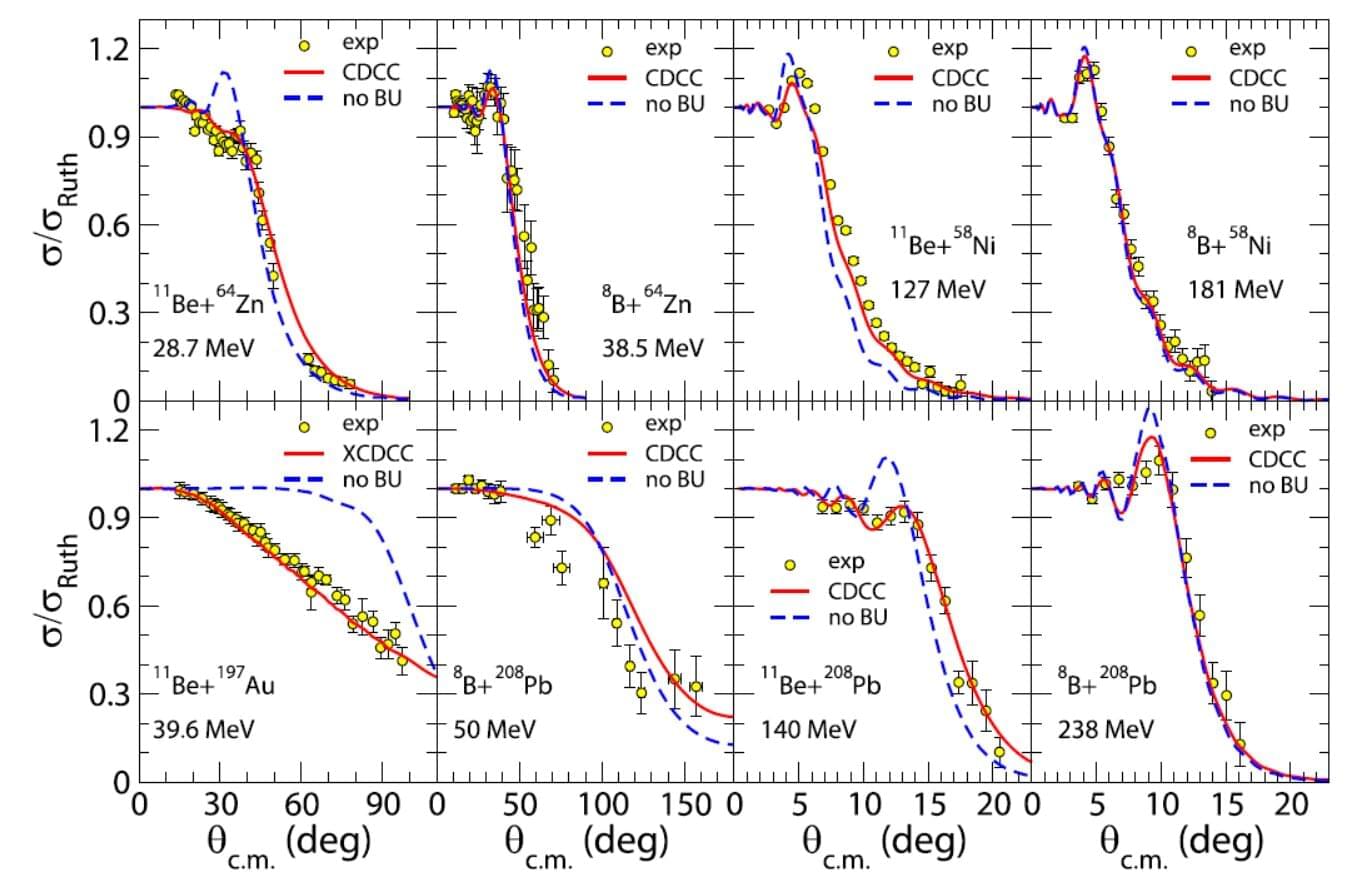
Researchers from the Institute of Modern Physics (IMP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences have reported new experimental results that advance our understanding of reaction dynamics and exotic nuclear structures of weakly bound nuclei.
The findings are published in Physics Letters B.
Weakly bound nuclei are characterized by their extremely low binding energy of protons and neutrons. Investigating their reaction mechanisms and exotic structures represents a frontier field in nuclear physics.