In a short talk at Caltech, physicist Richard Feynman laid out a vision of manipulating and controlling atoms at the tiniest scale. It would precede the field of nanotechnology by decades.

Professor John Donoghue explains why quantum physics and gravity actually work perfectly together. He tackles quadratic gravity, effective field theory, and random dynamics, arguing that grand unification and naturalness aren’t required for a theory of everything.
As a listener of TOE you can get a special 20% off discount to The Economist and all it has to offer! Visit https://www.economist.com/toe.
SUPPORT:
Support me on Substack: https://curtjaimungal.substack.com/su…
JOIN MY SUBSTACK (Personal Writings): https://curtjaimungal.substack.com LISTEN ON SPOTIFY: https://open.spotify.com/show/4gL14b9… TIMESTAMPS:
LINKS MENTIONED:
SOCIALS:
Guests do not pay to appear. Theories of Everything receives revenue solely from viewer donations, platform ads, and clearly labelled sponsors; no guest or associated entity has ever given compensation, directly or through intermediaries. #science.
Support me on Crypto: https://commerce.coinbase.com/checkou…
Support me on PayPal: https://www.paypal.com/donate?hosted_…
JOIN MY SUBSTACK (Personal Writings): https://curtjaimungal.substack.com.
LISTEN ON SPOTIFY: https://open.spotify.com/show/4gL14b9…
TIMESTAMPS:

Grab the Guide here👉: https://technomics.gumroad.com/l/ai-survival-guide.
Everyone is obsessing over chatbots, but the true Singularity isn’t happening on a screen. It starts the moment super-intelligence gets a body.
In this video, we break down The Robot Singularity: the moment AGI enters the physical economy and makes human labor mathematically obsolete.
Video Timestamps:
00:00 — The Hook: Why Digital AGI is Just the Beginning.
00:48 — The Roadmap: Realizing Science Fiction.
Bose–Einstein Condensate (BEC) explained: Cool a dilute gas of atoms to billionths of a degree above absolute zero and they merge into one coherent matter wave—a Bose–Einstein condensate. This video covers laser cooling, magnetic/optical traps, evaporative cooling, the onset of quantum degeneracy, and why a BEC behaves like a superfluid. See signatures: interference fringes, quantized vortices, long coherence length, and frictionless flow. Applications include atom interferometers (precision gravity and rotation sensing), quantum simulation of complex materials, and space-based experiments (ISS Cold Atom Lab). We also touch on first BECs (1995, rubidium/sodium), critical temperature, and why bosons condense while fermions do not.
Great paper highlighting key challenges for genetically engineered bacterial therapies in the human gut. It is respectable that this paper was published in Science despite some “negative” results. Although the genetically engineered bacteria were all supposed to die after removal of porphyrin from the diet, they sometimes rebounded. Even with an improved porphyrin pathway which was supposed to resist mutational rebound, the bacteria still persisted in a mouse model, apparently by mysterious non-mutational means. Maybe the microbiomes of the mice somehow supplied porphyrin to the bacteria without the knowledge of the researchers. Furthermore, therapeutic application of the genetically engineered bacteria in humans only resulted in modest (and not statistically significant) decreases in urine oxalate. This was partly due to horizontal gene transfer which replaced the engineered oxalate degradation pathway and partly due to the general fitness burden of the engineered oxalate degradation pathway. As such, this paper revealed a lot of important obstacles which will need to be worked on for bacterial therapies to move forward in the future.
(https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.adu8000)
Precision microbiome programming for therapeutic applications is limited by challenges in achieving reproducible colonic colonization. Previously, we created an exclusive niche that we used to engraft engineered bacteria into diverse microbiota in mice by using a porphyran prebiotic. Building on this approach, we have now engineered conditional attenuation into a porphyran-utilizing strain of Phocaeicola vulgatus by replacing native essential gene regulation with a porphyran-inducible promoter to allow reversible engraftment. Engineering a five-gene oxalate degradation pathway into the reversibly engrafting strain resulted in a therapeutic candidate that reduced hyperoxaluria, a cause of kidney stones, in preclinical models.
Please see this news story on a remarkable new technological cybersecurity breakthrough for mitigating the threats of Q-Day and AI:
#cybersecurity #quantum #tech
The next leap in technology: a quantum computer unlike anything humanity has seen, capable of breaking all encryption and challenging the most crucial national security defenses.
Tal Shenhav from i24NEWS Hebrew channel has the story.

