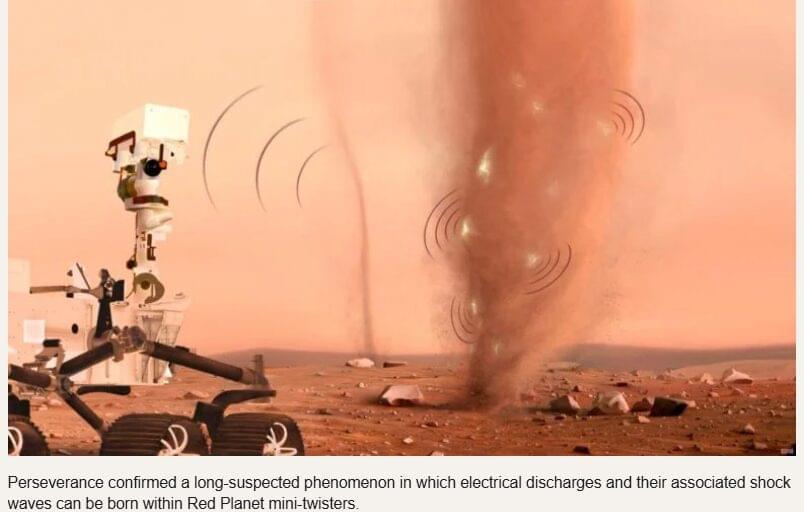

Perseverance confirmed a long-suspected phenomenon in which electrical discharges and their associated shock waves can be born within Red Planet mini-twisters.
NASA’s Perseverance Mars rover has recorded the sounds of electrical discharges —sparks — and mini-sonic booms in dust devils on Mars. Long theorized, the phenomenon has now been confirmed through audio and electromagnetic recordings captured by the rover’s SuperCam microphone. The discovery, published Nov. 26 in the journal Nature, has implications for Martian atmospheric chemistry, climate, and habitability, and could help inform the design of future robotic and human missions to Mars.
A frequent occurrence on the Red Planet, dust devils form from rising and rotating columns of warm air. Air near the planet’s surface becomes heated by contact with the warmer ground and rises through the denser, cooler air above. As other air moves along the surface to take the place of the rising warmer air, it begins to rotate. When the incoming air rises into the column, it picks up speed like spinning ice skaters bringing their arms closer to their body. The air rushing in also picks up dust, and a dust devil is born.
Further Reading.
This ‘digital brain’ could soon simulate ethically forbidden experiments.
https://ebrains.eu/news-and-events/2025/ten-years-of-pd14-mi…i-research.
A foundation model to predict and capture human cognition.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-025-09215-4
First totally synthetic human brain model has been realized.
https://newatlas.com/medical/synthetic-human-brain-models/
#science #news #explained #research #sciencenews #biotech #robots #ai #artificialintelligence #organoid

Previously, we described that Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, and Guanine nucleobases were superconductors in a quantum superposition of phases on each side of the central hydrogen bond acting as a Josephson Junction. Genomic DNA has two strands wrapped helically around one another, but during transcription, they are separated by the RNA polymerase II to form a molecular condensate called the transcription bubble. Successive steps involve the bubble translocation along the gene body. This work aims to modulate DNA as a combination of n-nonperturbative circuits quantum electrodynamics with nine Radio-Frequency Superconducting Quantum Interference Devices (SQUIDs) inside. A bus can be coupled capacitively to a single-mode microwave resonator. The cavity mode and the bus can mediate long-range, fast interaction between neighboring and distant DNA SQUID qubits.

Galaxies announce themselves through the light of billions of stars, all embedded in vast clumps, or “halos,” of dark matter. But researchers may have spotted, for the first time, a starless halo of dark matter—containing only a gas cloud. The result was announced by Rachael Beaton of the Space Telescope Science Institute in Maryland at the meeting of the American Astronomical Society in Phoenix, Arizona. Using observations from the Hubble Space Telescope, Beaton and her collaborators showed that the object, known as Cloud-9, contains a negligible amount of stars [1]. “There is nothing like this that we have found so far in the Universe,” Beaton said in a press conference last week.
