A large-scale study tested whether AI personas can detect when humans are lying—and found that while AI can sometimes spot deception, it’s still far from trustworthy.


We had the honor of welcoming Eileen Collins, the first woman to pilot and command a Space Shuttle, to Florida Tech’s campus for a special screening of her new documentary, ‘SPACEWOMAN.’
It was an inspiring evening celebrating perseverance and leadership. Before the event, Collins also met with a small group of students to discuss space exploration and her experiences as a trailblazer in NASA’s history.
Thank you to our campus community and friends of Florida Tech for joining us for this special event!
Learn more about Florida Institute of Technology: https://www.floridatech.edu/

Even small amounts of bisphenol A can lead to long-term health effects. When researchers studied adult rats exposed in the fetal stage, they found that females had developed a more masculine and males a more feminine gene expression pattern. This led to females progressing towards a cancer-like state, while males progressed towards metabolic syndrome, which can increase the risk of diabetes and heart disease.
Bisphenol A is a synthetic chemical with estrogen-like properties that is commonly used in food packaging materials. The substance is banned in many products, but is still present in some packaging. Levels of bisphenol A in people’s bodies are often above levels considered safe, with previous research showing that the substance can cause adverse health effects.
Females masculinized and males feminized In the current study, published in Communications Medicine, researchers investigated how bisphenol A affects the body during the fetal stage.
Subscribe: http://bit.ly/1Wq6gwm.
Connect with Singularity University:
Website: http://singularityu.org.
Singularity HUB: http://singularityhub.com.
Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/singularityu.
Twitter: https://twitter.com/singularityu.
Linkedin: https://www.linkedin.com/company/singularity-university.
Google+: https://plus.google.com/+singularityu.
About Singularity University:
Singularity University is a benefit corporation headquartered at NASA’s research campus in Silicon Valley. We provide educational programs, innovative partnerships and a startup accelerator to help individuals, businesses, institutions, investors, NGOs and governments understand cutting-edge technologies, and how to utilize these technologies to positively impact billions of people.
