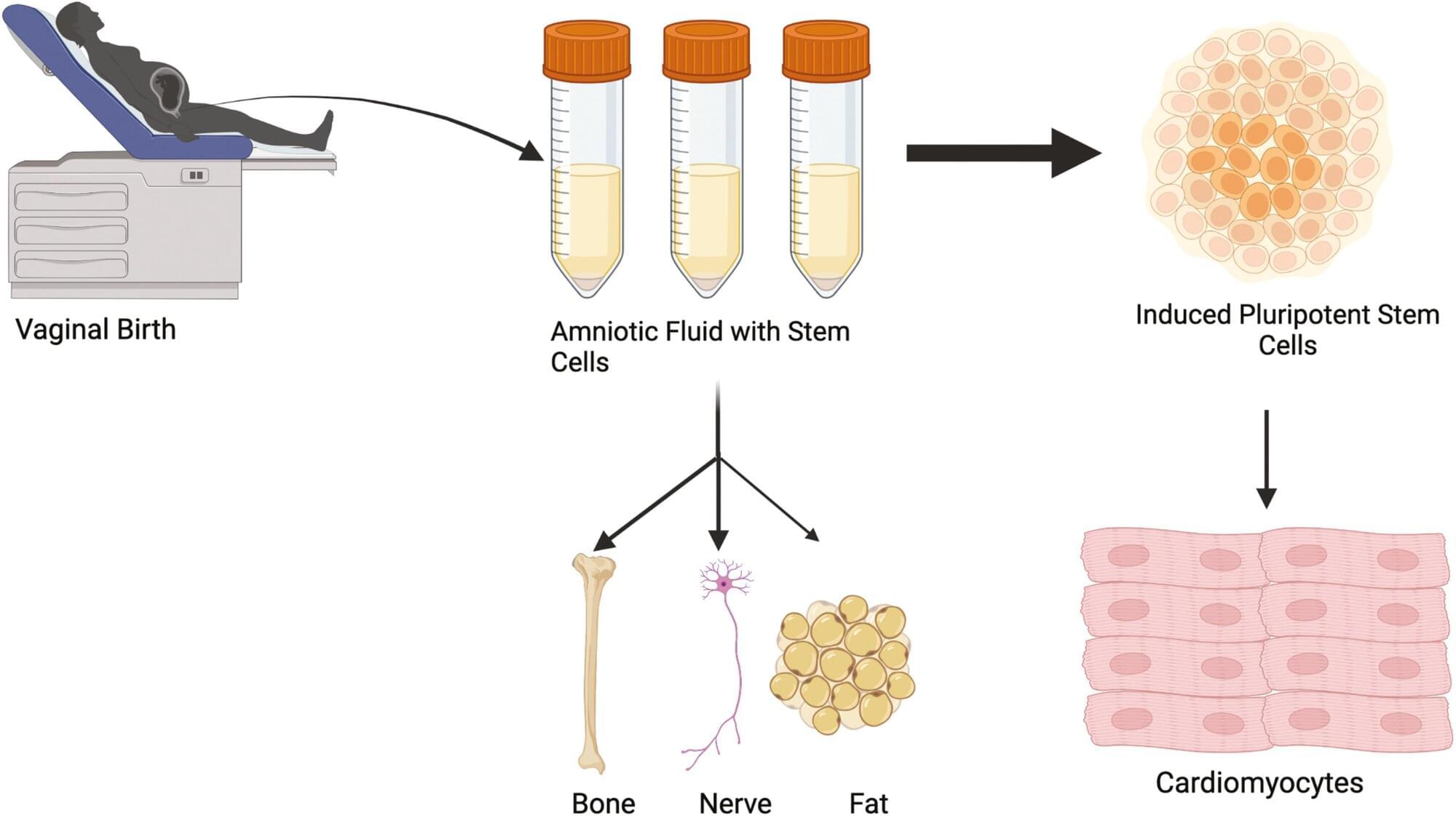
Researchers at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus have discovered that amniotic fluid stem cells can be safely collected from vaginal fluid after childbirth rather than relying on more invasive methods that can pose some risk to the mother and fetus.
“We can then turn those cells into beating heart cells and use them later in treating congenital heart defects,” said the study’s senior author Jeffrey Jacot, Ph.D., associate professor of pediatrics and bioengineering at the University of Colorado Center for Bioengineering in the CU School of Medicine. “These results allow for an expanded and readily available source of amniotic stem cells beyond traditional collection through amniocentesis.”
The study was published today in the journal Stem Cells Translational Medicine.