I very much enjoyed reading this nicely done preclinical study on using nebulized vasopressin to improve social cognition in low-sociality rhesus monkeys. Reading about their study design in particular was highly informative/educational! #preclinical #medicine #biomedicine
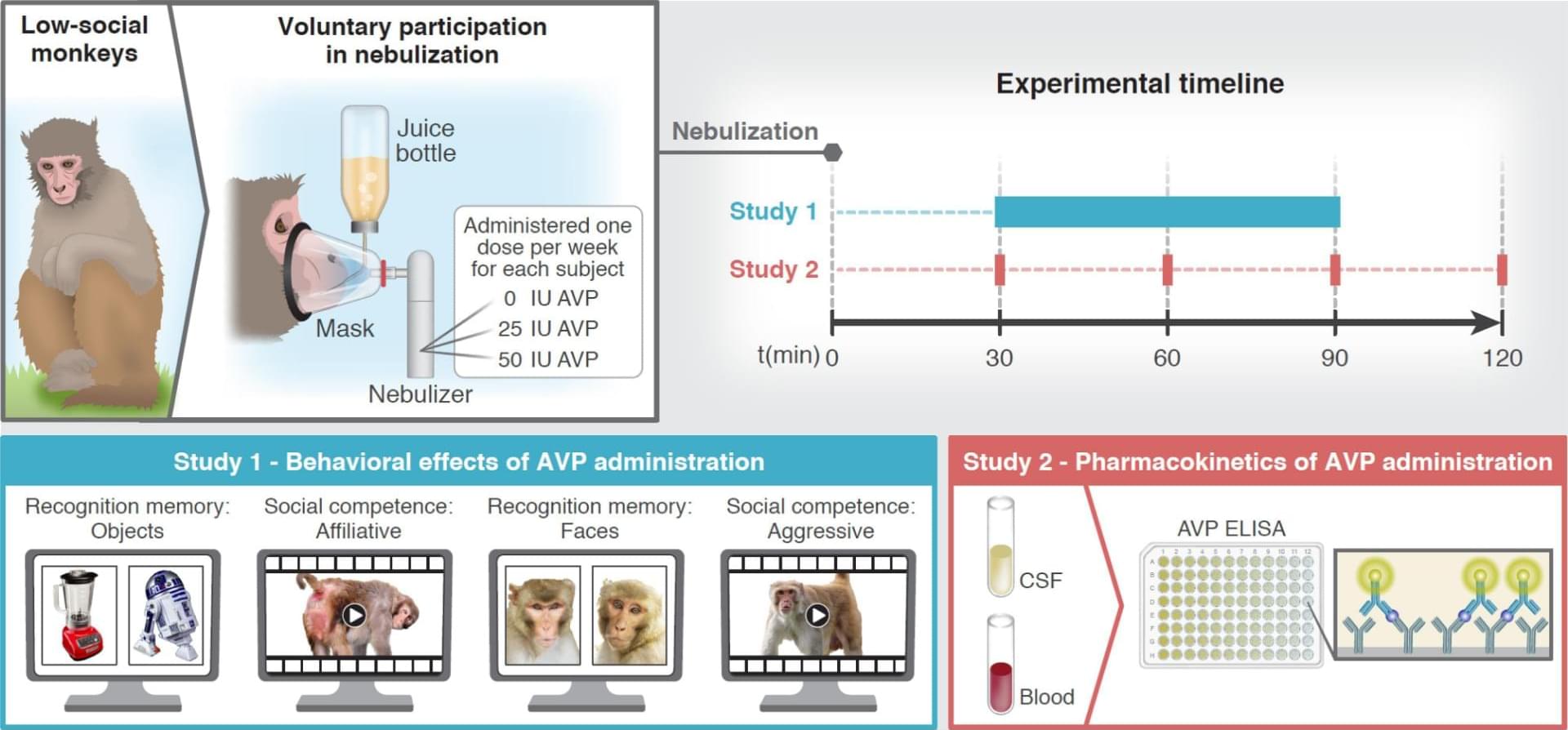
Low cerebrospinal (CSF) arginine vasopressin (AVP) concentration is a biomarker of social impairment in low-social monkeys and children with autism, suggesting that AVP administration may improve primate social functioning. However, AVP administration also increases aggression, at least in “neurotypical” animals with intact AVP signaling. Here, we tested the effects of a voluntary drug administration method in low-social male rhesus monkeys with high autistic-like trait burden. Monkeys received nebulized AVP or placebo, using a within-subjects design. Study 1 (N = 8) investigated the effects of AVP administration on social cognition in two tests comparing responses to social versus nonsocial stimuli. Test 1: Placebo-administered monkeys lacked face recognition memory, whereas face recognition memory was “rescued” following AVP administration.