Read a case of anti-Ma2 encephalitis–associated secondary narcolepsy in an elderly man, in whom the diagnosis was delayed because of multiple confounders, but the sleep study was crucial to suspect the final diagnosis.
Background and Objectives.
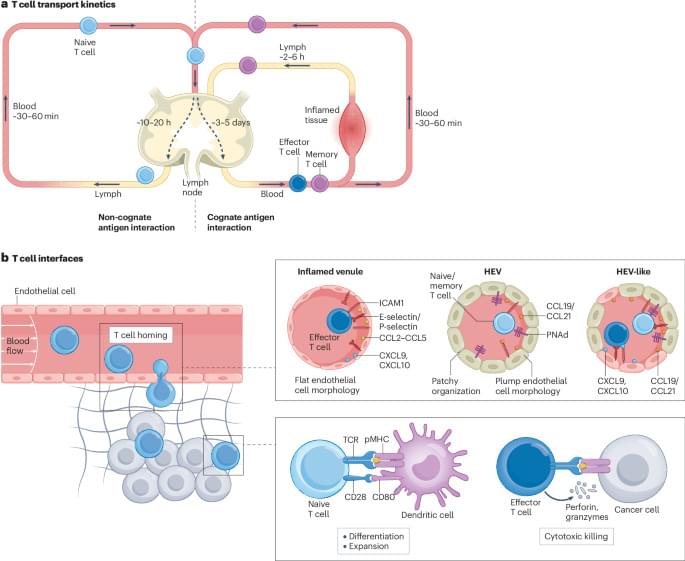
The function and fate of T cells are dictated by their various dynamic interactions with cells and tissues. This Review discusses the recreation of key T cell interfaces using nanotechnologies and microtechnologies for the mechanistic study of T cell biology, as well as the manufacturing and sorting of T cell products.

Malignant tumors remain a primary cause of human mortality. Among the various treatment modalities for neoplasms, tumor vaccines have consistently shown efficacy and promising potential. These vaccines offer advantages such as specificity, safety, and tolerability, with mRNA vaccines representing promising platforms. By introducing exogenous mRNAs encoding antigens into somatic cells and subsequently synthesizing antigens through gene expression systems, mRNA vaccines can effectively induce immune responses. Katalin Karikó and Drew Weissman were awarded the 2023 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their great contributions to mRNA vaccine research. Compared with traditional tumor vaccines, mRNA vaccines have several advantages, including rapid preparation, reduced contamination, nonintegrability, and high biodegradability.
Imagine a container of tomatoes arriving at the container terminal in Aarhus. The papers state that the tomatoes are from Spain, but in reality, we have no way of knowing if that is true.
That is, unless we take a sample and have it analyzed in a laboratory, where scientists use DNA markers to determine whether the tomato is Spanish, South American or Chinese. This is both time-consuming and expensive.
But thanks to a scientific breakthrough, we will be able to examine tomatoes a lot quicker and cheaper, using special light producing proteins and our phones camera. Not right now, but in the near future.
The results were recently published in the journal Nature Communications.
“We have figured out how to instruct the proteins to generate light when specific DNA sequences appear. This could be used, as in the example with the tomatoes, but could also be useful in the healthcare sector, agriculture, or the pharmaceutical industry to analyze samples easily and cheaply,” the senior author explains.
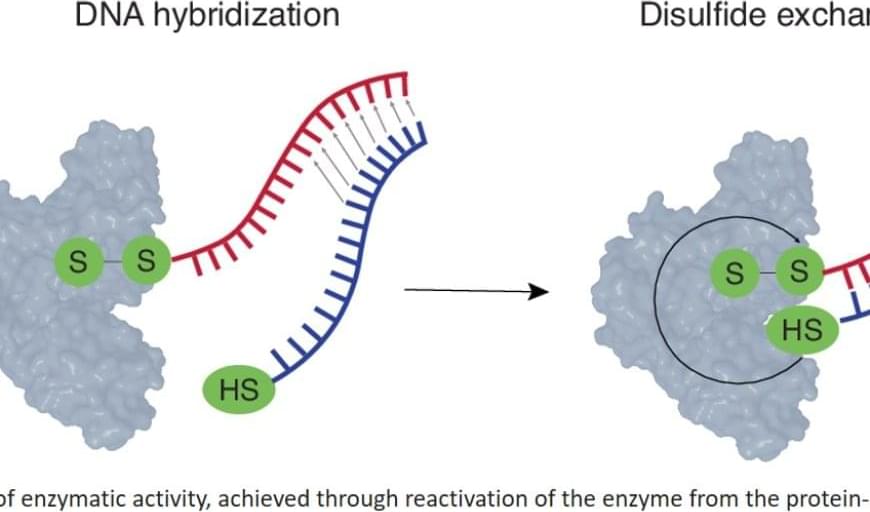
The authors did this via “thiol switching”, using thiolated oligonucleotides: a protein is inactivated by conjugation to an oligonucleotide via a disulfide linkage; hybridization of the thiolated complementary oligonucleotide ensues disulfide exchange, the liberation of the enzyme, and the activation of enzymatic catalysis. In doing so, the researchers couple the most specific recognition event (hybridization) to the most effective tool of signal amplification (catalysis).
