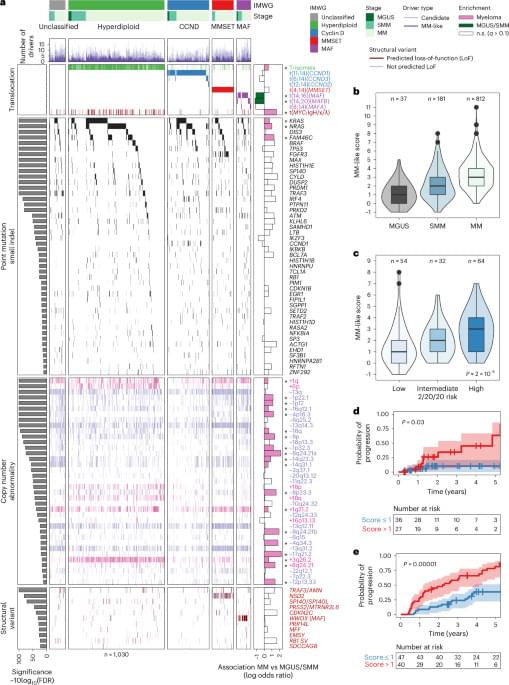
The genomic features of precursor conditions of multiple myeloma provide multiple biological insights into disease origins and evolution, together with opportunities to identify those at highest risk of progression.

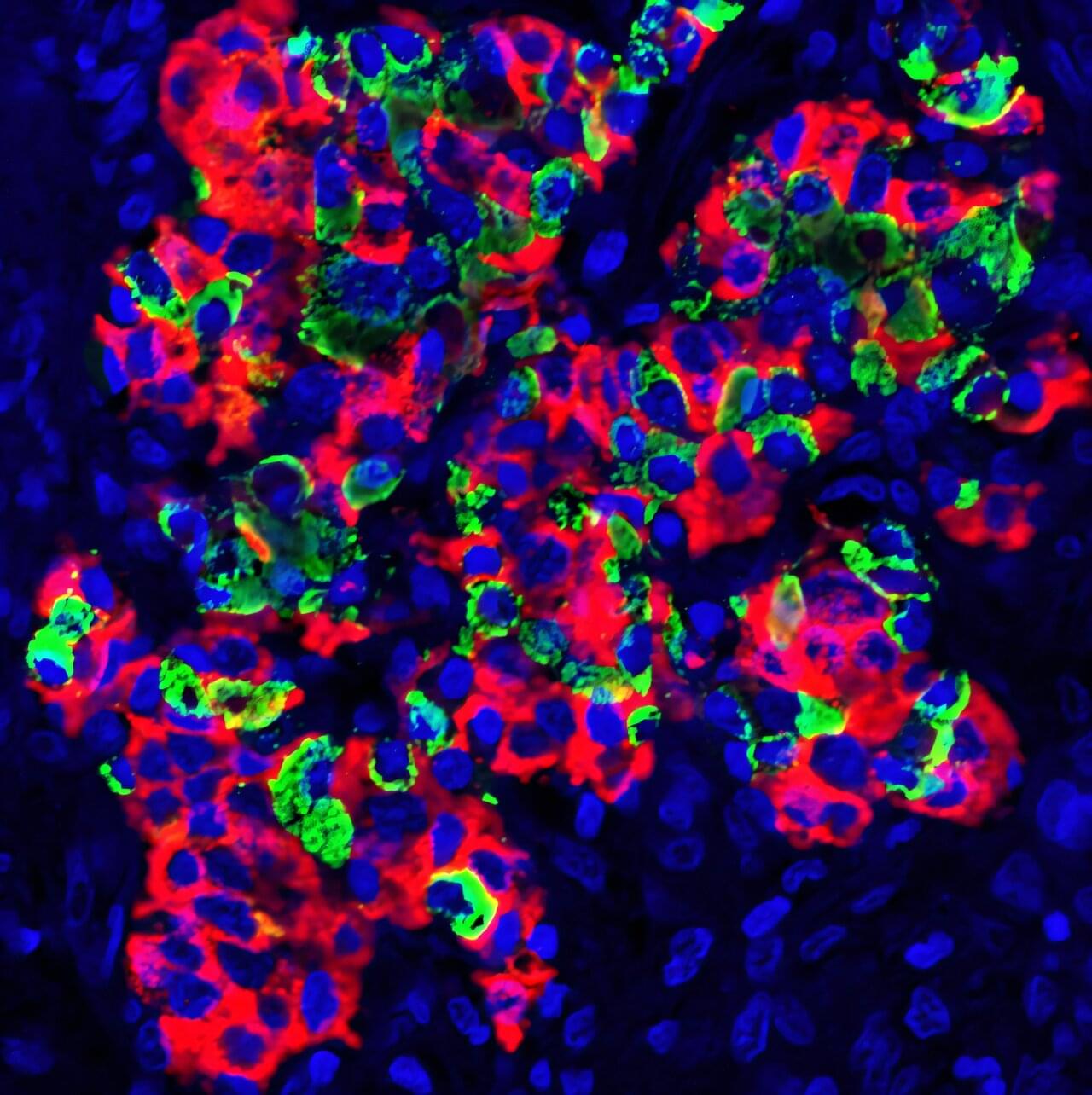
Wenzhou Medical University researchers have reimagined the spleen as a viable site for islet transplantation, enabling long-term diabetes control without the burden of full immunosuppression. Nanoparticle-driven spleen remodeling allowed transplanted mouse, rat, and human islets to restore normal blood sugar in diabetic rodents and cynomolgus macaques.
In type 1 diabetes, the immune system destroys native beta cells, the insulin-producing cells housed within pancreatic clusters called islets of Langerhans. Islet transplantation transfers these clusters from donor pancreases into the portal vein of the recipient’s liver, where they settle in the hepatic microvasculature. Once in place, they resume insulin secretion to reduce or eliminate injections and restore glycemic control.
Liver-based transplantation has significant drawbacks. Immune attack, low oxygen tension, and the rigidity of hepatic tissue often destroy most transplanted islets within hours. Upward of 70% of cells are destroyed before engraftment, forcing reliance on multiple donors per recipient and blunting therapeutic success.
The new gaming dimension is here. The Odyssey 3D brings stunning glasses-free 3D experience to life – making games feel more real and the action more exciting.
Discover more at http://www.samsung.com.
• Glasses-free 3D experience.
• AI 3D Video Conversion.
• 165Hz refresh rate and 1ms response time (GtG)
• Nvidia G-Sync Compatible.
#Odyssey #3D #G90XF #Gamingmonitor #Gaming #Samsung

