More than two years after the blockbuster launch of ChatGPT, artificial intelligence continues to be the white hot center of venture capital and the business world at large.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.

“Scientists Stunned as CERN Unveils Tiny Particle”: Groundbreaking Discovery at Large Hadron Collider Sends Shockwaves Through Physics Community
IN A NUTSHELL 🔬 Toponium discovery at CERN could revolutionize our understanding of particle physics. 📊 The CMS collaboration detected an unexpected excess of top quark-antiquark pairs, hinting at this elusive particle. 🚀 If confirmed, toponium would be the smallest hadron ever discovered, challenging existing theories. 🧩 Researchers aim to refine their models and collaborate

Carbon battery startup aims to make energy storage circular
Ukrainian startup SorbiForce said they’ve created the world’s first sustainable battery using four key ingredients: carbon, water, salt and agricultural waste.
“With the current way energy storage systems and batteries are designed, they have really big sustainability implications for the planet,” Kevin Drolet, SorbiForce’s CMO, told pv magazine USA. He explained that material scientist Serhii Kaminskyi, SorbiForce’s CEO and co-founder, had long been bothered by those environmental ramifications.
Kaminskyi pulled together a team of experts in the late 2010s to work on solving the problem. This ultimately landed them a spot in the University of Arizona Center for Innovation startup incubator following the start of the Russia-Ukraine war through the U.S. Department of State’s Global Innovation through Science and Technology initiative.
SorbiForce, a Ukrainian energy storage company now in Arizona, has developed metal-free organic batteries made entirely from agricultural waste.

Viral oncogenes, viruses, and cancer: a third-generation sequencing perspective on viral integration into the human genome
The link between viruses and cancer has intrigued scientists for decades. Certain viruses have been shown to be vital in the development of various cancers by integrating viral DNA into the host genome and activating viral oncogenes. These viruses include the Human Papillomavirus (HPV), Hepatitis B and C Viruses (HBV and HCV), Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV), and Human T-Cell Leukemia Virus (HTLV-1), which are all linked to the development of a myriad of human cancers. Third-generation sequencing technologies have revolutionized our ability to study viral integration events at unprecedented resolution in recent years. They offer long sequencing capabilities along with the ability to map viral integration sites, assess host gene expression, and track clonal evolution in cancer cells.

