A new brain imaging study finds that children with ADHD show disrupted development in white matter connecting emotional and cognitive brain regions. The research links these differences to symptom severity across childhood and adolescence.



A new study is providing a clearer picture of the genetic landscape of major depression, revealing that the disorder may have fundamentally different biological roots depending on the age at which it first appears. The research, published in Nature Genetics, found that depression beginning in adolescence or young adulthood has a stronger genetic basis, is linked to early brain development, and carries a much higher genetic association with suicide attempts compared to depression that starts later in life.
Major depressive disorder is recognized as a clinically diverse condition, meaning its symptoms and course can vary substantially from person to person. Researchers have long suspected that this clinical variability might stem from different underlying causes.
One of the most apparent distinctions among individuals with depression is their age at onset. Depression that emerges early in life is often associated with more severe outcomes, including suicidal behavior, while late-onset depression has been linked more frequently to cognitive decline and cardiovascular problems.
Join us on Patreon! https://www.patreon.com/MichaelLustgartenPhD
Discount Links/Affiliates:
Blood testing (where I get the majority of my labs): https://www.ultalabtests.com/partners/michaellustgarten.
At-Home Metabolomics: https://www.iollo.com?ref=michael-lustgarten.
Use Code: CONQUERAGING At Checkout.
Clearly Filtered Water Filter: https://get.aspr.app/SHoPY
Epigenetic, Telomere Testing: https://trudiagnostic.com/?irclickid=U-s3Ii2r7xyIU-LSYLyQdQ6…M0&irgwc=1
Use Code: CONQUERAGING
NAD+ Quantification: https://www.jinfiniti.com/intracellular-nad-test/
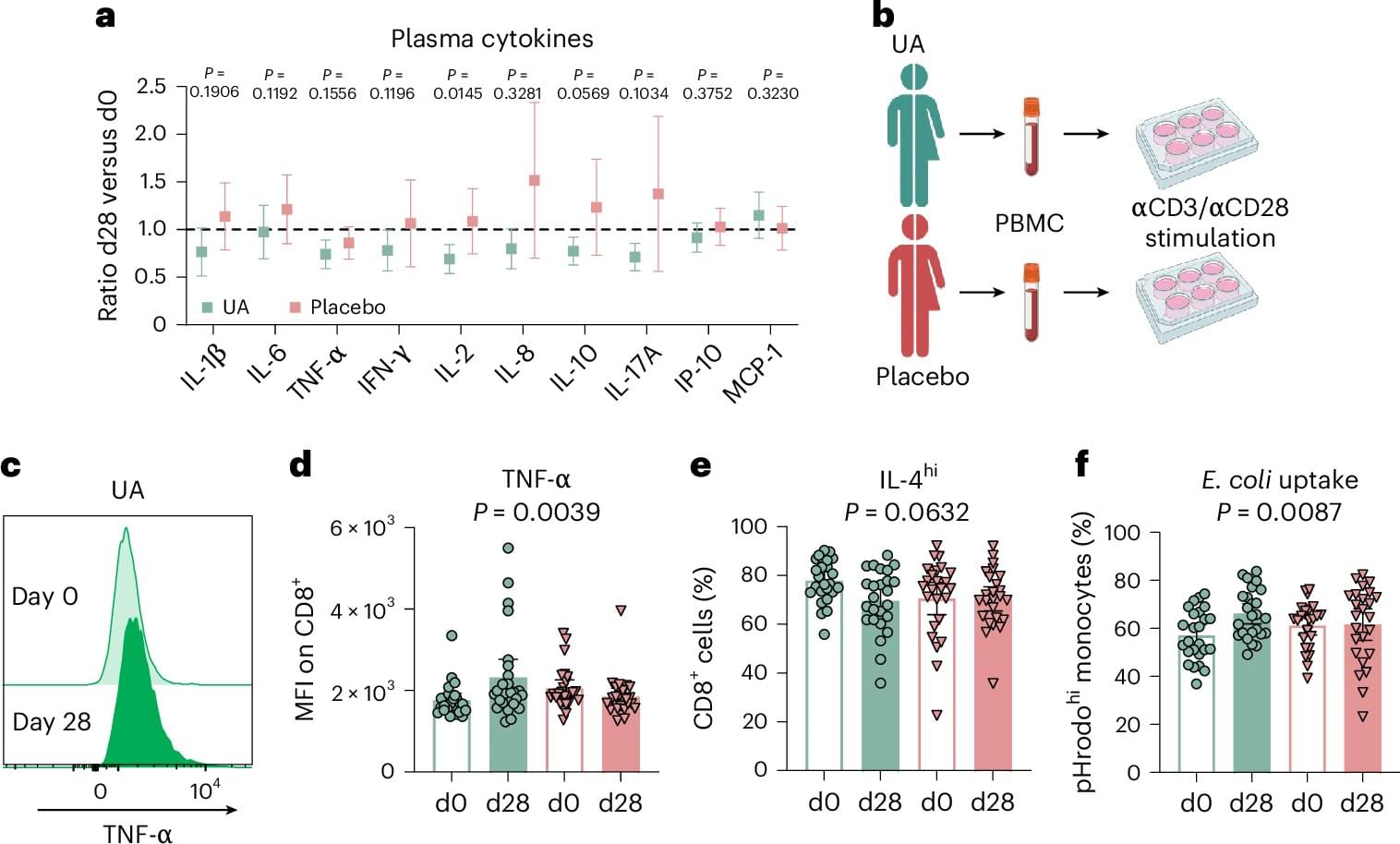
An international research team focused on aging reports that urolithin A at 1,000 mg per day shifted human immune profiles toward a more naive-like, less exhausted CD8+ state and increased fatty acid oxidation capacity, with additional functional gains.
