Google’s DeepMind spinoff Isomorphic Labs expects clinical trial of drugs it designed using AI to start this year.



F Y I [ https://exploredeepspace.com/](https://exploredeepspace.com/)
America is leading the bold new initiative to take mankind to Mars and beyond. Click to learn about the history behind and importance of space exploration.
Check out my own course on Brilliant! First 30 days are free and 20% off the annual premium subscription when you use our link ➜ https://brilliant.org/sabine.
Up until last week, physicists believed that matter is made up of only two types of particles: those whose spin has full-integer values (bosons) and those whose spin comes has half-integer values (fermions). But in a new paper, a group of researchers turned the world of physics upside down by mathematically proving that a third type of particles – the “paraparticles” are possible.
Paper: https://www.nature.com/articles/s4158…
🤓 Check out my new quiz app ➜ http://quizwithit.com/
💌 Support me on Donorbox ➜ https://donorbox.org/swtg.
📝 Transcripts and written news on Substack ➜ https://sciencewtg.substack.com/
👉 Transcript with links to references on Patreon ➜ / sabine.
📩 Free weekly science newsletter ➜ https://sabinehossenfelder.com/newsle…
👂 Audio only podcast ➜ https://open.spotify.com/show/0MkNfXl…
🔗 Join this channel to get access to perks ➜
/ @sabinehossenfelder.
🖼️ On instagram ➜ / sciencewtg.
#science #sciencenews #physics #math
A computing chip, developed by a team from KAIST, mimics the way brain processes information and is ready for uses on various smart devices.

Astrophysicists have long been intrigued by the possibility of dark stars-massive celestial objects fueled not by nuclear fusion but by the enigmatic energy of dark matter. Thanks to images taken by the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), the scientific community has perhaps also found signs of such elusive entities. Could these dark stars, which shine billions of times brighter than our sun, rewrite the story of the universe’s infancy?
Dark stars, despite the word “dark”, are hypothesized luminous sources that may have existed in the universe’s infancy. In contrast to traditional stars that work with nuclear fusion, dark stars are speculated to obtain their energy from self-annihilation of dark matter particles.
As a result, energy is released that warms the ambient hydrogen and helium, and this leads the primordial clouds to glow brightly and expand to enormous scale-some up to a million times mass of the sun. These stars may have also been born in “minihaloes”, dense pockets of dark matter in the early universe.

The rising trend of early-onset cancers in adults under 50, particularly women, is alarming. Genetic, lifestyle, and environmental factors contribute to this increase. Maintaining a healthy weight, quitting tobacco, avoiding alcohol, consuming fiber-rich foods, using sunscreen, and regular physical activity are small lifestyle changes that can significantly reduce cancer risk.
Click this link https://sponsr.is/bootdev_anastasi and use my code ANASTASI to get 25% off your first payment for boot.dev.
Timestamps:
00:00 — New computing paradigm.
10:02 — How this new chip works.
My course on Technology and Investing ➜ https://www.anastasiintech.com/course.
Let’s connect on LinkedIn ➜ / anastasiintech.
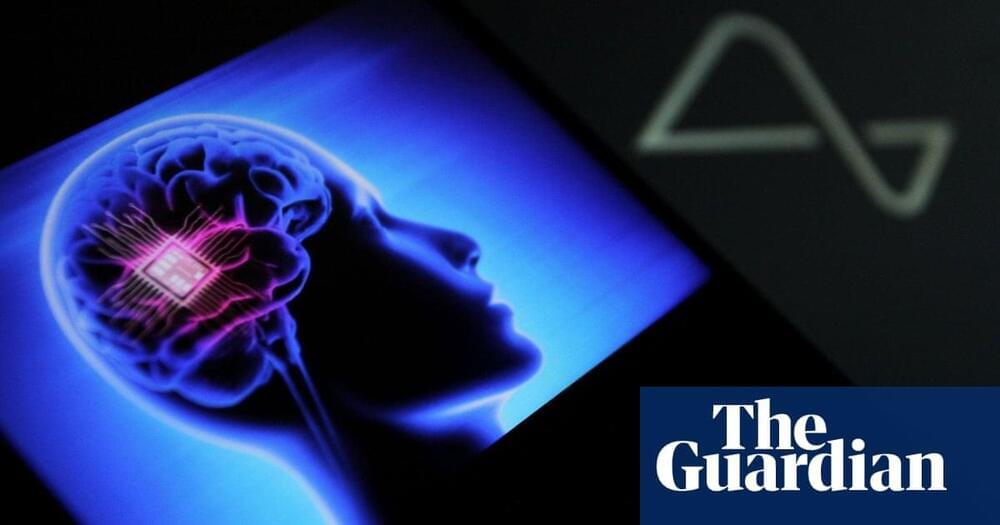

In future, doctors hope the technology could revolutionise the treatment of conditions such as depression, addiction, OCD and epilepsy by rebalancing disrupted patterns of brain activity.
Jacques Carolan, Aria’s programme director, said: “Neurotechnologies can help a much broader range of people than we thought. Helping with treatment resistant depression, epilepsy, addiction, eating disorders, that is the huge opportunity here. We are at a turning point in both the conditions we hope we can treat and the new types of technologies emerging to do that.”
The trial follows rapid advances in brain-computer-interface (BCI) technology, with Elon Musk’s company Neuralink launching a clinical trial in paralysis patients last year and another study restoring communication to stroke patients by translating their thoughts directly into speech.

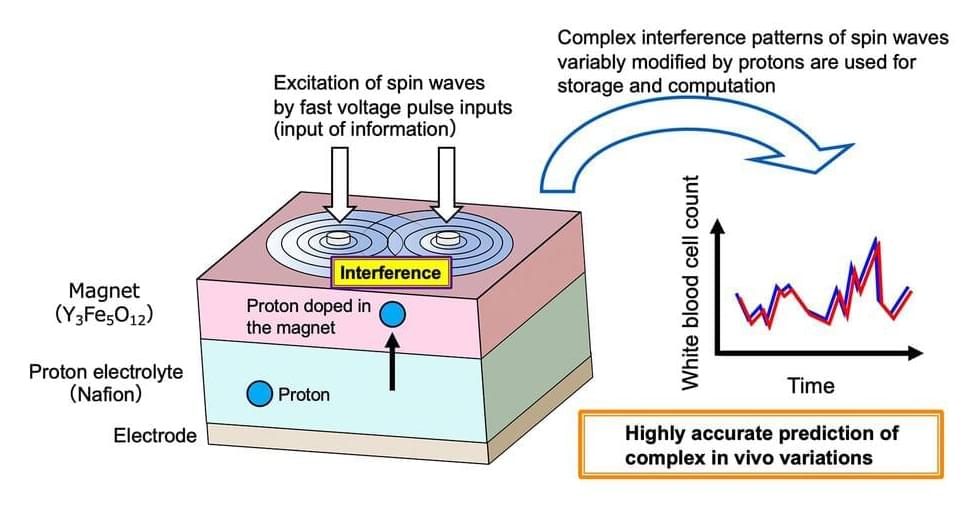
A research team from NIMS and the Japan Fine Ceramics Center (JFCC) has developed a next-generation AI device—a hardware component for AI systems—that incorporates an iono-magnonic reservoir. This reservoir controls spin waves (collective excitations of electron spins in magnetic materials), ion dynamics and their interactions.
The work is published in the journal Advanced Science.
The technology demonstrated significantly higher information processing performance than conventional physical reservoir computing devices, underscoring its potential to transform AI technologies.