One stormy Monday in March, 1827, the German composer Ludwig van Beethoven passed away after a protracted illness.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
A marine robot that can swim, crawl and glide untethered in the deepest parts of the ocean
A team of mechanical engineers at Beihang University, working with a deep-sea diving specialist from the Chinese Academy of Sciences and a mechanic from Zhejiang University, all in China, have designed, built, and tested a marine robot that can swim, crawl, and glide untethered in the deepest parts of the ocean.
In their paper published in the journal Science Robotics, the group describes the factors that went into their design and how well their robot performed when tested.
Over the past several decades, underwater robots have become very important tools for studying the various parts of the world’s oceans and the creatures that live in them. More recently, it has been noted that most such craft, especially those that are sent to very deep parts of the sea, are cumbersome and not very agile.
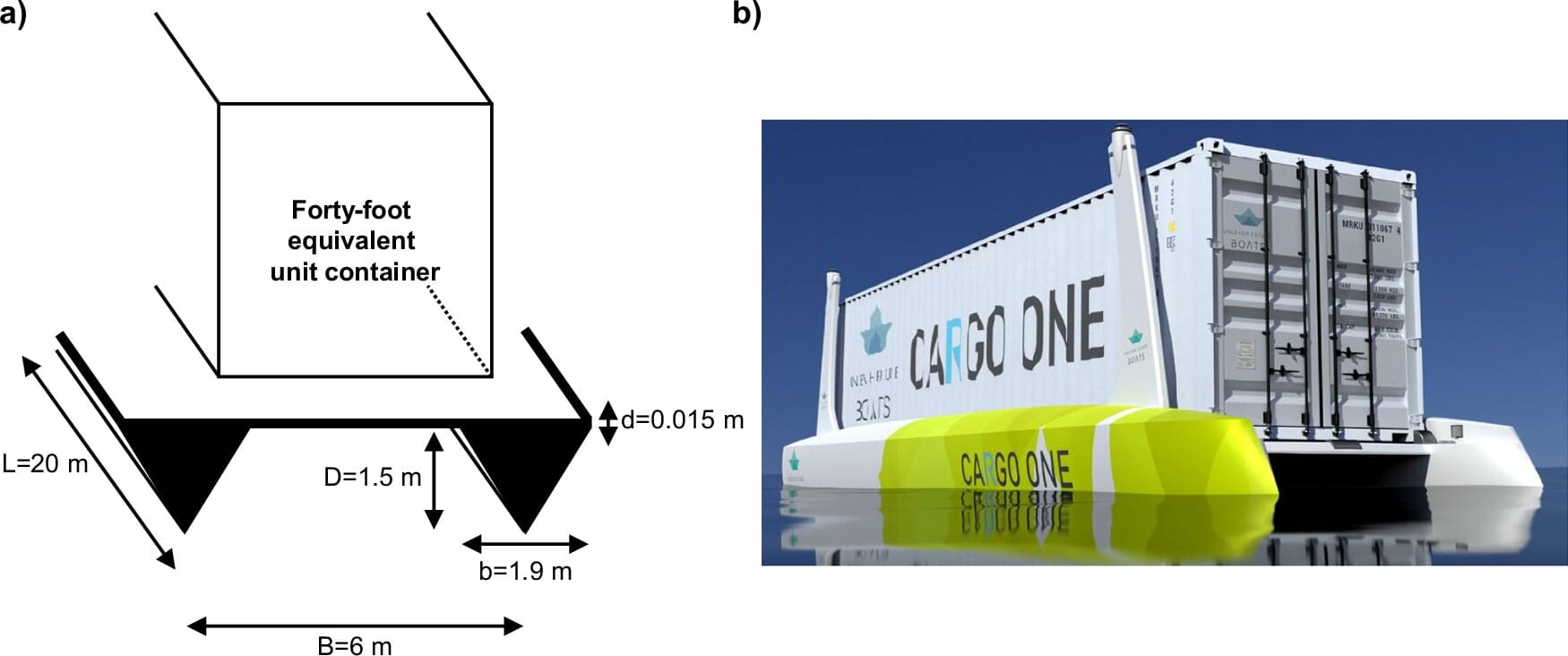
Hydrogen-powered boats offer climate-friendly alternative to road transport
Cargo transport is responsible for an enormous carbon footprint. Between 2010 and 2018, the transport sector generated about 14% of global greenhouse gas emissions. To address this problem, experts are looking for alternative, climate-friendly solutions—not only for road transport, but also for shipping, a sector in which powering cargo ships with batteries has proved especially difficult.
One promising but under-researched solution involves small, autonomous, hydrogen-powered boats that can partially replace long-haul trucking. A research team led by business chemist Prof Stephan von Delft from the University of Münster has now examined this missing link in a new study published in Communications Engineering.
The team has mathematically modeled such a boat for the first time and carried out a life cycle- and cost analysis. “Our calculations show in which scenarios hydrogen-powered boats are not only more sustainable but also more economical compared to established transport solutions,” explains von Delft. “They are therefore relevant for policymakers and industry.”
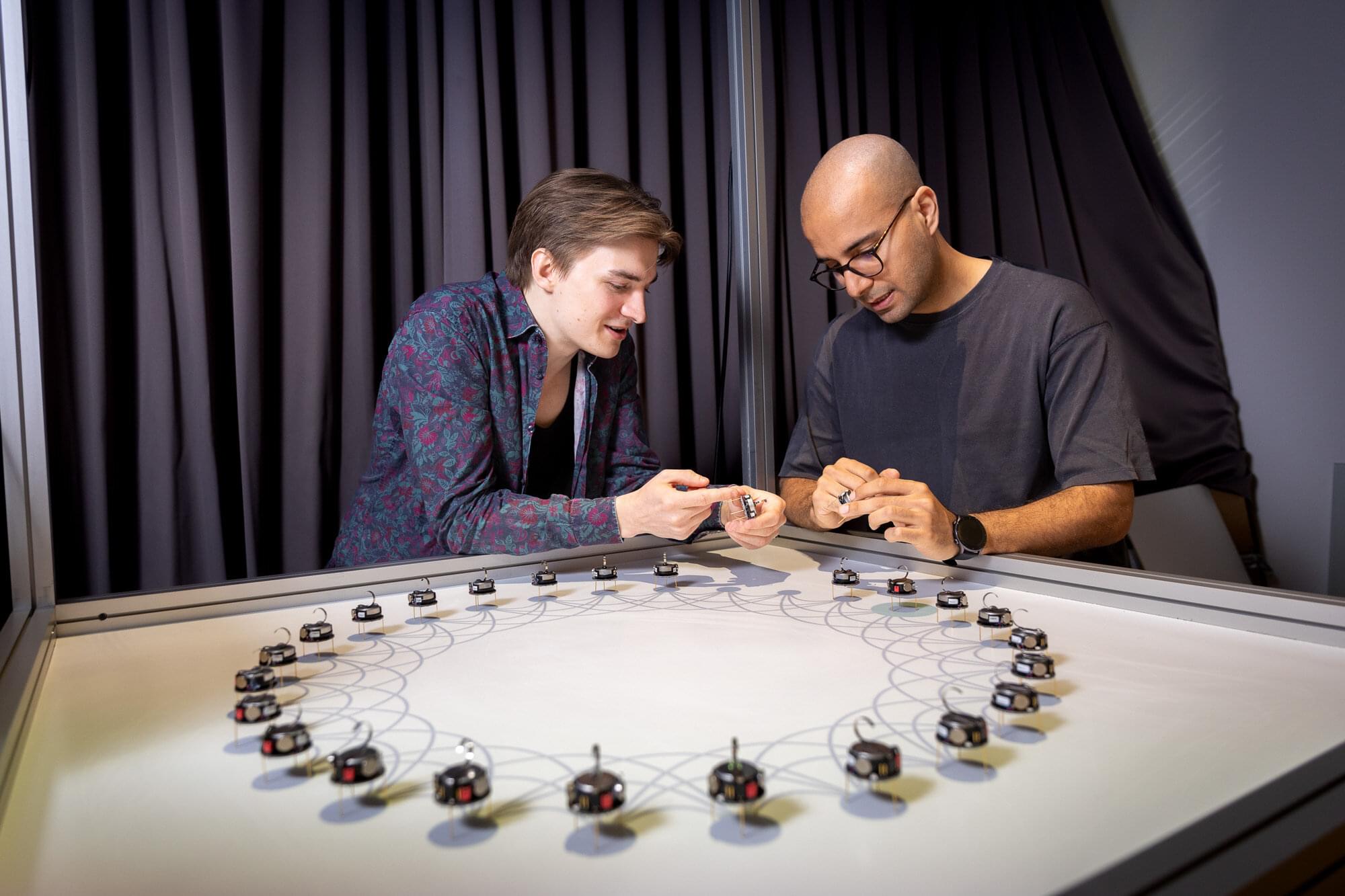

