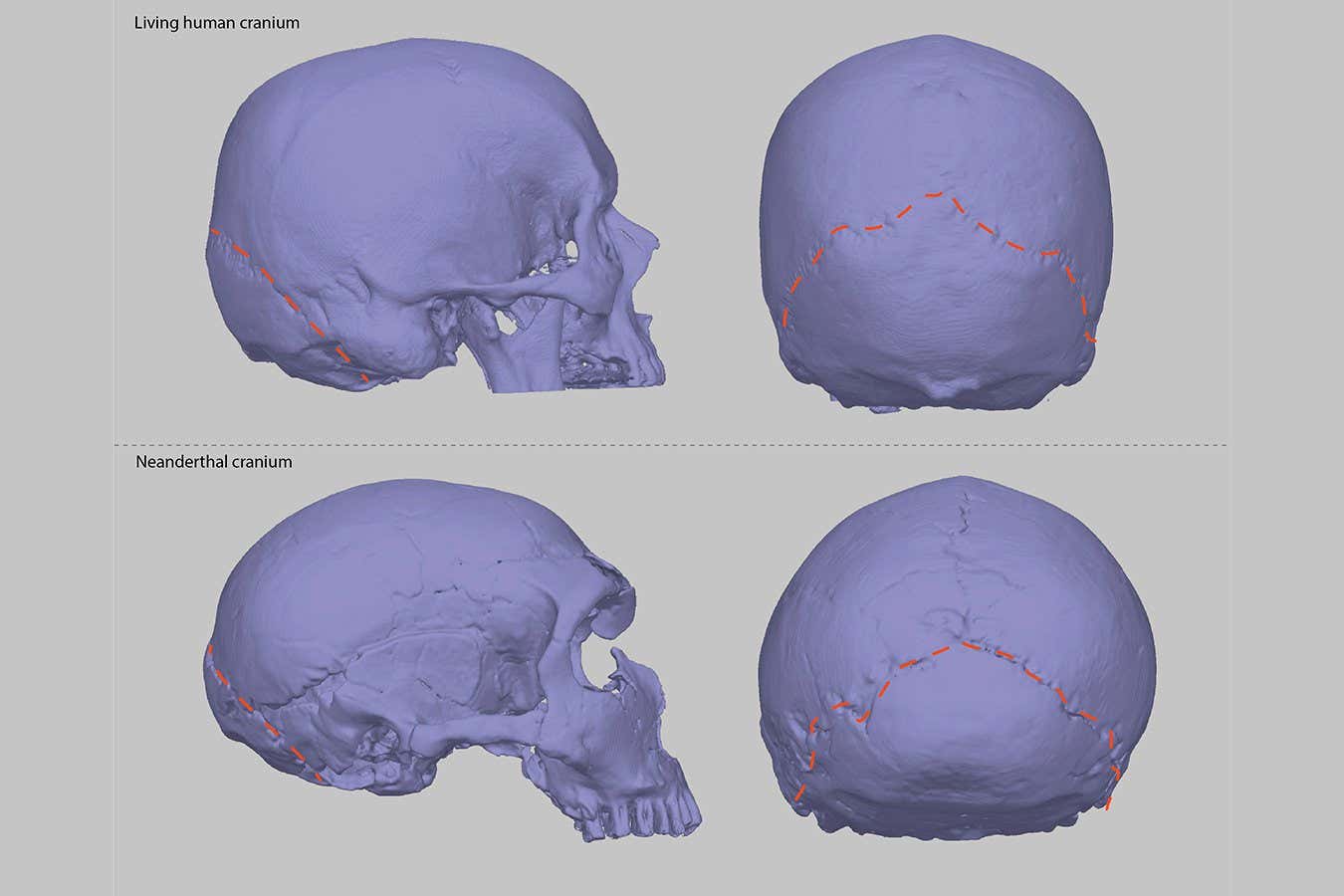
People with Chiari malformations have a skull shape similar to Neanderthals, suggesting that the condition may be caused by DNA inherited from archaic humans


Dr. Robert Schwab, MD is a Resident Physician, Research Specialist, and Hematology-Oncology Fellow at Penn Medicine, University of Pennsylvania Health System…
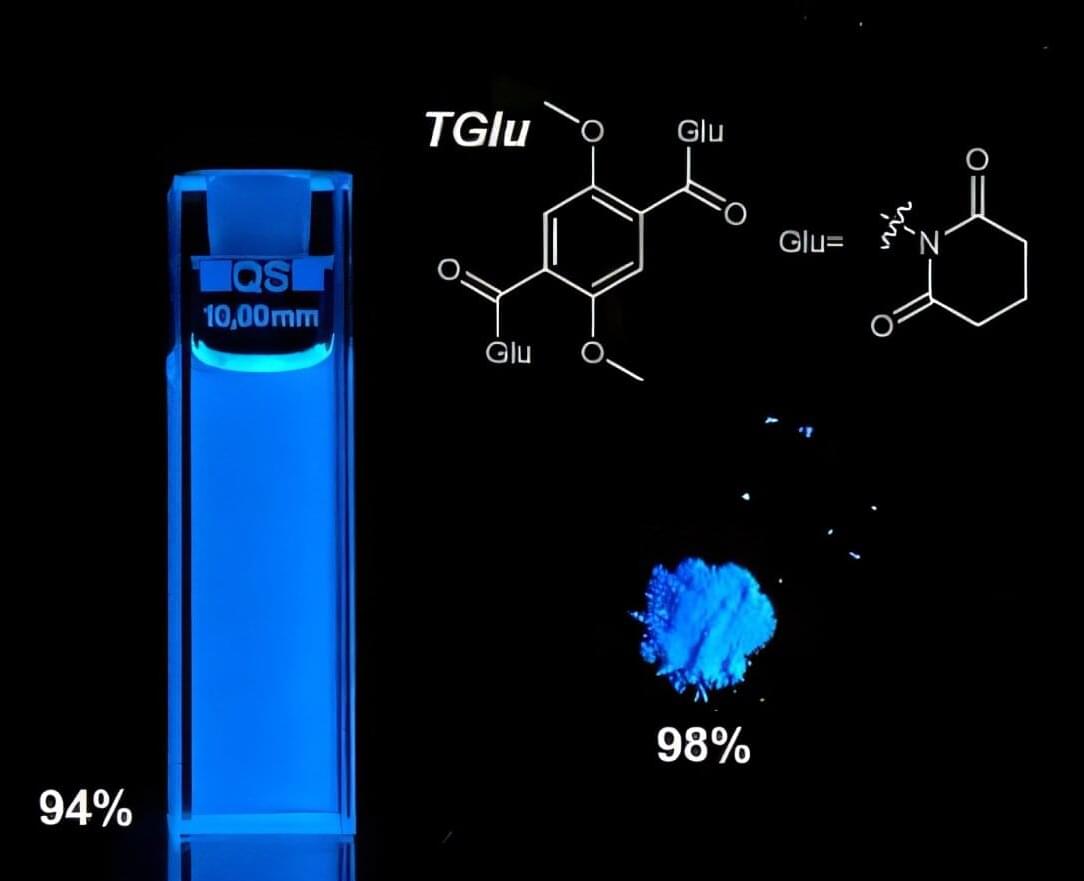
A new blue fluorescent molecule set new top emission efficiencies in both solid and liquid states, according to a University of Michigan-led study that could pave the way for applications in technology and medicine.
Able to absorb light and emit it at lower energy levels, fluorescent molecules called fluorophores glow in OLED displays and help doctors and scientists figure out what’s happening in cells and tissues. They need to be solid in displays and many sensing applications, but liquids are typically preferred for biological uses. Most fluorophores don’t work well in both forms, but this one does.
