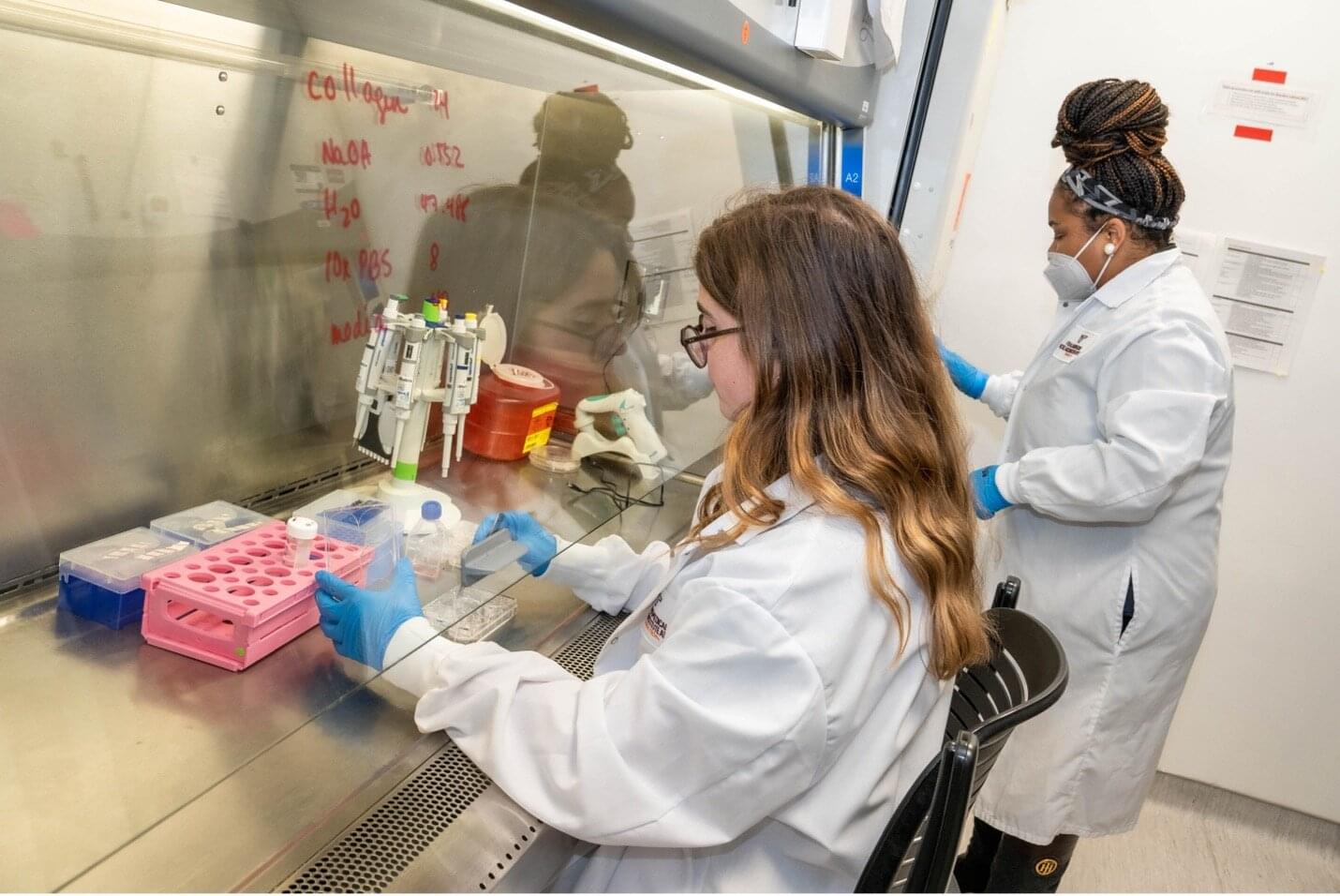
Cancer is a challenging enough diagnosis, but many patients are dealt a second blow, even as they heal: “chemo brain.”
Also called “brain fog,” this mix of cognitive issues— memory problems, struggling to find words, an inability to concentrate—affects up to three-in-four cancer patients, according to multiple studies. For many, the effects last years beyond cancer treatment.
A new study offers new models for studying causes of chemo brain and points to the effects of chemotherapy drugs on the brain’s lymphatic system, which is a network of tiny vessels in the brain’s protective membranes that help remove waste and transport immune cells. The study was published Oct. 13 in Communications Biology.