Intro to Nanotechnology with Ralph Merkle | Singularity University.
https://www.youtube.com/user/SingularityU


🌌 Unifying AI Through the Feynman Path Integral: From Deep Learning to Quantum AI https://lnkd.in/g4Cfv6qd I’m pleased to share a framework that brings many areas of AI into a single mathematical structure inspired by the Feynman path integral — a foundational idea in quantum physics. Instead of viewing supervised learning, reinforcement learning, generative models, and quantum machine learning as separate disciplines, this framework shows that they all follow the same underlying principle: Learning is a weighted sum over possible solutions (paths), based on how well each one explains the data. In other words, AI can be viewed the same way Feynman viewed physics: as summing over all possible configurations, weighted by an action functional.
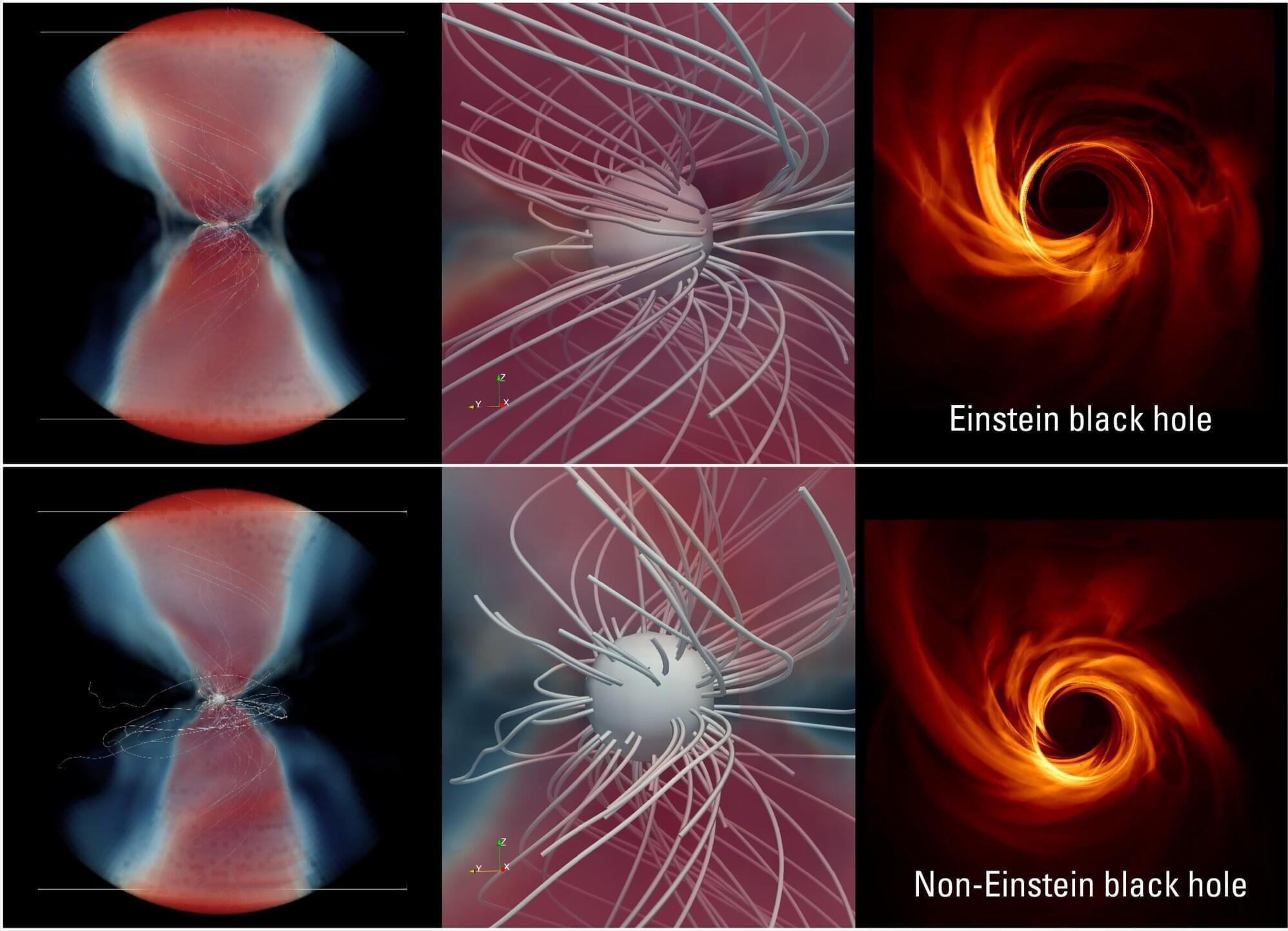
Black holes are considered cosmic gluttons, from which not even light can escape. That is also why the images of black holes at the center of the galaxy M87 and our Milky Way, published a few years ago by the Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) collaboration, broke new ground.
“What you see on these images is not the black hole itself, but rather the hot matter in its immediate vicinity,” explains Prof. Luciano Rezzolla, who, along with his team at Goethe University Frankfurt, played a key role in the findings.
“As long as the matter is still rotating outside the event horizon —before being inevitably pulled in—it can emit final signals of light that we can, in principle, detect.”
Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T cell therapies have revolutionized cancer treatment—but so far, their success has been largely limited to blood cancers. Solid tumors, which account for around 90% of all adult cancers, remain a major challenge because they are difficult for CAR T cells to infiltrate and are often highly heterogeneous, making them harder to target with a single therapy.
Researchers at Monash University, in collaboration with scientists from the Peter MacCallum Cancer Center, used CRISPR-based gene editing or a PTPN2 inhibitor to enhance the function of human CAR T cells engineered to recognize an antigen expressed on many solid tumors.
The study, led by Professor Tony Tiganis and Dr. Florian Wiede, was published in Science Translational Medicine.