Think of cells as the biological answer to battery-powered electronics. Mitochondria are the batteries that supply them with enough energy to keep going. Unfortunately, just like the two standard AAs in your remote control, they eventually run out of power and die—but (much like actual batteries) they can also be recharged and replaced.
Breakdown of mitochondria causes cells to glitch. Wear and tear can happen with age, usually from years of exposure to free radicals that cause oxidative stress and inflammation, but can also be caused by injury from degenerative diseases or mitochondrial toxicity from certain drugs and other harmful substances. When there is damage to the cell, mitochondria begin to lose their capacity to generate energy. Losing mitochondria is detrimental to cell function. This is why biomedical engineer Akhilesh Gaharwar and his research team at Texas A&M University have come up with a way to regenerate them.
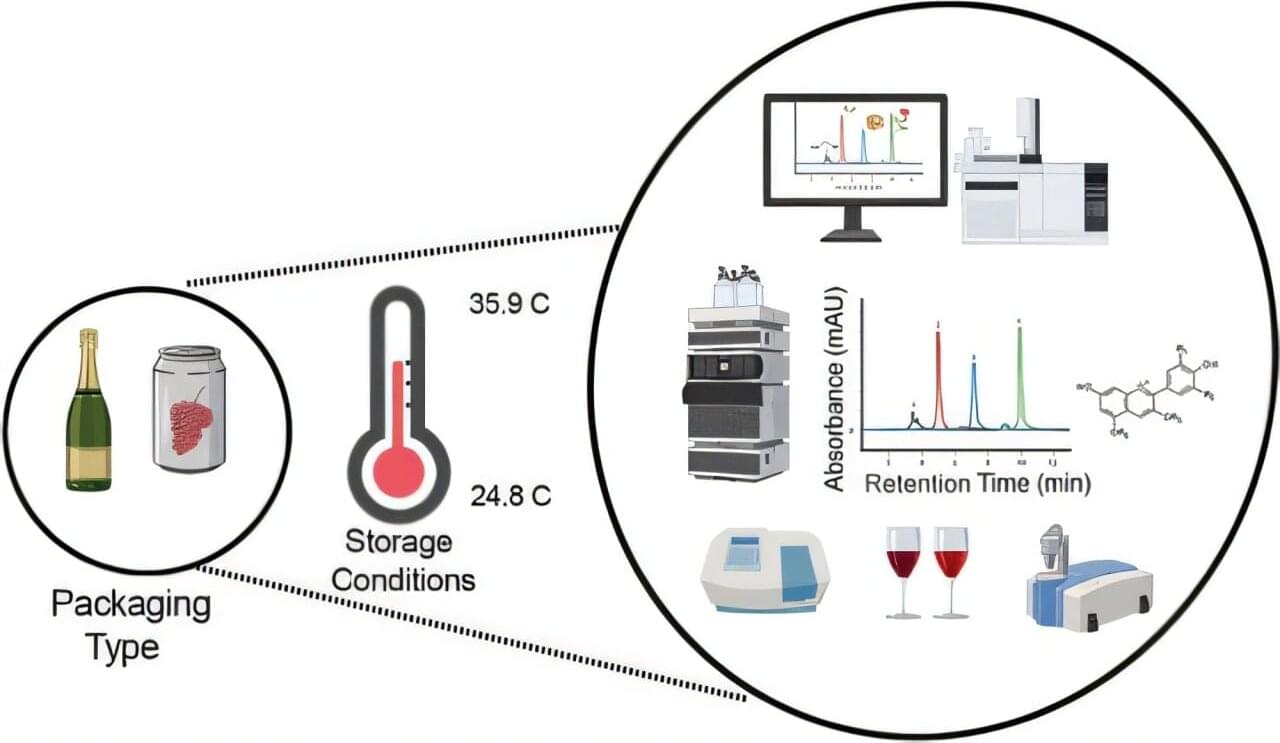
One of the main reasons wine traditionally comes in bottles is to protect its quality. Glass is nonreactive, and the cork or screw cap provides an airtight seal that prevents oxygen from spoiling the liquid. In recent years, a new rival has appeared on the scene—aluminum cans. But there are concerns that the metal may interact with the wine, altering its unique flavor.
However, for red muscadine wine, new research published in ACS Food Science & Technology suggests that cans may be just as effective as glass at keeping the wine fresh.