Researchers in China have developed a unique running stance for their four-legged robot, which allows it to move at far greater speeds than similar machines.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.

Sam Altman Says OpenAI Will Adopt AI Approaches From DeepSeek And Meta
In today’s AI news, When rivals take a different approach and succeed, it sometimes pays to change course. This is what Sam Altman said OpenAI will do, according to a Reddit AMA session on Friday. Altman was asked about DeepSeek, which has taken the tech world by storm after rolling out top-performing AI models that are relatively cheap to use.
Then, Andreessen Horowitz general partner and Mistral board member Anjney “Anj” Midha first spied DeepSeek’s jaw-dropping performance six months ago. That’s when DeepSeek introduced Coder V2, which rivaled OpenAI’s GPT4-Turbo for coding-specific tasks, according to a paper it released last year.
S V3 and R1 models. These efforts “achieved significant bypass rates, with little to no specialized knowledge or expertise being necessary.” ‘ + And, MLCommons, a nonprofit AI safety working group, has teamed up with AI dev platform Hugging Face to release one of the world’s largest collections of public domain voice recordings for AI research. The dataset, called Unsupervised People’s Speech, contains more than a million hours of audio spanning at least 89 languages.
In videos, in this episode of “How To Build The Future,” YC President and CEO Garry Tan sits down with Bob to discuss the lessons learned from his time at OpenAI, scaling laws, his advice for startups, and what all of this means for the jobs of the future.
Then, “Maybe I Got Carried Away” is an experimental short film that fuses playful visuals with a surreal narrative. It was created by [@panaviscope](https://www.youtube.com/@panaviscope) using Sora generated shots. The story follows a protagonist who begins releasing vibrant balloons into the sky as a personal act of rebellion against her city’s monotony.
Meanwhile, Shashank Dogra breaks down AI Agents in the simplest way possible. AI Agents: The Future of Business & Technology Agents are the new apps. In the near future, we expect to see thousands of AI agents transforming the way businesses operate.
We close out with NVIDIA Developer showing how DeepSeek-R1 model is packaged as NVIDIA NIM microservice delivers superior throughput performance and can be easily deployed on any GPU-accelerated system with standard API. Get started now at build.nvidia.com.

Physicists Harness 13,000 Entangled Spins To Unlock the Power of the “Dark State”
Scientists have harnessed many-body physics to transform quantum dots into scalable, stable quantum nodes. By entangling nuclear spins into a ‘dark state,’ they created a quantum register capable of storing and retrieving quantum information with high fidelity. This leap forward brings quantum networks closer to reality, unlocking new possibilities for communication and computing.

Treating Hair Loss Could Be As Simple as Flipping a Molecular “Switch”
Treating hair loss may be as simple as developing therapies to flip a molecular “switch,” according to a new study by researchers from Penn State; the University of California, Irvine; and National Taiwan University.
The researchers reviewed the biological and social evolution of human scalp hair. Based on their analysis, they proposed a novel theory that points to a molecular basis underlying the ability to grow long scalp hair.
In short, human ancestors may have always had the ability to grow long scalp hair, but the trait remained dormant until certain environmental and biological conditions — like walking upright on two legs — turned on the molecular program. The team published their findings, which they said could serve as the basis for future experimental work, in the British Journal of Dermatology.
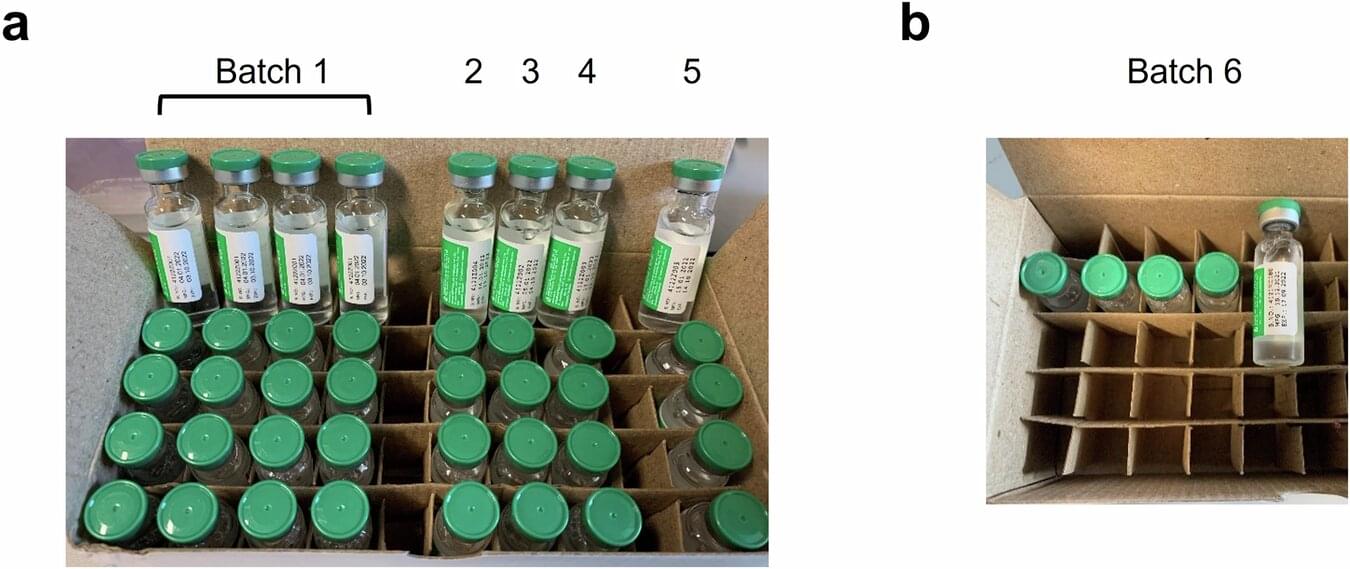

