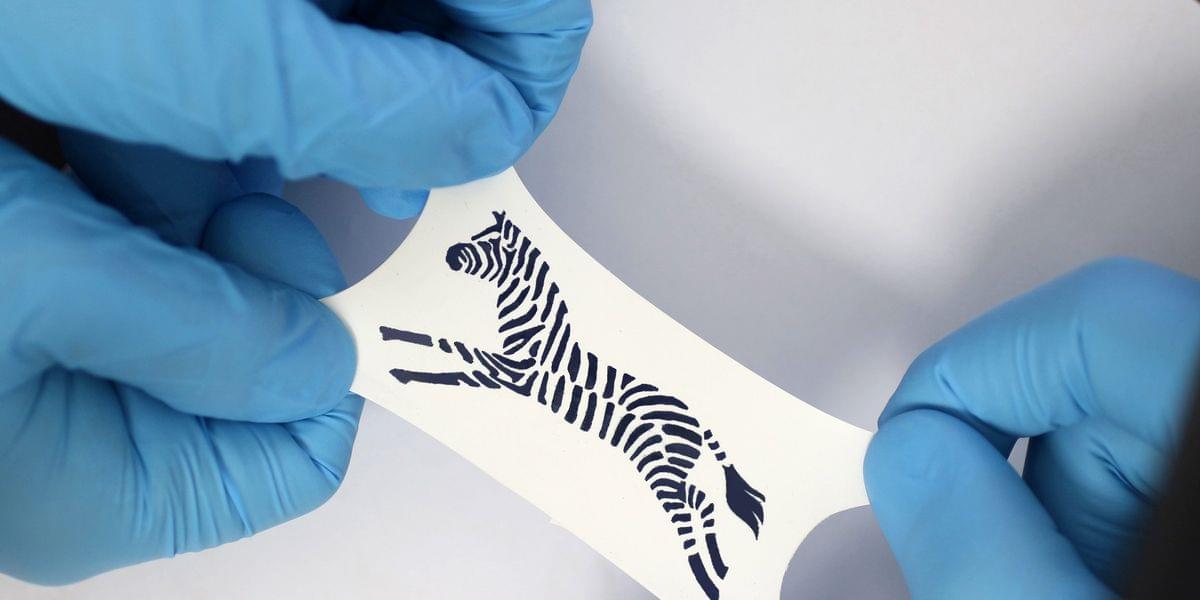
Phones, appliances, and humans all generate heat that usually escapes into the environment as waste energy. Thermoelectric generators, which convert temperature differences into electricity, are a way to capture that wasted heat for power.
Researchers have now made a thermoelectric generator (TEG) that is soft and stretchy and that biodegrades completely when exposed to the environment. Unlike conventional rigid thermoelectric devices, this one, reported in the journal Science Advances, could be easily integrated into fabrics, allowing for body-heat-powered wearable sensors or temperature-detecting disposable face masks.