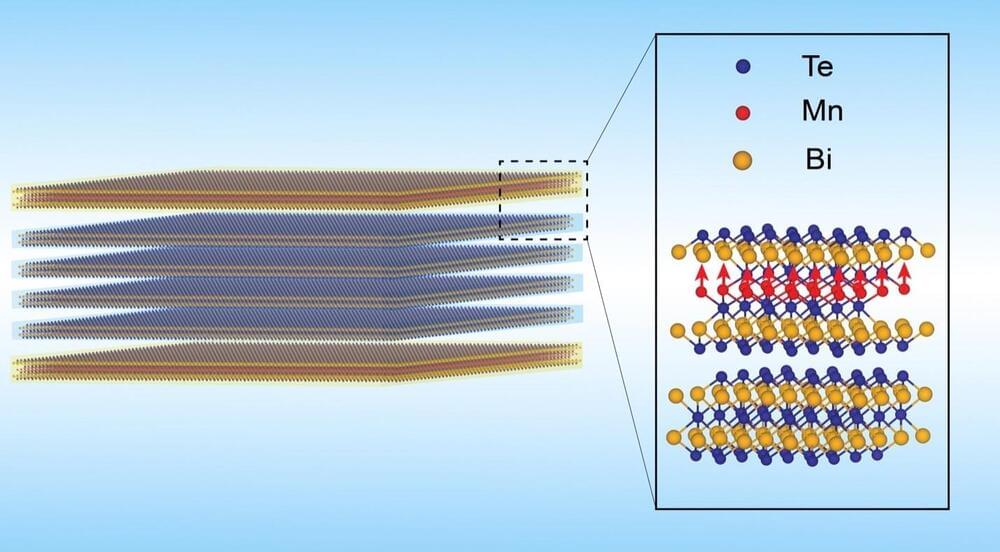
Researchers have developed a new “sandwich” structure material that exhibits the quantum anomalous Hall effect, enabling electrons to travel with almost no resistance at higher temperatures.
This breakthrough could significantly enhance computing power while dramatically reducing energy consumption. The structure is based on a layered approach with bismuth telluride and manganese bismuth telluride, promising faster and more efficient future electronic devices.
Quantum Material Innovations