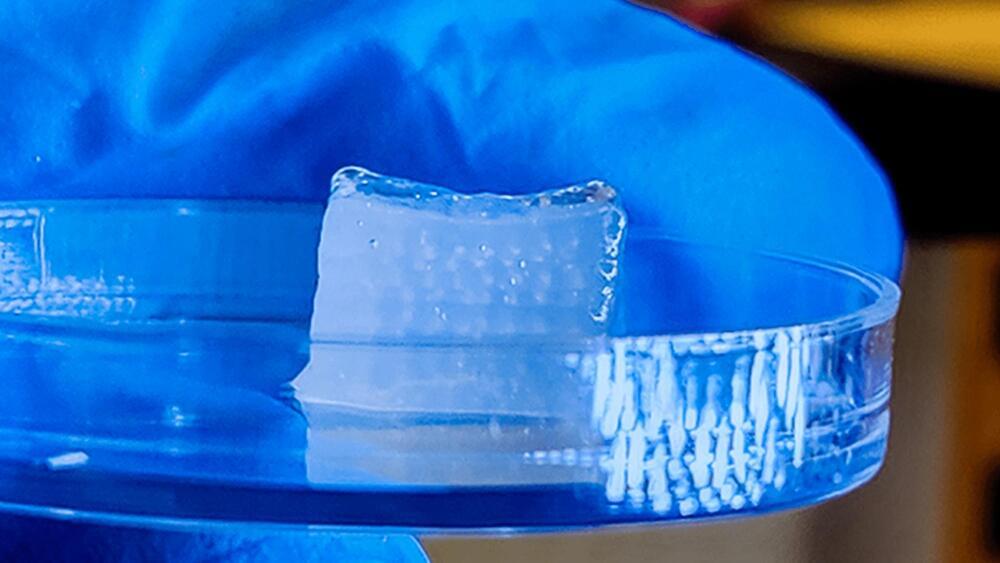
HITS-Bio is the first tool to bioprint directly on a wound.
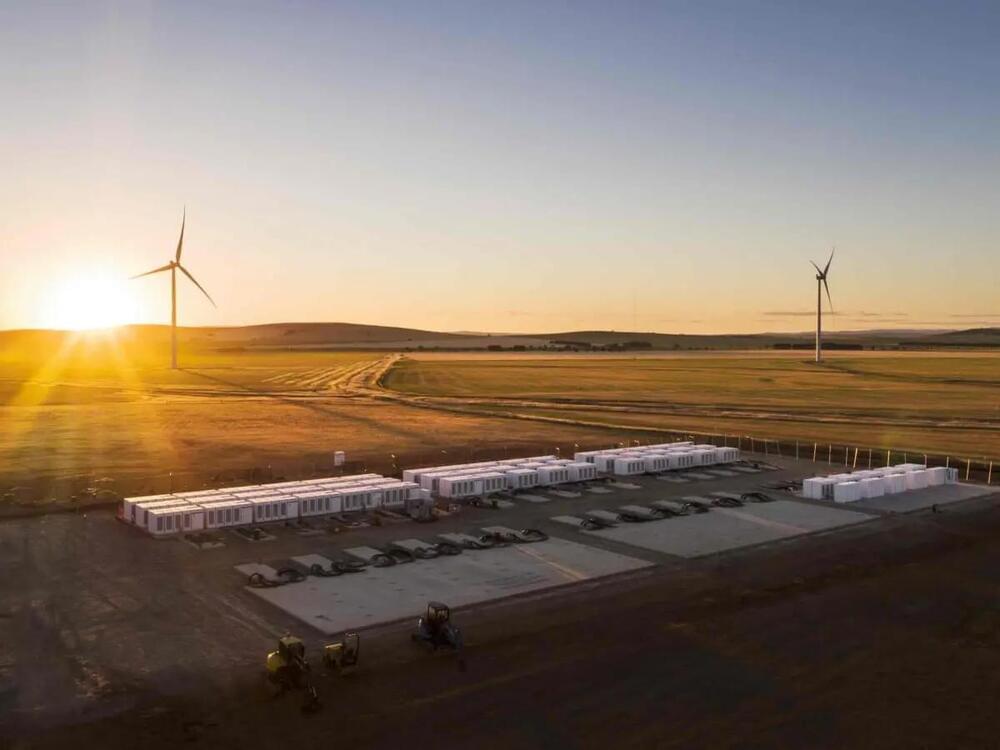


South Australia has the highest wind and solar share – an average of around 72 per cent over the last 12 months – vastly more than other state in Australia, and higher than any other gigawatt scale grid in the world.