“Our primary goal is to control the activity of molecules in space and time, inside and outside of the cell. Specifically we focus on enzymes that can create ATP, which is the cell’s fuel, and polymerases, which the cell uses to build RNA and DNA.”

Children whose fathers took valproate within three months prior to conception were more likely to have neurodevelopmental disorders than children of men exposed to lamotrigine or levetiracetam.
Researchers behind a new study believe that it is the first to show an increased risk of neurodevelopmental disorders in offspring of fathers who took valproate rather than lamotrigine or levetiracetam prior to conceiving children.
Children whose fathers took valproate within the three months prior to their conception were more likely to have neurodevelopmental disorders, including autism spectrum disorders, than children of men exposed to lamotrigine or levetiracetam, according to a study published in JAMA Network Open in November.
The European research team—which analyzed medical records from Denmark, Norway, and Sweden—concluded that “health care practitioners should consider the potential risks associated with paternal valproate exposure and discuss alternative treatment options with male patients of reproductive age.” The team also said that “findings should be interpreted with caution due to the heterogeneity in the unadjusted estimates.”
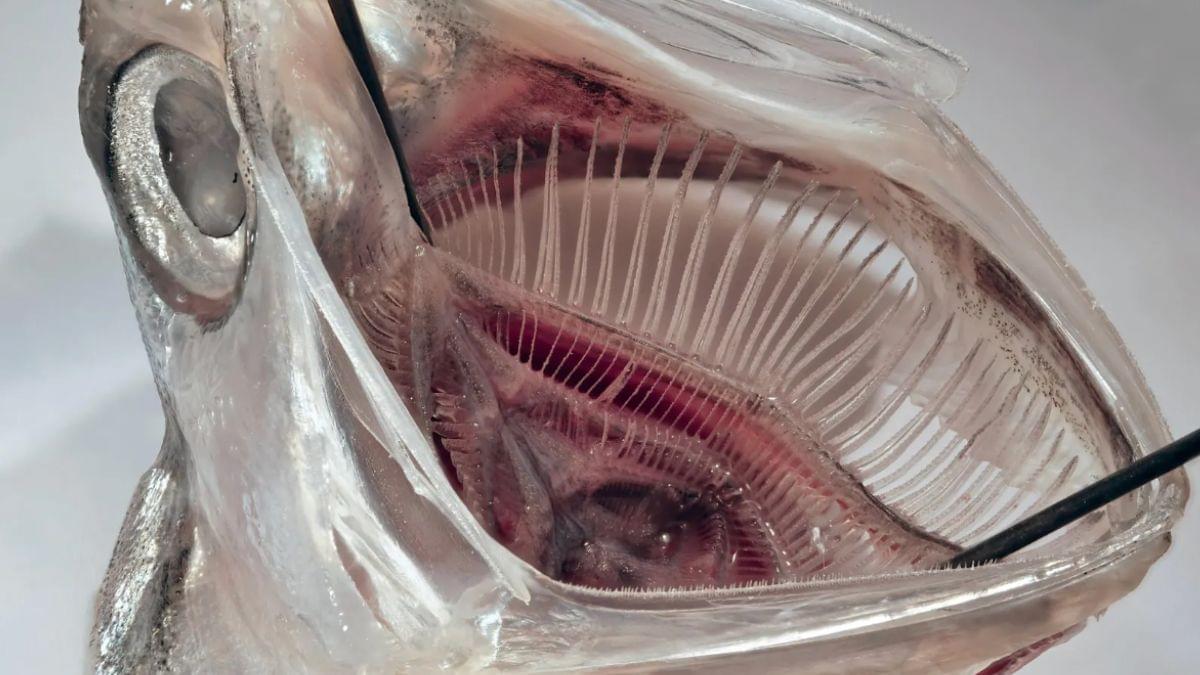
The ancient evolution of fish mouths could help solve a modern source of plastic pollution.
Inspired by these natural filtration systems, scientists in Germany have invented a way to remove 99 percent of plastic particles from water. It’s based on how some fish filter-feed to eat microscopic prey.
The research team has already filed a patent in Germany, and in the future, they hope their creation will help curb a ubiquitous form of plastic pollution that many are unaware of.
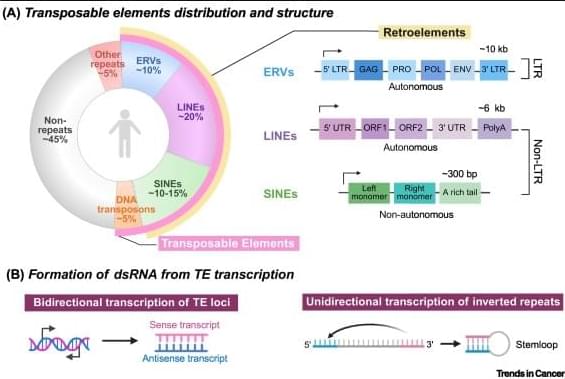
Transposable elements in cancer therapy.