Urolithin A is a metabolite produced by gut bacteria after breaking down ellagic acid from certain foods, such as pomegranates and walnuts. While produced naturally through microbial digestion, it is in much smaller quantities than available as a supplement or used in the study.
Aging bodies face reduced production of mature T cells, shrinking naive T cell pools and chronic low-grade inflammation. Mitochondrial dysfunction and waning autophagy sit at the core of these shifts, with mitophagy failure linked to immune dysregulation and disease.
A Penn-led team has revealed how hydralazine, one of the world’s oldest blood pressure drugs and a mainstay treatment for preeclampsia, works at the molecular level. In doing so, they made a surprising discovery—it can also halt the growth of aggressive brain tumors.
Over the last 70 years, hydralazine has been an indispensable tool in medicine—a front-line defense against life-threatening high blood pressure, especially during pregnancy. But despite its essential role, a fundamental mystery has persisted: No one knows its “mechanism of action”—essentially how it works at a molecular level, which allows for improved efficacy, safety, and what it can treat.
“Hydralazine is one of the earliest vasodilators ever developed, and it’s still a first-line treatment for preeclampsia—a hypertensive disorder that accounts for 5%–15% of maternal deaths worldwide,” says Kyosuke Shishikura, a physician-scientist at the University of Pennsylvania. “It came from a ‘pre-target’ era of drug discovery, when researchers relied on what they saw in patients first and only later tried to explain the biology behind it.”
Japanese researchers are testing a surprising, minimally invasive way to repair spine fractures.
A team at Osaka Metropolitan University found that stem cells from fat tissue can repair breaks similar to those common in people with the bone-weakening disease osteoporosis.
“This simple and effective method can treat even difficult fractures and may accelerate healing,” said study co-leader Dr. Shinji Takahashi, an orthopedic surgeon and clinical lecturer at the university.


We show that an agentic large language model (LLM) (OpenAI o3 with deep research) can autonomously reason, write code, and iteratively refine hypotheses to derive a physically interpretable equation for competitive adsorption on metal-organic layers (MOLs)—an open problem our lab had struggled with for months. In a single 29-min session, o3 formulated the governing equations, generated fitting scripts, diagnosed shortcomings, and produced a compact three-parameter model that quantitatively matches experiments across a dozen carboxylic acids.
Timothy Donald Cook (born November 1, 1960) [ 1 ] is an American business executive who is the current chief executive officer of Apple. Cook had previously been the company’s chief operating officer under its co-founder Steve Jobs. [ 2 ] Cook joined Apple in March 1998 as a senior vice president for worldwide operations, and then as vice president for worldwide sales and operations. [ 3 ] He was appointed chief executive of Apple on August 24, 2011, after Jobs resigned.
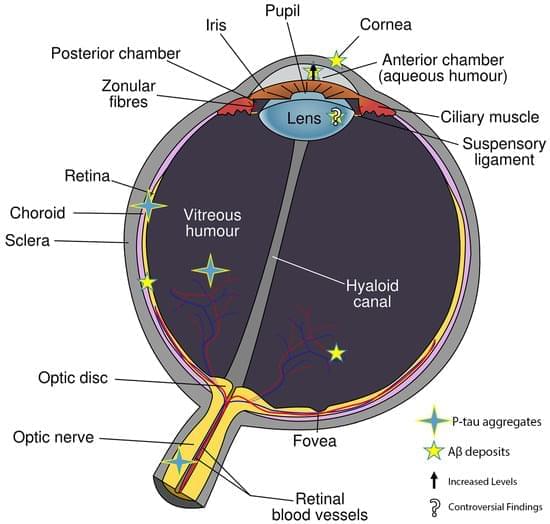
In the early stages of Alzheimer–Perusini’s disease (AD), individuals often experience vision-related issues such as color vision impairment, reduced contrast sensitivity, and visual acuity problems. As the disease progresses, there is a connection with glaucoma and age-related macular degeneration (AMD) leading to retinal cell death. The retina’s involvement suggests a link with the hippocampus, where most AD forms start. A thinning of the retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) due to the loss of retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) is seen as a potential AD diagnostic marker using electroretinography (ERG) and optical coherence tomography (OCT). Amyloid beta fragments (Aβ), found in the eye’s vitreous and aqueous humor, are also present in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and accumulate in the retina. Aβ is known to cause tau hyperphosphorylation, leading to its buildup in various retinal layers.