Renewable energy critics, particularly those that don’t understand the way that grids work, instantly assume that this means South Australia’s grid must be weak and unreliable. But that is simply not true, and a new report from Australian Energy Market Operator on “system strength” underlines why this is so.
System strength is an important part of grid security, and – according to AEMO – describes the ability of the power system to maintain and control the voltage waveform at a given location, when the grid is running normally and particularly when it has to deal with a major disturbance.
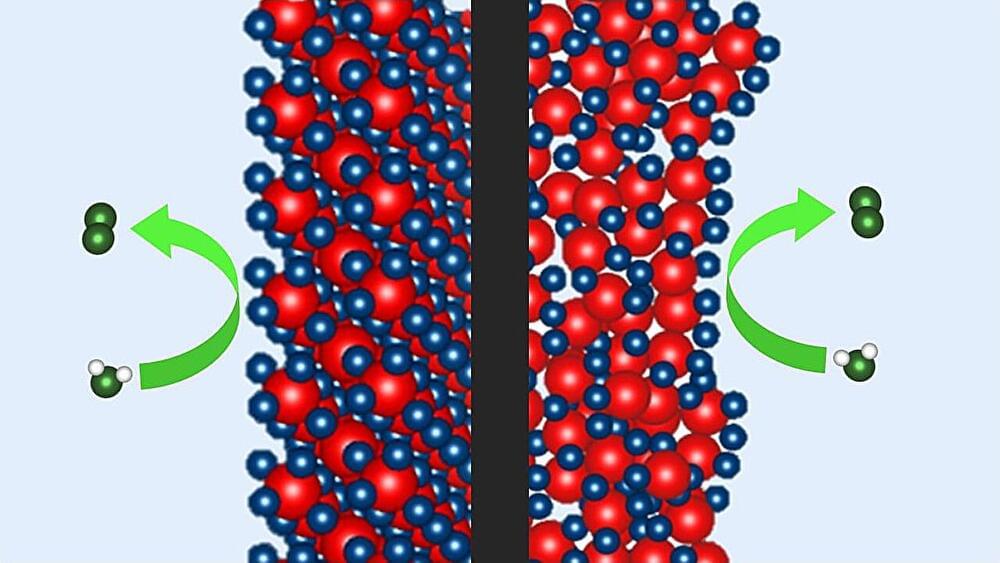
Iridium-based catalysts are needed to produce hydrogen using water electrolysis. Now, a team at HZB has shown that the newly developed P2X catalyst, which requires only a quarter of the iridium, is as efficient and stable over time as the best commercial catalyst. Measurements at BESSY II have now revealed how the special chemical environment in the P2X catalyst during electrolysis promotes the oxygen evolution reaction during water splitting.
In the future, hydrogen will be needed in a climate-neutral energy system to store energy, as a fuel, and a raw material for the chemical industry. Ideally, it should be produced in a climate-neutral way, using electricity generated from harnessing the sun’s or wind energy, via the electrolysis of water.
In that respect, Proton Exchange Membrane Water Electrolysis (PEM-WE) is currently considered a key technology. Both electrodes are coated with special electrocatalysts to accelerate the desired reaction. Iridium-based catalysts are best suited for the anode, where the sluggish oxygen evolution reaction occurs. However, iridium is one of the rarest elements on earth, and one of the major challenges is to significantly reduce the demand for this precious metal.