Cloud-9’s makeup—as inferred from radio and optical observations—would qualify it as the first example of a REionization-Limited H I Cloud (RELHIC), a starless dark matter halo filled with neutral hydrogen gas (H I). RELHICs are thought to be leftovers of dark matter clumps that couldn’t accrue a sufficient amount of gas to form stars, says the project’s principal investigator Alejandro Benítez-Llambay of the University of Milano-Bicocca in Italy. A RELHIC is “a tale of a failed galaxy,” he says.
Starless halos arise naturally within the standard paradigm of cosmology: the lambda cold dark matter (ΛCDM) model, where Λ refers to a “cosmological constant” that describes dark energy. According to ΛCDM, dark matter can cluster into halos that provide the gravitational backbone for galaxy formation. The model also predicts that there is a critical mass below which halos would be too small to ever form stars. Spotting unlit halos might sound hopeless, but simulations by Benítez-Llambay and collaborators in 2017 suggested that halos within a narrow mass range may exist as RELHICs (a term they coined) [2]. According to their calculations, RELHICs would have masses close to the critical value for galaxy formation. Crucially, the compact, hydrogen-filled cores of these objects provide a potential observational window, since hydrogen clouds have a characteristic radio emission.
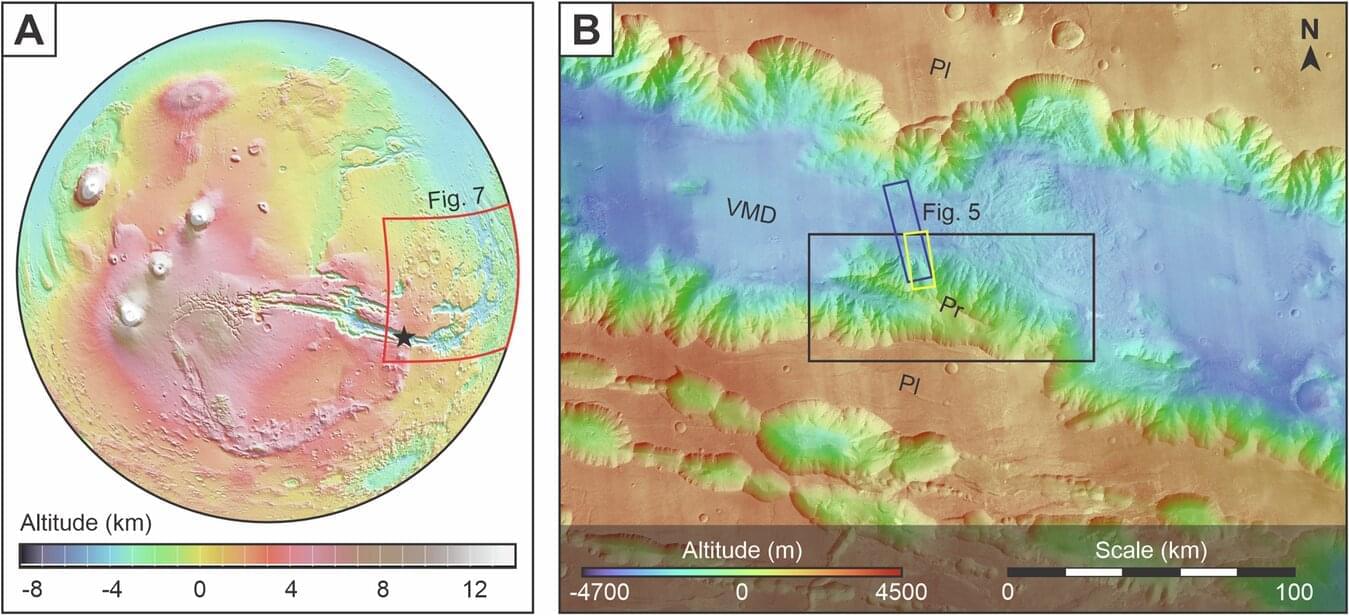
Using images from cameras on Mars orbiters, an international research team has discovered structures on Mars that are very similar to classic river deltas on Earth. These are traces of rivers that have deposited their sediments into an ocean. This shows that Mars was a “blue planet” around 3 billion years ago.
