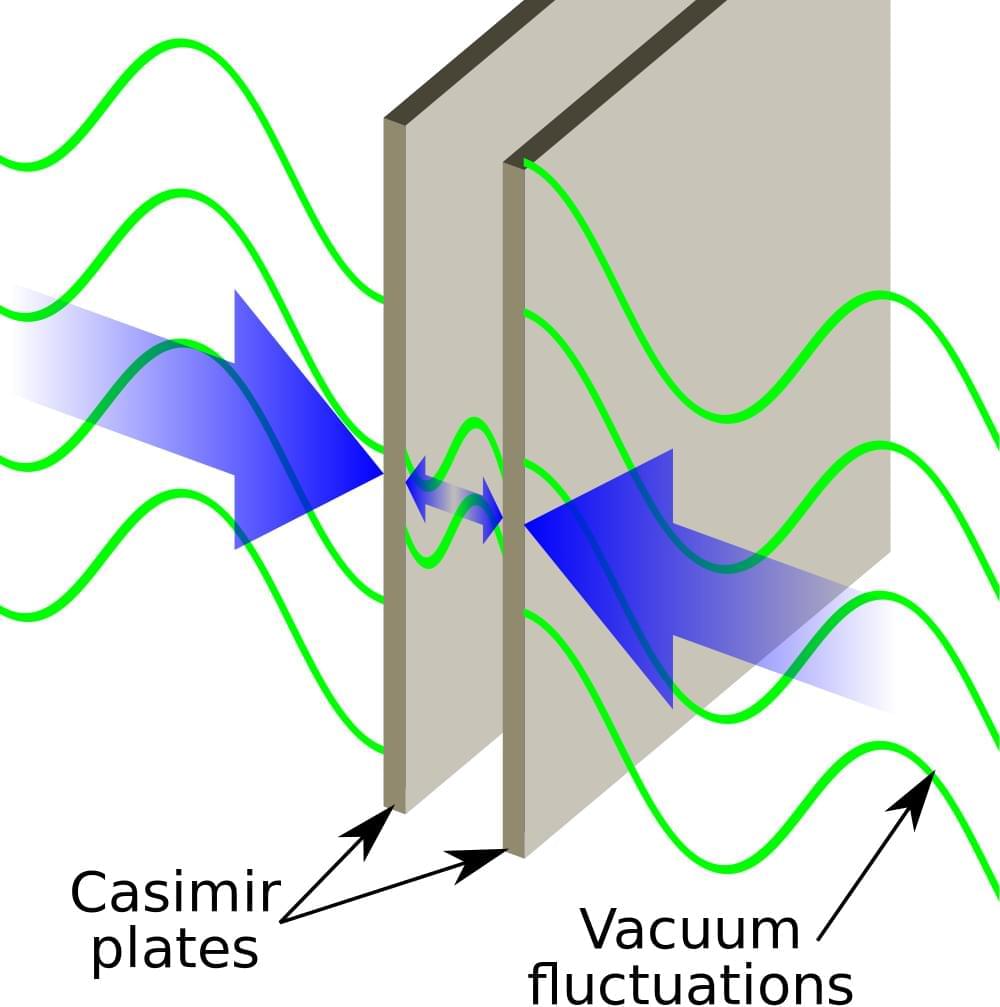
Recently I saw a post on twitter claiming that AI could be powered with quantum vacuum energy. The post was accompanied by a figure from a paper published in Nature. Unfortunately for the poster, but fortunately for science, the paper had nothing to do with extracting energy from the vacuum. Rather, it was a description of an experimental realization of a transistor that uses the Casimir effect to mediate and amplify energy transfer across a new kind of transistor.
The report features six studies that thoroughly examined MIT’s superconducting magnets design used in its breakthrough fusion test.
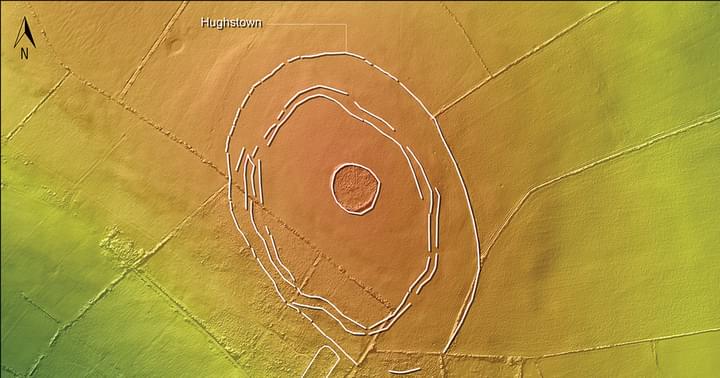
An archaeologists has been able to find forgotten structures hidden in Ireland that were probably used as pathways for the dead.
Using Olympics for pushing food agenda, I wonder how that food will influence sport results?
With 60% of the food served to the public being meat-free and 80% sourced locally, the Paris Olympic Games are setting a new standard for environmental sustainability.
1/ Researchers have found that AI models can solve complex tasks like “3SUM” by using simple dots like “…” instead of sentences.
Researchers have found that specifically trained LLMs can solve complex problems just as well using dots like “…” instead of full sentences. This could make it harder to control what’s happening in these models.
The researchers trained Llama language models to solve a difficult math problem called “3SUM”, where the model has to find three numbers that add up to zero.
Usually, AI models solve such tasks by explaining the steps in full sentences, known as “chain of thought” prompting. But the researchers replaced these natural language explanations with repeated dots, called filler tokens.
As electric vehicle (EV) sales skyrocket, more than doubling in 2021 compared to 2020, and automotive companies announce massive investments in batteries and EVs, the transition from gas to electricity-powered vehicles is looking all the more inevitable.
Still, misinformation abounds during this exciting technological change. Here are seven of the biggest myths about EVs.
1. Electric cars will always be more expensive. Up front electric vehicle prices have steadily fallen since the turn of the century, to the point where they are closing in on parity with gas vehicles.
Cosmological puzzles are tempting astronomers to rethink our simple picture of the universe – and ask whether dark matter is even stranger than we thought.
By Stuart Clark
Boston Dynamics is retiring the original Atlas at the age of 11. TechCrunch’s Brian Heater discusses the pioneering bot’s legacy and what the company has in mind for its offspring.