Electron transport in bilayer graphene nanoconstrictions patterned using atomic force microscope nanolithography
Here we report on low temperature transport measurements of encapsulated bilayer graphene nano constrictions fabricated employing electrode-free AFM-based local anodic oxidation (LAO) nanolithography. This technique allows for the creation of constrictions as narrow as 20 nm. While larger constrictions exhibit an enhanced energy gap, single quantum dot (QD) formation is observed within smaller constrictions with addition energies exceeding 100 meV, which surpass previous experiments on patterned QDs. These results suggest that transport through these narrow constrictions is governed by edge disorder combined with quantum confinement effects. Our findings introduce electrode-free AFM-LAO lithography as an easy and flexible method for creating nanostructures with tunable electronic properties without relying on patterning techniques such as e-beam lithography. The excellent control and reproducibility provided by this technique opens exciting opportunities for carbon-based quantum electronics and spintronics.
Citation.
Physical Review B
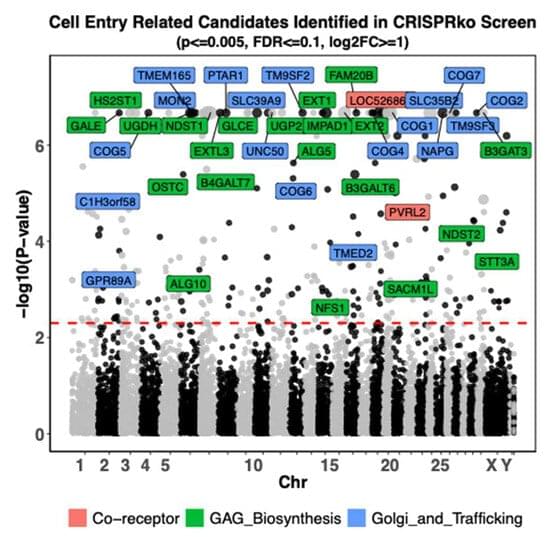
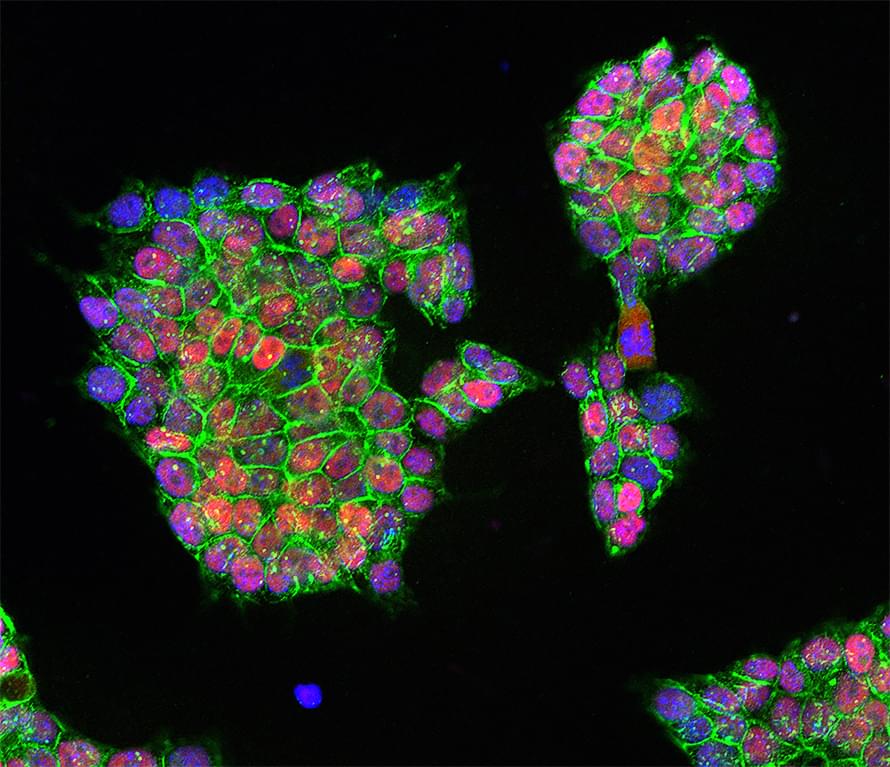
Validation of Candidate Host Cell Entry Factors for Bovine Herpes Virus Type-1 Based on a Genome-Wide CRISPR Knockout Screen
To identify host factors that affect Bovine Herpes Virus Type 1 (BoHV-1) infection we previously applied a genome wide CRISPR knockout screen targeting all bovine protein coding genes. By doing so we compiled a list of both pro-viral and anti-viral proteins involved in BoHV-1 replication. Here we provide further analysis of those that are potentially involved in viral entry into the host cell. We first generated single cell knockout clones deficient in some of the candidate genes for validation. We provide evidence that Polio Virus Receptor-related protein (PVRL2) serves as a receptor for BoHV-1, mediating more efficient entry than the previously identified Polio Virus Receptor (PVR). By knocking out two enzymes that catalyze HSPG chain elongation, HST2ST1 and GLCE, we further demonstrate the significance of HSPG in BoHV-1 entry. Another intriguing cluster of candidate genes, COG1, COG2 and COG4-7 encode six subunits of the Conserved Oligomeric Golgi (COG) complex. MDBK cells lacking COG6 produced fewer but bigger plaques compared to control cells, suggesting more efficient release of newly produced virions from these COG6 knockout cells, due to impaired HSPG biosynthesis. We further observed that viruses produced by the COG6 knockout cells consist of protein(s) with reduced N-glycosylation, potentially explaining their lower infectivity. To facilitate candidate validation, we also detailed a one-step multiplex CRISPR interference (CRISPRi) system, an orthogonal method to KO that enables quick and simultaneous deployment of three CRISPRs for efficient gene inactivation. Using CRISPR3i, we verified eight candidates that have been implicated in the synthesis of surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans (HSPGs). In summary, our experiments confirmed the two receptors PVR and PVRL2 for BoHV-1 entry into the host cell and other factors that affect this process, likely through the direct or indirect roles they play during HSPG synthesis and glycosylation of viral proteins.
Cutting-edge energy company makes major breakthrough in replicating the process that powers the sun: ‘Setting the gold standard’
Type One Energy just published a study outlining the first practical fusion power plant.