In recent years, scientists discovered something strange: When mice with Alzheimer’s disease inhale menthol, their cognitive abilities improve.
It seems the chemical compound can stop some of the damage done to the brain that’s usually associated with the disease.
In particular, researchers noticed a reduction in the interleukin-1-beta (IL-1β) protein, which helps to regulate the body’s inflammatory response – a response that can offer natural protection but one that leads to harm when it’s not controlled properly.
Fr. Michael Baggot joins the podcast to provide a Catholic perspective on transhumanism and superintelligence. We also discuss the meta-narratives, the value of cultural diversity in attitudes toward technology, and how Christian communities deal with advanced AI.
You can learn more about Michael’s work here:
https://catholic.tech/academics/faculty/michael-baggot.
Timestamps:
00:00 Meta-narratives and transhumanism.
15:28 Advanced AI and religious communities.
27:22 Superintelligence.
38:31 Countercultures and technology.
52:38 Christian perspectives and tradition.
01:05:20 God-like artificial intelligence.
01:13:15 A positive vision for AI.
Who i am and all my stuff here: https://hey.link/w8yiD ✅🎁🚀
Wanna watch more Free audiobook? Click here: • The Future is Matrix: AI, Virtual Worlds,… ✅
The Physics of Space Travel: Exploring Faster-Than-Light Travel is an exhilarating journey into the world of cutting-edge science and theoretical physics. Imagine a future where interstellar travel is not just a dream, but a reality. In this comprehensive and accessible guide, you’ll dive deep into the science behind faster-than-light travel, exploring concepts like Einstein’s theory of relativity, wormholes, warp drives, and quantum tunneling.
Whether you’re a space enthusiast, a science fiction fan, or simply curious about the future of space exploration, this book breaks down complex ideas into engaging, easy-to-understand chapters. Discover the latest theories in space travel technology, the role of dark matter and dark energy, and the tantalizing possibility of time travel. Along the way, we’ll explore the search for advanced extraterrestrial civilizations and how their discoveries could guide our own journey to the stars.
With vivid explanations, real scientific insights, and thought-provoking possibilities, The Physics of Space Travel is your essential guide to understanding how humanity might one day break the light-speed barrier and unlock the mysteries of the cosmos.
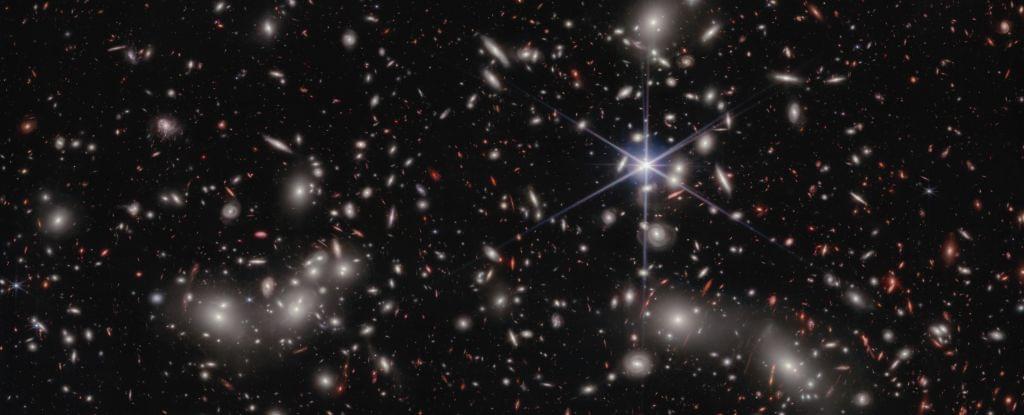

We finally know what brought light to the dark and formless void of the early Universe.
According to data from the Hubble and James Webb Space Telescopes, the origins of the free-flying photons in the early cosmic dawn were small dwarf galaxies that flared to life, clearing the fog of murky hydrogen that filled intergalactic space. A paper about the research was published in February 2024.
“This discovery unveils the crucial role played by ultra-faint galaxies in the early Universe’s evolution,” said astrophysicist Iryna Chemerynska of the Institut d’Astrophysique de Paris.
#AbSciCon22 — Origins and Exploration: From Stars to CellsAbSciCon, the conference brings the astrobiology community together every two years to share resear…