Pain is a complex, multifaceted experience shaped by various factors beyond physical sensation, such as a person’s mindset and their expectations of pain. The placebo effect, the tendency for a person’s symptoms to improve in response to inactive treatment, is a well-known example of how expectations can significantly alter a person’s experience. Mindfulness meditation, which has been used for pain management in various cultures for centuries, has long been thought to work by activating the placebo response. However, scientists have now shown that this is not the case.
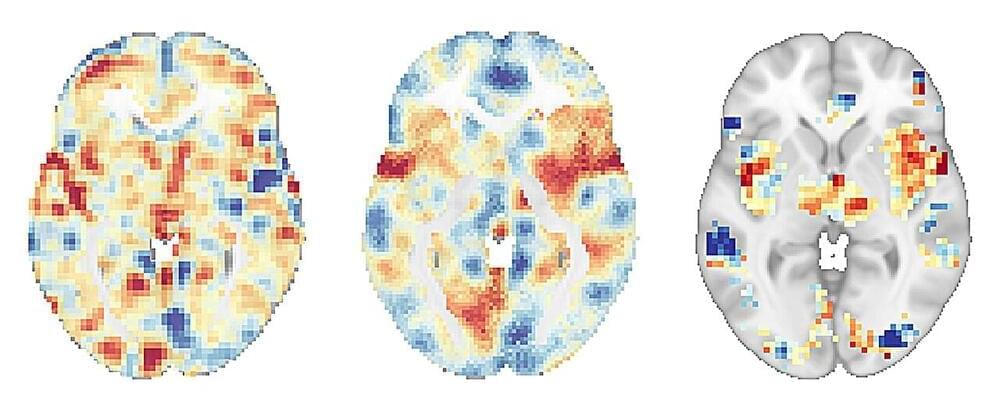
A new study, published in Biological Psychiatry, has revealed that mindfulness meditation engages distinct brain mechanisms to reduce pain compared to those of the placebo response. The study, conducted by researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine, used advanced brain imaging techniques to compare the pain-reducing effects of mindfulness meditation, a placebo cream and a “sham” mindfulness meditation in healthy participants.
The study found that mindfulness meditation produced significant reductions in pain intensity and pain unpleasantness ratings, and also reduced brain activity patterns associated with pain and negative emotions. In contrast, the placebo cream only reduced the brain activity pattern associated with the placebo effect, without affecting the person’s underlying experience of pain.