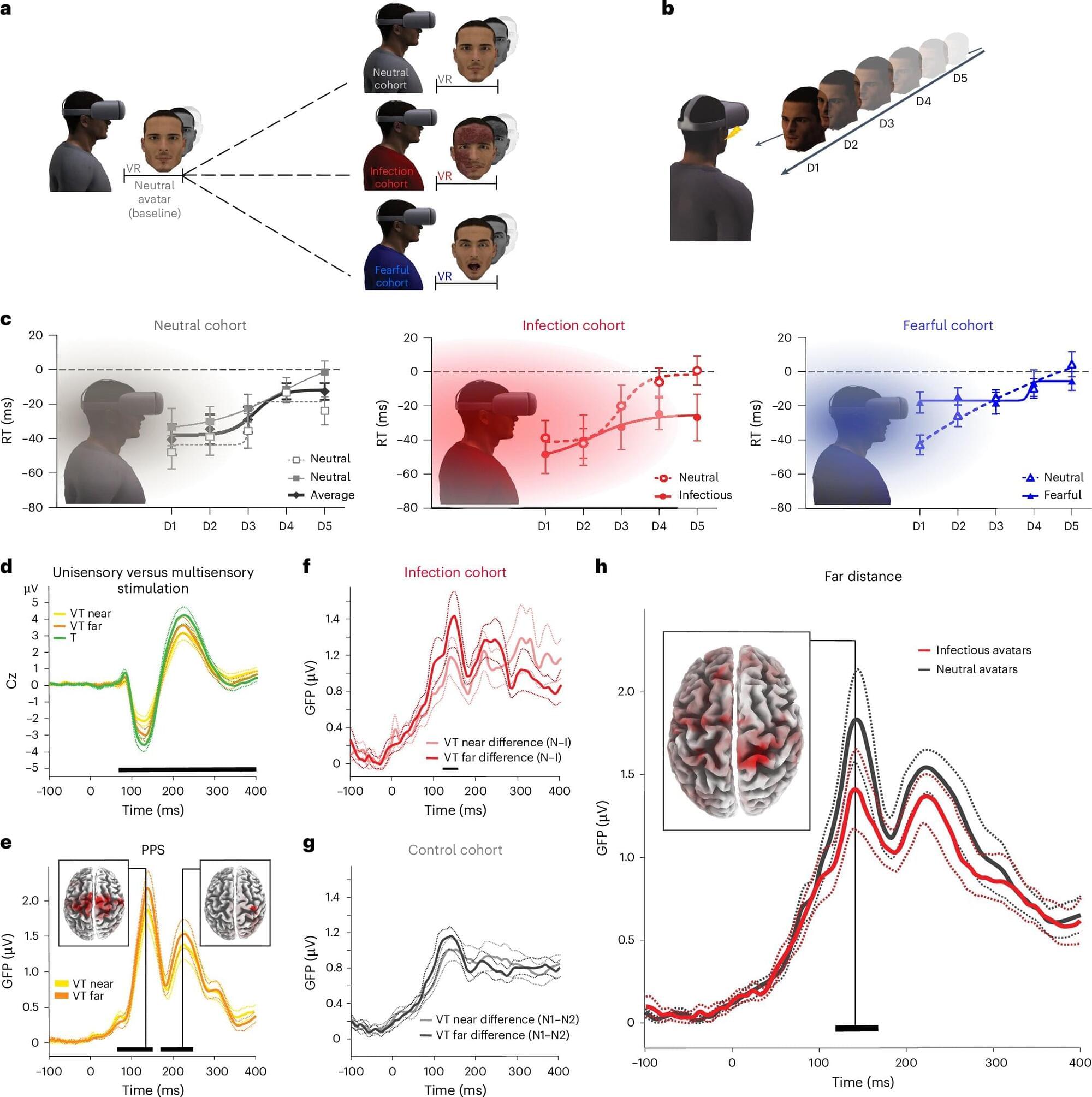
Researchers led by the University of Geneva and École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne report that neural anticipation of virtual infection triggers an immune response through activation of innate lymphoid cells.
Innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) are a type of immune cell crucial for early immune responses. They do not rely on antigen recognition like adaptive immune cells but respond quickly and effectively to various inflammatory signals and pathogen-associated cues, playing an essential role in early defense.
Protecting the body from pathogens typically involves a multitude of responses after actual contact. An anticipatory biological immune reaction to an infection had not been previously demonstrated.