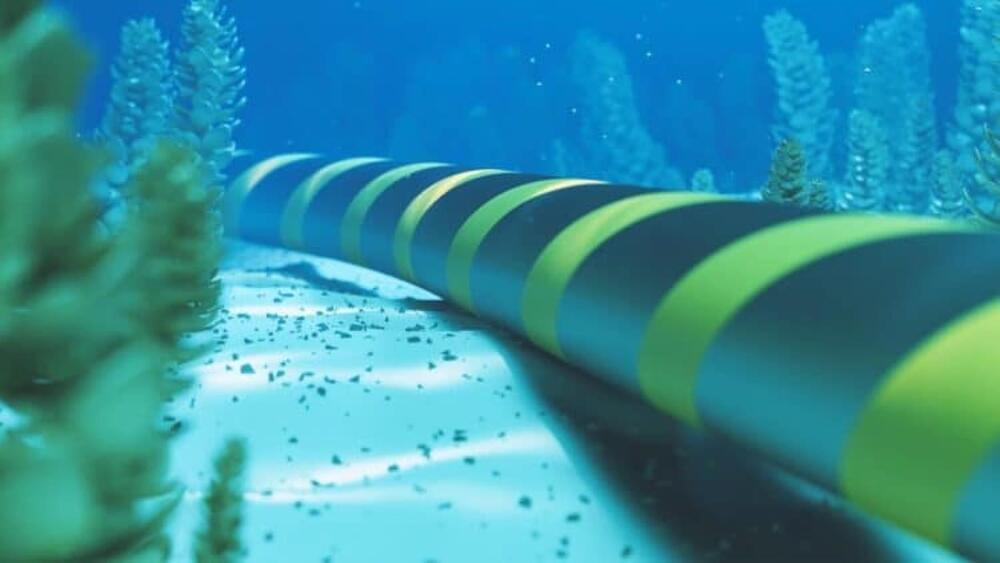
Envision a settlement where the sunlight that beams across Australia buoy on its vast outback powers millions of homes and industries across Southeast Asia. This is how the Australia-Asia PowerLink (AAPowerLink) is being realized: the longest sub-sea cable in the world, linking northern Australia to Singapore, presently is one of the all-time break-through renewable energy developments. By virtue of this mammoth solar farm with its advanced energy transmission technology, this ambitious vision will shape the future energy systems around the world while addressing some critical climate issues.
Taking enormous advantage from its plentiful sunlight, northern Australia houses the world’s biggest Solar Precinct in its Northern Territory gathering between 17–20 GW peak electricity, a size surpassing that of Australia’s largest coal-fired power station.
The project incorporates advanced storage of 36–42 GWh, supplying 800 MW to Darwin and 1.75 GW to Singapore. In addition to reducing emissions and electricity prices for the Darwin region, it creates a renewable energy export marketplace for the region and demonstrates the use of the solar-rich area to meet 15 percent of Singapore’s electricity demand.


Despite technological advances like electronic health records (EHRs) and dictation tools, the administrative load on healthcare providers has only grown, often overshadowing the time and energy dedicated to direct patient care. This escalation in clerical tasks is a major contributor to physician burnout and dissatisfaction, affecting not only the well-being of providers but also the quality of care they deliver.
During consultations, the focus on documentation can detract from meaningful patient interactions, resulting in fragmented, rushed, and sometimes impersonal communication. The need for a solution that both streamlines documentation and restores the patient-centred nature of healthcare has never been more pressing. This is where AI-powered medical scribes come into play, offering a promising path from traditional dictation to fully automated, integrated documentation support.
AI medical scribe software utilises advanced artificial intelligence and machine learning to transcribe, in real time, entire patient-physician consultations without the need for traditional audio recordings. Leveraging sophisticated speech recognition and natural-language processing (NLP) algorithms, AI scribes are capable of interpreting and processing complex medical conversations with impressive accuracy. These systems can intelligently filter out non-essential dialogue, such as greetings and small talk, to create a streamlined and detailed clinical note.