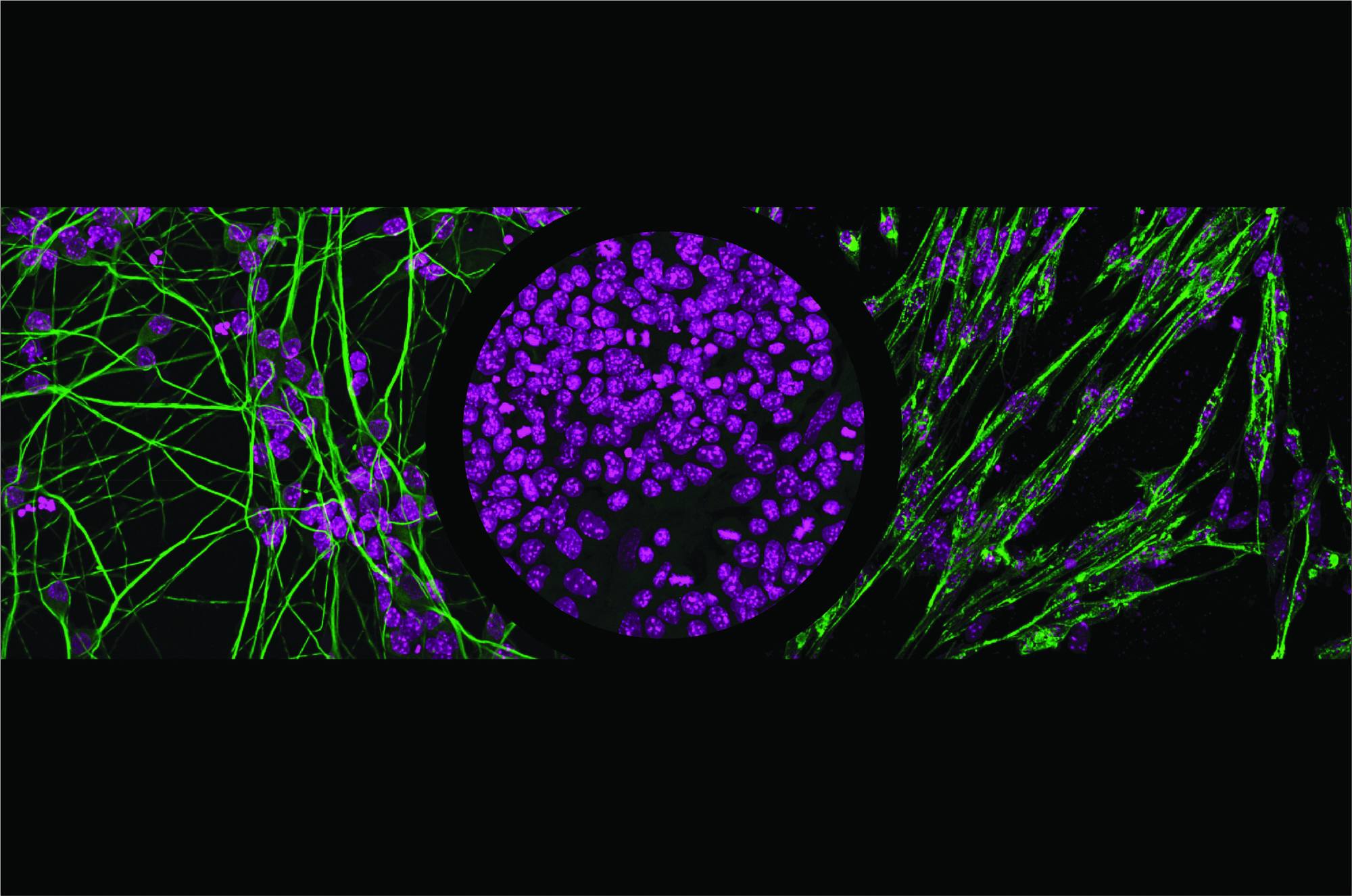
Every cell in the body has the same DNA, but different cell types—such as muscle or brain cells—use different parts of it. Transcription factors help cells activate specific genes by reading certain DNA sequences, but since these sequences are common across the genome, scientists have long wondered how the factors know exactly where to bind.
Researchers in the Schübeler lab set out to address this question by looking at two closely related transcription factors—NGN2 and MyoD1—that steer cells toward becoming neurons and muscle cells, respectively. Using stem cells, they switched these transcription factors on one at a time and watched where they attached to the DNA and how they influenced gene expression. Their research is published in the journal Molecular Cell.
They found that the binding of transcription factors to the DNA molecule depends not only on the DNA sequence but also on how open the DNA is and which partner proteins are present. Sometimes, transcription factors act as “pioneer factors” and are able to open tightly packed DNA at specific sites to turn on genes. Small DNA changes—sometimes just one letter—and the proteins these factors partner with can affect whether genes are activated.
The study has resolved a long-standing cosmic puzzle and provided strong evidence for the existence of widespread magnetic fields — likely relics from the early Universe.