The existence of water on Mars is a central topic in planetary research. Previous studies have already provided evidence of oceans and rivers on Mars, indicating a once humid and possibly habitable environment. Evidence of former water and a possible ocean have also been discovered for the Valles Marineris—the largest canyon system on Mars, which stretches along its equator. These come, among other things, from discoveries of minerals that have been altered by water.
A research team from the University of Bern, in collaboration with the INAF—Osservatorio Astronomico di Padova, has now gained new insights into the geological past of Valles Marineris: Using high-resolution images from various Mars cameras, the researchers have found geomorphologic structures near the canyon system that resemble river deltas on Earth. These structures represent the mouth of a river into an ocean. The new study thus provides clear evidence of a coastline and consequently of an earlier ocean on Mars.
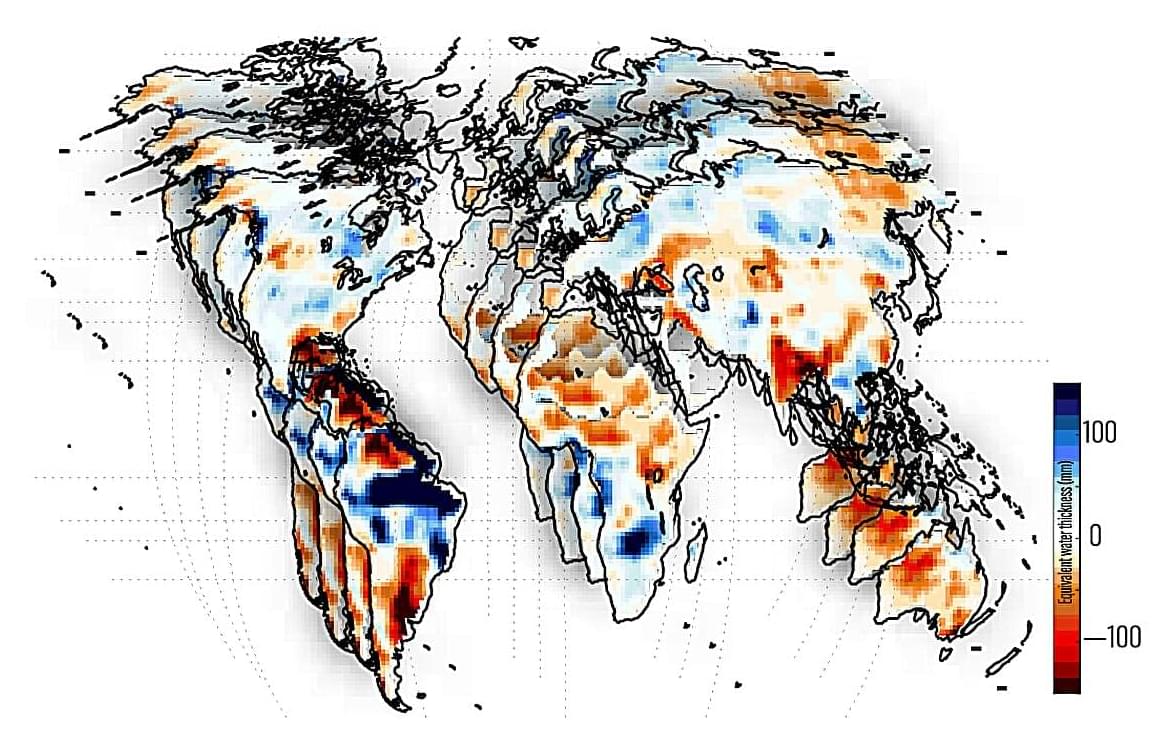
Water extremes such as droughts and floods have a huge impact on communities, ecosystems, and economies. Researchers with The University of Texas at Austin have turned their attention to tracking these extremes across Earth and have discovered what is driving them.
In a recent study published in AGU Advances, the researchers found that over the past two decades ENSO, a climate pattern in the equatorial Pacific Ocean that includes El Niño and La Niña, has been the dominant driver of total water storage extremes at the global level. What’s more, the researchers found that ENSO has a synchronizing effect on water storage extremes across continents.
Study co-author Bridget Scanlon, a research professor at the Bureau of Economic Geology at the UT Jackson School of Geosciences, said that understanding how extremes unfold across the world has humanitarian and policy impacts.