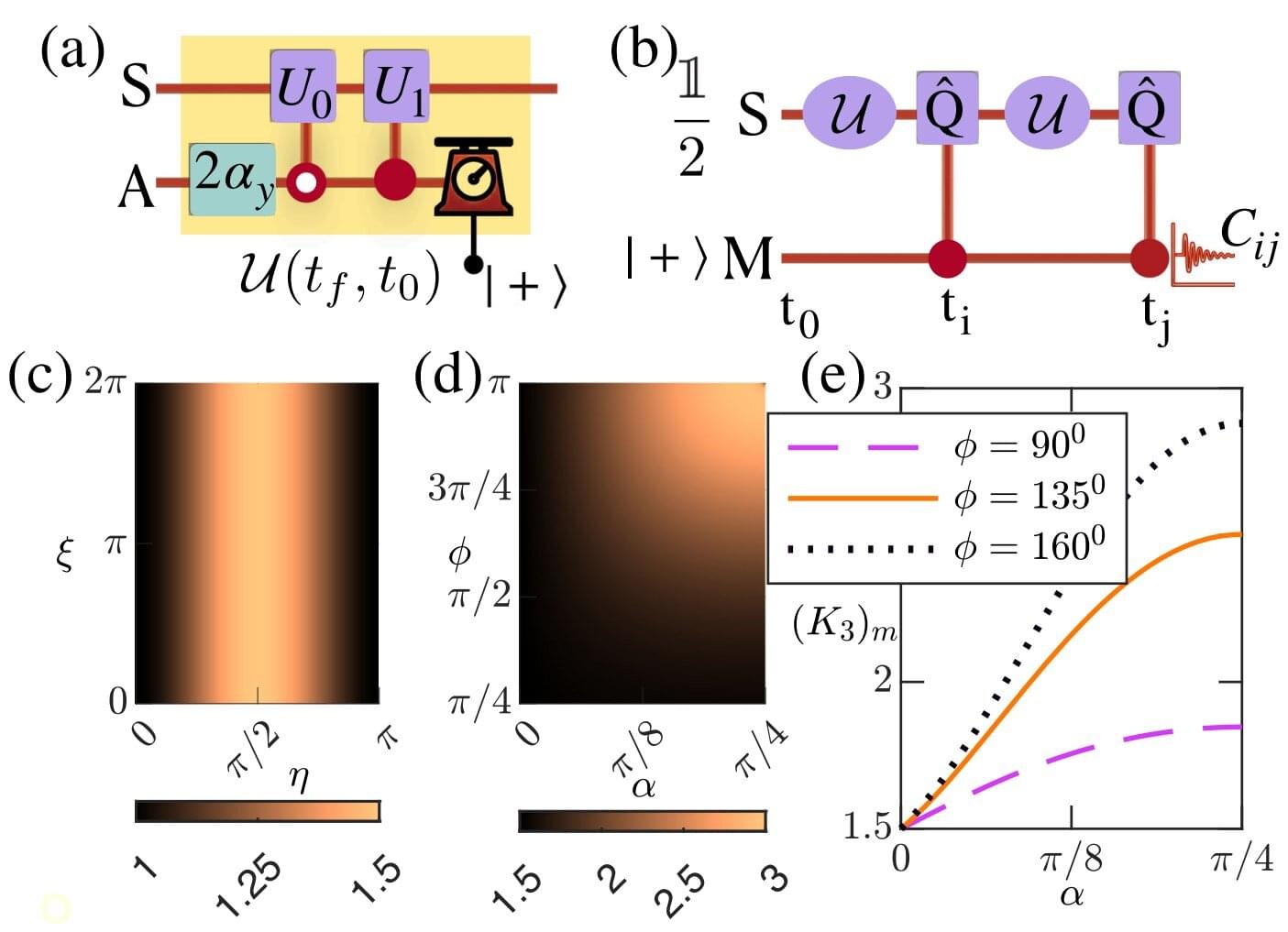
The quantum world is famously weird—a single particle can be in two places at once, its properties are undefined until they are measured, and the very act of measuring a quantum system changes everything. But according to new research published in Physical Review Letters, the quantum world is even stranger than previously thought.
What happens at the quantum level is in stark contrast to the classical world (what we see every day), where objects have definite properties whether or not we look at them, and observing them doesn’t change their nature. To see whether any system is behaving classically, scientists use a mathematical test called the Leggett-Garg inequality (LGI). Classical systems always obey the LGI limit while quantum systems violate it, proving they are non-classical.