Innovative method can identify fake COVID-19 vaccines without opening the vaccine vial
Researchers at the University of Oxford and their collaborators, including the Serum Institute of India, have developed an innovative method to identify falsified vaccines without opening the vaccine vial.
The new method, published in npj Vaccines, analyzes the vaccine vial label and its adhesive and therefore allows the vaccine vials to be retained in the supply chain. Furthermore, the study has shown that the technique can also differentiate genuine COVID-19 vaccine liquid from falsified vaccine surrogates, using a recently published method developed using non-COVID vaccines.
The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that 10.5% of medicines worldwide in low and middle-income countries are substandard or are falsified medicines made by criminals. This threatens global health since the medicines and vaccines fail to prevent and treat the diseases for which they were intended, and they risk additional adverse health consequences if the ingredients used by criminals in the falsified products are harmful.
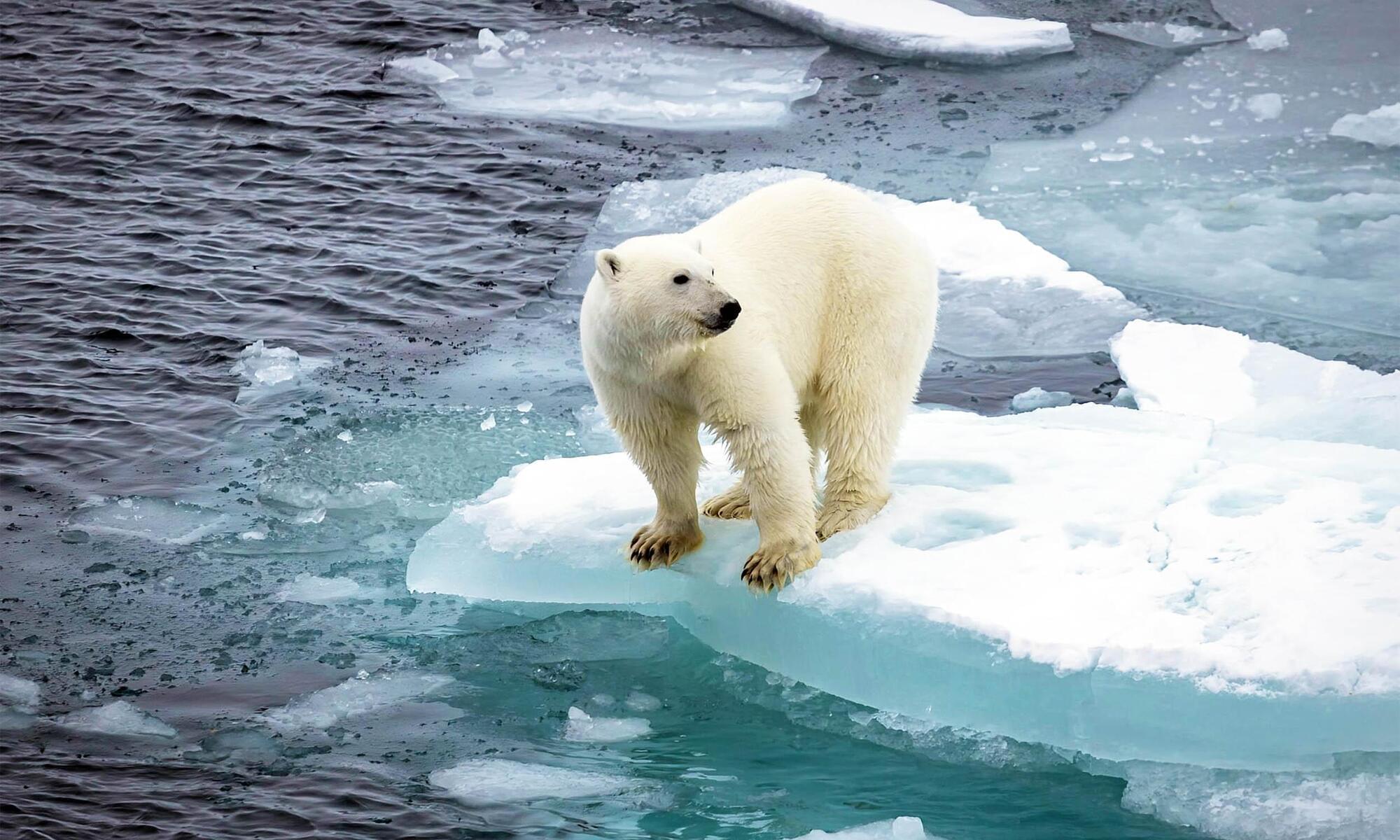