From robot swarms to human societies, good decisions rely on the right mix of perspectives
When groups make decisions—whether it’s humans aligning on a shared idea, robots coordinating tasks, or fish deciding where to swim—not everyone contributes equally. Some individuals have more reliable information, whereas others are more connected and have higher social influence.
A new study by researchers at the Cluster of Excellence Science of Intelligence shows that a combination of uncertainty and heterogeneity plays a crucial role in how groups reach consensus.
The findings, published in Scientific Reports by Vito Mengers, Mohsen Raoufi, Oliver Brock, Heiko Hamann, and Pawel Romanczuk, show that groups make faster and more accurate decisions when individuals factor in not only the opinions of their neighbors but also their confidence about these opinions and how connected those others are within the group.


Water Futures: Mobilizing Multi-Stakeholder Action for Resilience
Access to freshwater is changing rapidly, with water stress affecting billions of people and countless businesses each year. Droughts and floods are becoming more frequent and severe, water pollution continues to rise and, without urgent action, we will soon reach a tipping point. This report outlines key pathways to strengthen water resilience, through private sector and multi-stakeholder action, and secure the future of water for society and the global economy.
Every industry depends on water. This makes water resilience not just an environmental concern, but a cornerstone of economic stability, business continuity and prosperity. Rising demand, driven by population growth, shifting consumption and the energy transition, is further straining resources. With an economic value estimated at $58 trillion, water’s critical importance and the scale of the challenge cannot be overstated.
No company or government can build water resilience alone. The World Economic Forum’s Water Futures Community brings together public and private sector sectors leaders to accelerate investment and action. In collaboration with McKinsey & Company, this report offers a systems approach for our community of partners to strengthen water resilience and highlights opportunities for collective action to accelerate solutions at scale.


The way we train AI is fundamentally flawed
To understand exactly what’s going on, we need to back up a bit. Roughly put, building a machine-learning model involves training it on a large number of examples and then testing it on a bunch of similar examples that it has not yet seen. When the model passes the test, you’re done.
What the Google researchers point out is that this bar is too low. The training process can produce many different models that all pass the test but—and this is the crucial part—these models will differ in small, arbitrary ways, depending on things like the random values given to the nodes in a neural network before training starts, the way training data is selected or represented, the number of training runs, and so on. These small, often random, differences are typically overlooked if they don’t affect how a model does on the test. But it turns out they can lead to huge variation in performance in the real world.
In other words, the process used to build most machine-learning models today cannot tell which models will work in the real world and which ones won’t.