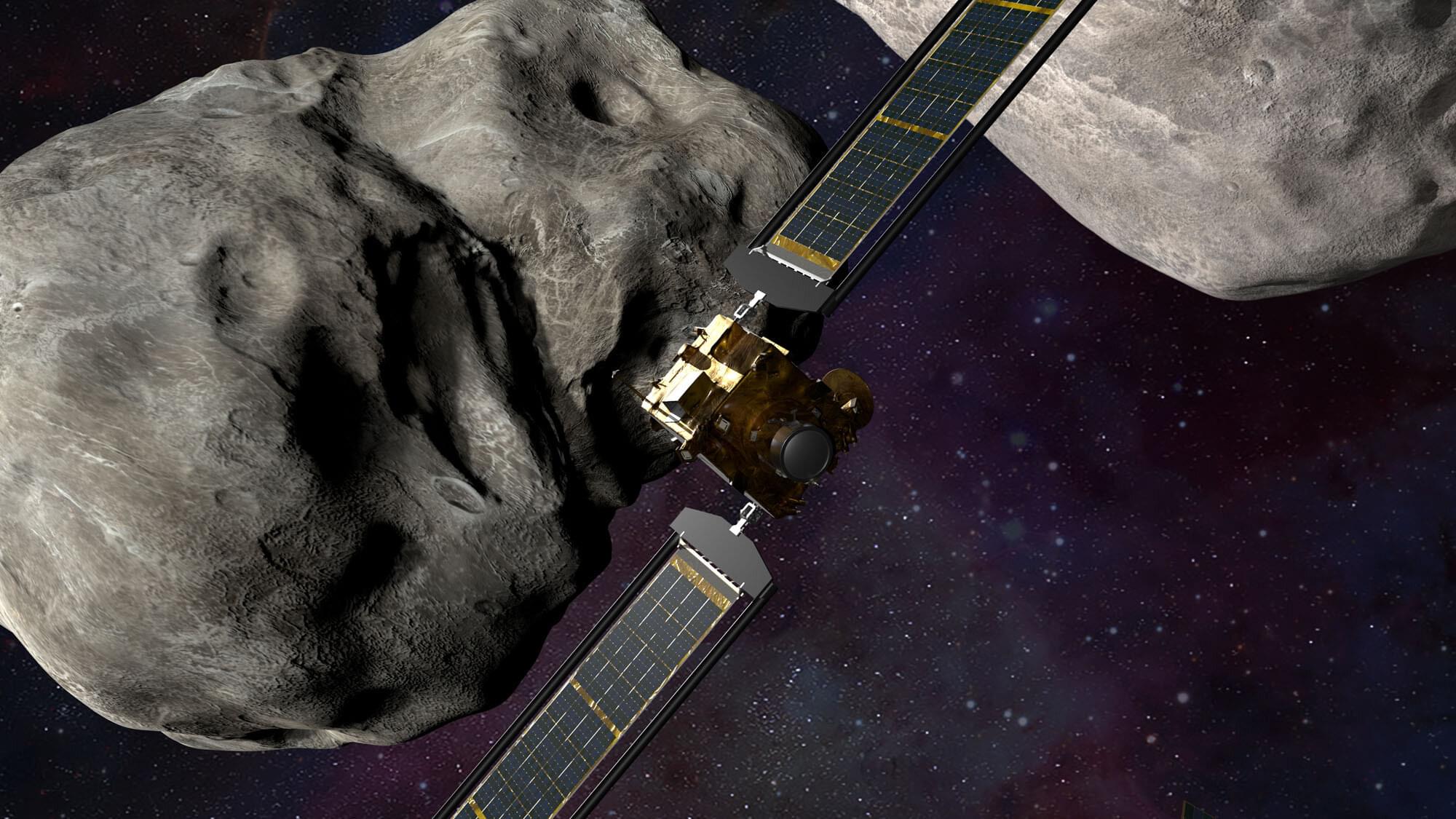
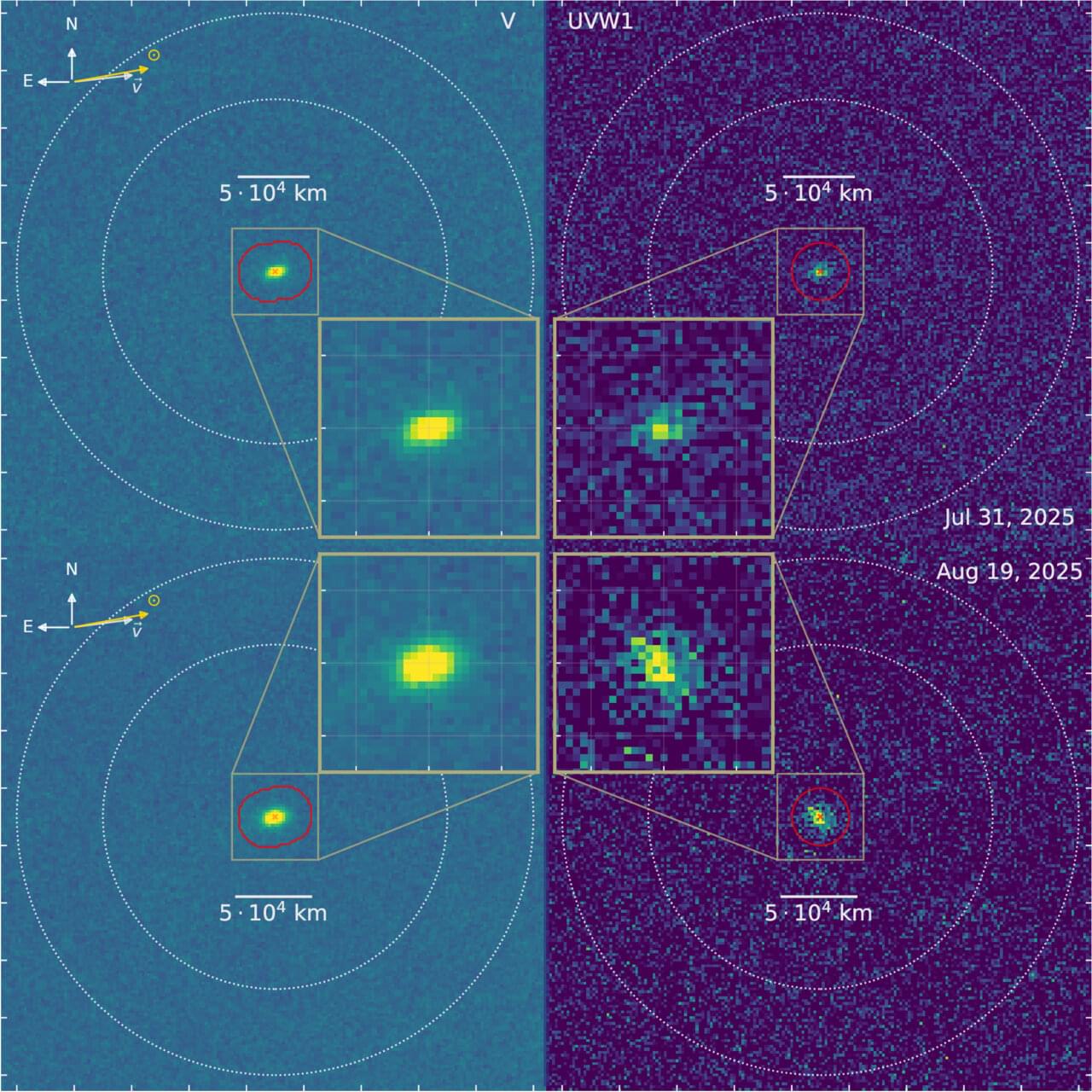
For millions of years, a fragment of ice and dust drifted between the stars—like a sealed bottle cast into the cosmic ocean. This summer, that bottle finally washed ashore in our solar system and was designated 3I/ATLAS, only the third known interstellar comet. When Auburn University scientists pointed NASA’s Neil Gehrels Swift Observatory toward it, they made a remarkable find: the first detection of hydroxyl (OH) gas from this object, a chemical fingerprint of water.
Swift’s space-based telescope could spot the faint ultraviolet glow that ground observatories can’t see—because, high above Earth’s atmosphere, it captures light that never reaches Earth’s surface.
Detecting water—through its ultraviolet by-product, hydroxyl—is a major breakthrough for understanding how interstellar comets evolve. In solar-system comets, water is the yardstick by which scientists measure their overall activity and track how sunlight drives the release of other gases. It’s the chemical benchmark that anchors every comparison of volatile ices in a comet’s nucleus.