The study, “Elucidating the molecular structural origin of efficient emission across solid and solution phases of single benzene fluorophores,” is published in the journal Nature Communications.

IN A NUTSHELL 🐍 Researchers discovered a new species of snake, the Dendrelaphis atra, on Misima Island, known for its striking black eyes and color-changing abilities. 🌿 Misima Island, part of the Milne Bay Province, is a recognized biodiversity hotspot, hosting numerous endemic species of reptiles and amphibians. 🏗️ The discovery in human-modified settings highlights
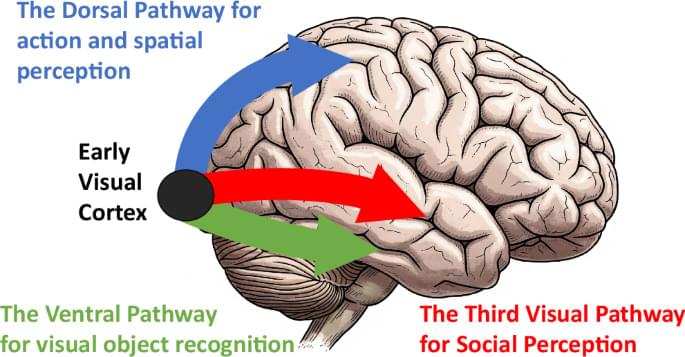
Recent evidence suggests the existence of a neural pathway specialized for social perception projecting between the well-established “what” and “where” pathways. A new study of neuropsychological patients demonstrates that this social pathway is causally essential for recognizing dynamic facial expressions.
Zoltan Istvan, a leading transhumanist, proposes a new economic model for the age of AI and robots.
Tech entrepreneur and investor Vinod Khosla’s prediction of AI automating 80% of high-value jobs by 2030 coincides with a reckoning for Fortune 500 companies.
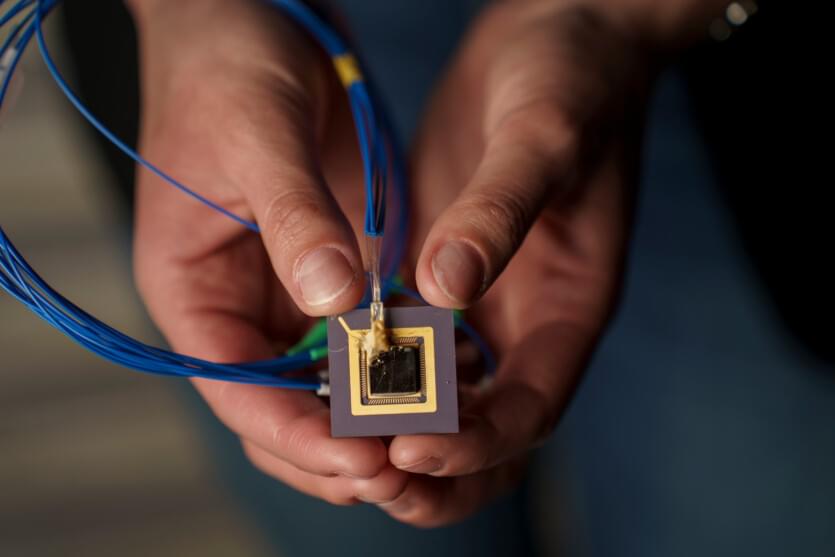
Researchers from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in the United States have created a tiny 3D printer chip-sized device that forms the necessary objects using light in a matter of seconds.
A team of researchers led by Professor Elena Nataros has created a 3D printer that emits a reconfigurable beam of light into resin to create solid forms. This tiny printer fits in the palm of your hand. It is expected that users will be able to quickly create customized, low-cost objects.
According to the developers, the system consists of a single photonic chip measuring a few millimeters, without any additional moving parts. It emits visible light into the resin, allowing for non-mechanical 3D printing.
