Warp drive space ships don’t exist now, but two researchers looked into what might happen if one crossed into a black hole.
Humanity is on the verge of AGI (Artificial General Intelligence). Futurist Ray Kurzweil predicted decades ago that we would reach AGI in 2029. AI and Large Language Models could reach AGI sooner than 2029. However, the definitions of artificial intelligence that surpasses individual humans has issues around definitions and measurement.
Kurzweil also predicted the Singularity in 2045. He defined that as having cumulative artificial intelligence beyond the total intelligence of humanity.
Beyond the Singularity is Computronium and the limits of technology and the limits of computing.
The brain’s white matter comprises areas of the central nervous system made up of myelinated axons. Its name is derived from the pale appearance of the lipids that comprise myelin. Myelin is a segmented sheath that insulates axons, ensuring the conduction of neural signals. The loss of myelin is documented in a number of neurodegenerative pathologies, including Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease, and perhaps most notably, multiple sclerosis. As people age, demyelination becomes more likely.
Researchers have long suspected a relationship between cardiorespiratory fitness and the integrity of the brain’s white matter as people age. However, a lack of specific evidence has led researchers at the National Institutes of Health to conduct a study examining the strength of this correlation, now published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
To establish a correlation between cardiovascular fitness and cerebral myelination, the researchers recruited a cohort of 125 participants from age 22 to 94 years old. The cardiovascular fitness of the participants was quantified as the maximum rate of oxygen consumption, popularly and succinctly known as VO2max. Myelin content was defined as the myelin water fraction, which the researchers estimated through an advanced multicomponent relaxometry MRI method.
AUSTIN (KXAN) — The most sensitive dark matter detector in the world is showing results in the hunt for the hypothetical particle. The results: they can’t find it.
“If you think of the search for dark matter like searching for buried treasure,” said Scott Kravitz, an associate professor in the physics department at the University of Texas, “we’ve basically dug part of the way down to where it might be, it could still be deeper below what we’ve searched so far.”
Kravitz is part of the LEX-ZEPLIN project, a Department of Energy hunt for dark matter in a cavern in South Dakota.
The nature of Earth’s deep past can often feel intangible. From our modern moment, eons billions of years in the past seem hard to touch. Among some of our planet’s rocks, however, are tatters and fragments from those distant times that can offer us a peek at what our planet was like when our ancestors were single-celled organisms. By studying some of these vestiges, geologists have been able to detect what was transpiring under the Earth’s crust over 2.5 billion years ago.
Below our feet—and our planet’s outer crust— Earth’s mantle makes up the vast majority of the planet’s volume. Different layers of the mantle are made up of different rock types, and one of the most common is an igneous rock high in silica content called peridotite. In the past, when geologists have compared samples of prehistoric peridotite from Earth’s mantle and their modern equivalents, they’ve found a significant discrepancy.
Shan C, Gong YL, Zhuang QQ, Hou YF, Wang SM, Zhu Q, et al. Protective effects of β- nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide against motor deficits and dopaminergic neuronal damage in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Prog Neuro Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2019, 94: 109670.
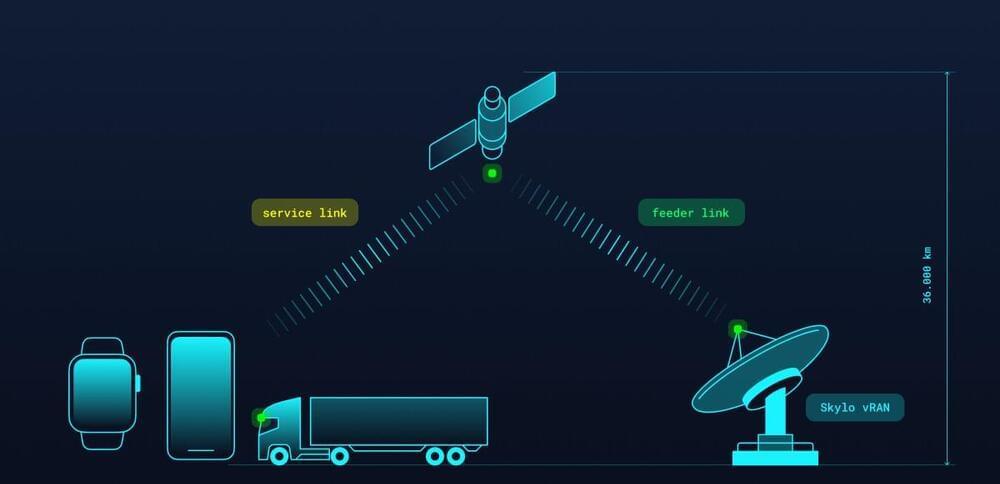
TAMPA, Fla. — Verizon is launching satellite-enabled emergency text and location services this fall for compatible Android smartphones in the United States at no extra cost for customers.
The telecoms giant announced a partnership Aug. 28 to deliver the service with Skylo, which has developed ground infrastructure enabling L-band geostationary satellites to reach devices using the latest standards-based chipsets.
Google’s family of Pixel Pro devices and the Samsung Galaxy S25 are set to be among the first to get access to Skylo’s partner satellites, enabling emergency narrowband connectivity when cell towers are out of reach.
TOC 00:00:00 Intro 00:03:38 Reasoning 00:13:09 Potential AI Breakthroughs Reducing Computation Needs 00:20:39 Memorization vs. Generalization in AI 00:25:19 Approach to the ARC Challenge 00:29:10 Perceptions of Chat GPT and AGI 00:58:45 Abstract Principles of Jurgen’s Approach 01:04:17 Analogical…
Jürgen Schmidhuber, the father of generative AI shares his groundbreaking work in deep learning and artificial intelligence. In this exclusive interview, he discusses the history of AI, some of his contributions to the field, and his vision for the future of intelligent machines. Schmidhuber offers unique insights into the exponential growth of technology and the potential impact of AI on humanity and the universe.
MLST is sponsored by Brave:
The Brave Search API covers over 20 billion webpages, built from scratch without Big Tech biases or the recent extortionate price hikes on search API access. Perfect for AI model training and retrieval augmentated generation. Try it now — get 2,000 free queries monthly at http://brave.com/api.
TOC
00:00:00 Intro.
00:03:38 Reasoning.
00:13:09 Potential AI Breakthroughs Reducing Computation Needs.
00:20:39 Memorization vs. Generalization in AI
00:25:19 Approach to the ARC Challenge.
00:29:10 Perceptions of Chat GPT and AGI
00:58:45 Abstract Principles of Jurgen’s Approach.
01:04:17 Analogical Reasoning and Compression.
01:05:48 Breakthroughs in 1991: the P, the G, and the T in ChatGPT and Generative AI
01:15:50 Use of LSTM in Language Models by Tech Giants.
01:21:08 Neural Network Aspect Ratio Theory.
01:26:53 Reinforcement Learning Without Explicit Teachers.
Refs:
The futurist argues that advances in AI and medicine will offer us unprecedented freedom.
Now 76, the inventor and futurist hopes to reach “the Singularity” and live indefinitely. His margin of error is shrinking.