Transposable elements (TEs) are a major source of immunogenic nucleic acids that can be therapeutically reactivated in cancer cells to induce a state of viral mimicry.
TE expression can trigger innate immune sensing pathways, including type I interferon responses, and promote immunogenic cell death via sensors such as RIGI, MDA5, cGAS, and Z-DNA binding protein 1.
Although initially described in the context of epigenetic therapies, viral mimicry is now recognized as a shared response to diverse cancer treatment modalities, including chemotherapies and targeted therapies.
Despite their distinct primary mechanisms, these treatments converge on TE reactivation through disruption of DNA/histone methylation, p53 activation, and perturbation of mRNA splicing.
Therapeutic resistance to chemotherapy, radiation, and targeted agents is associated with TE silencing, identifying TE repression as a targetable axis of resistance.
Combination strategies to induce immunogenic TE expression can further enhance viral mimicry and boost antitumor immunity. https://sciencemission.com/Viral-mimicry-in-cancer-therapy
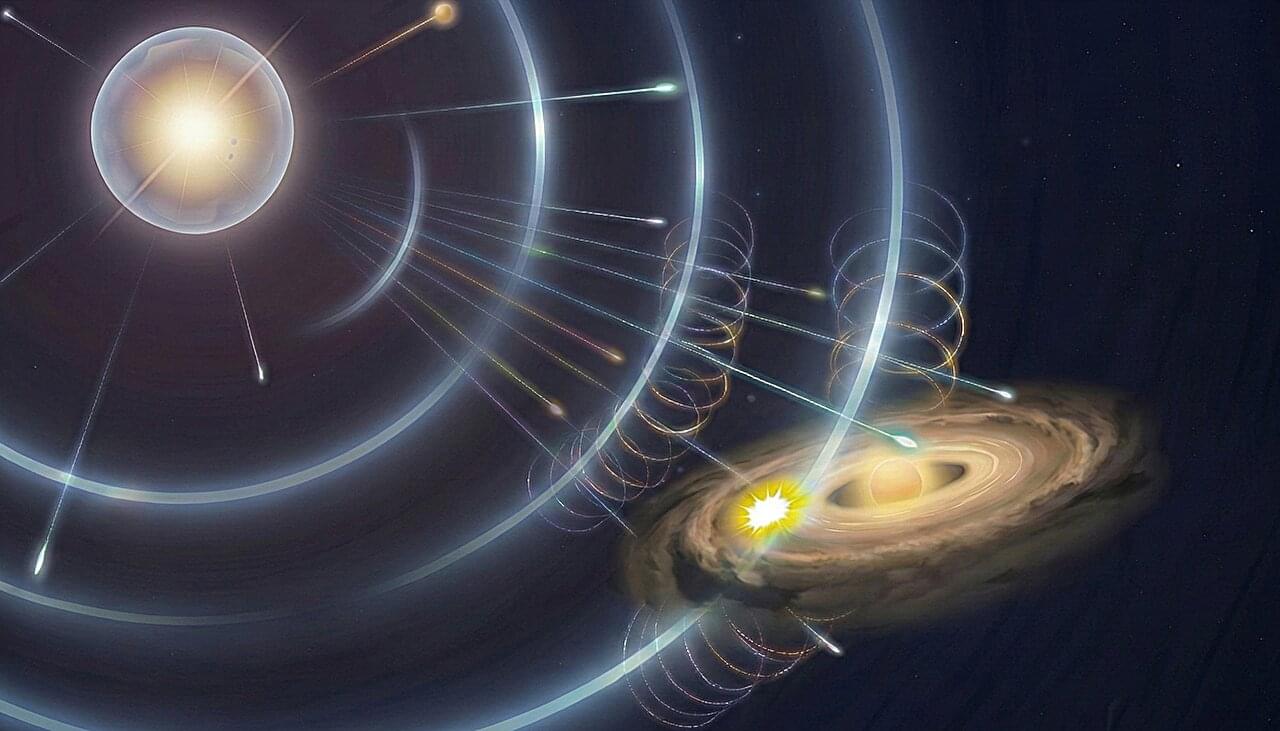
How common are Earth-like planets in the universe? When I started working on supernova explosions, I never imagined that my research would eventually lead me to ask a question about the origin of Earth-like planets. Yet that is exactly where it brought me.
For decades, planetary scientists have believed that the early solar system was enriched with short-lived radioactive elements—such as aluminum-26—by a nearby supernova. These radioactive elements played a crucial role in forming water-depleted rocky planets such as Earth. Their decay heated young planetesimals, causing them to lose much of their originally accreted water and other volatile materials.
There was just one problem that kept bothering me.