Polar bears are suffering from an “energy deficit” that is devastating their populations
As their primary food source becomes less accessible, the bears enter longer fasting periods, leading to declining health and population numbers.
“A loss of sea ice means bears spend less time hunting seals and more time fasting on land,” said Louise Archer, a postdoctoral researcher and lead author of the study.
This prolonged fasting drains polar bears’ energy reserves, reducing their ability to reproduce and raise cubs. Without enough stored fat, female bears struggle to give birth and nurse their young. Over time, this energy deficit has led to a sharp population decline.
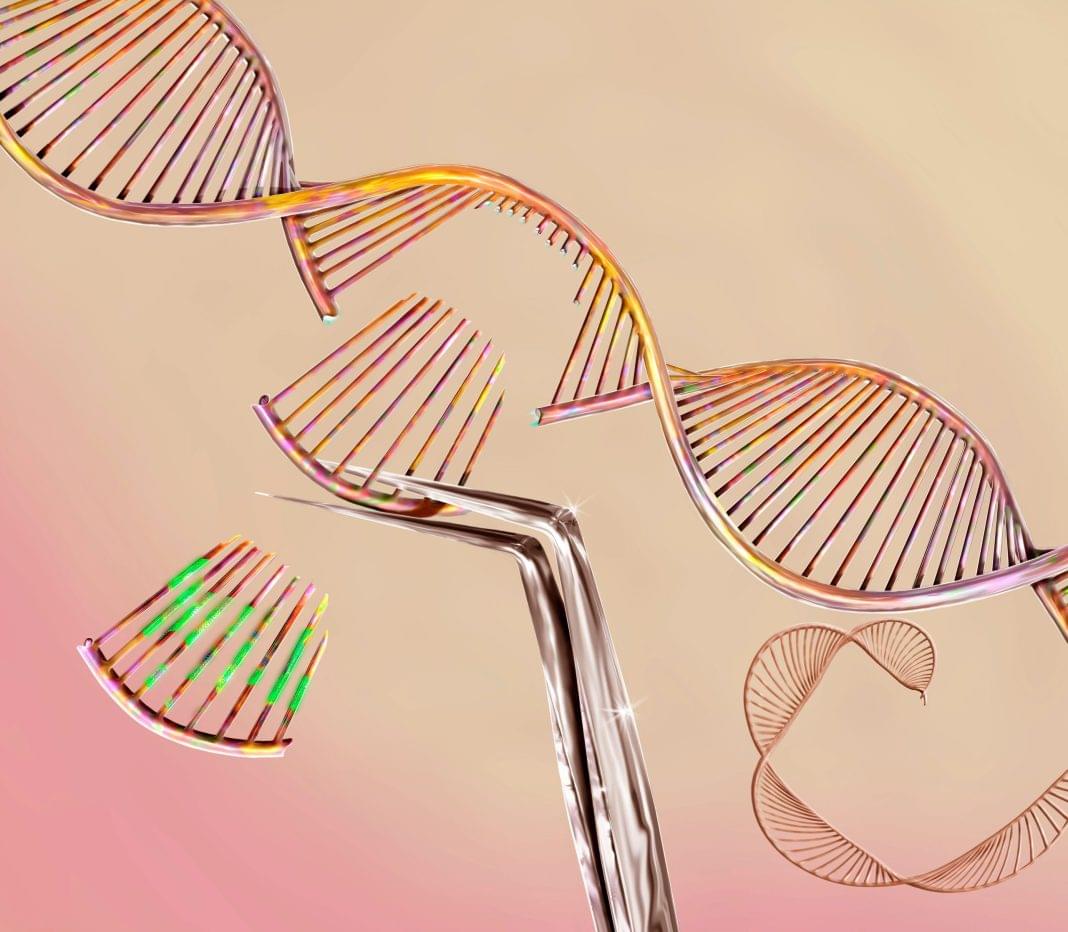
Next-Gen Cas12a System Enables Precise Single and Multiplexed Gene Editing in Cancer
Australian researchers have successfully introduced an improved version of Cas12a gene-editing enzyme in mice. Their work establishes a next-generation gene-editing tool that enhances genetic manipulation for cancer and medical research in a preclinical model.
The study, “Advancing the genetic engineering toolbox by combining AsCas12a knock-in mice with ultra-compact screening,” was published in Nature Communications.
“This is the first time Cas12a has been used in preclinical models, which will greatly advance our genome engineering capabilities,” said co-author Eddie La Marca, PhD, a postdoctoral researcher at the Olivia Newton-John Cancer Research Institute (ONJCRI) in Australia.