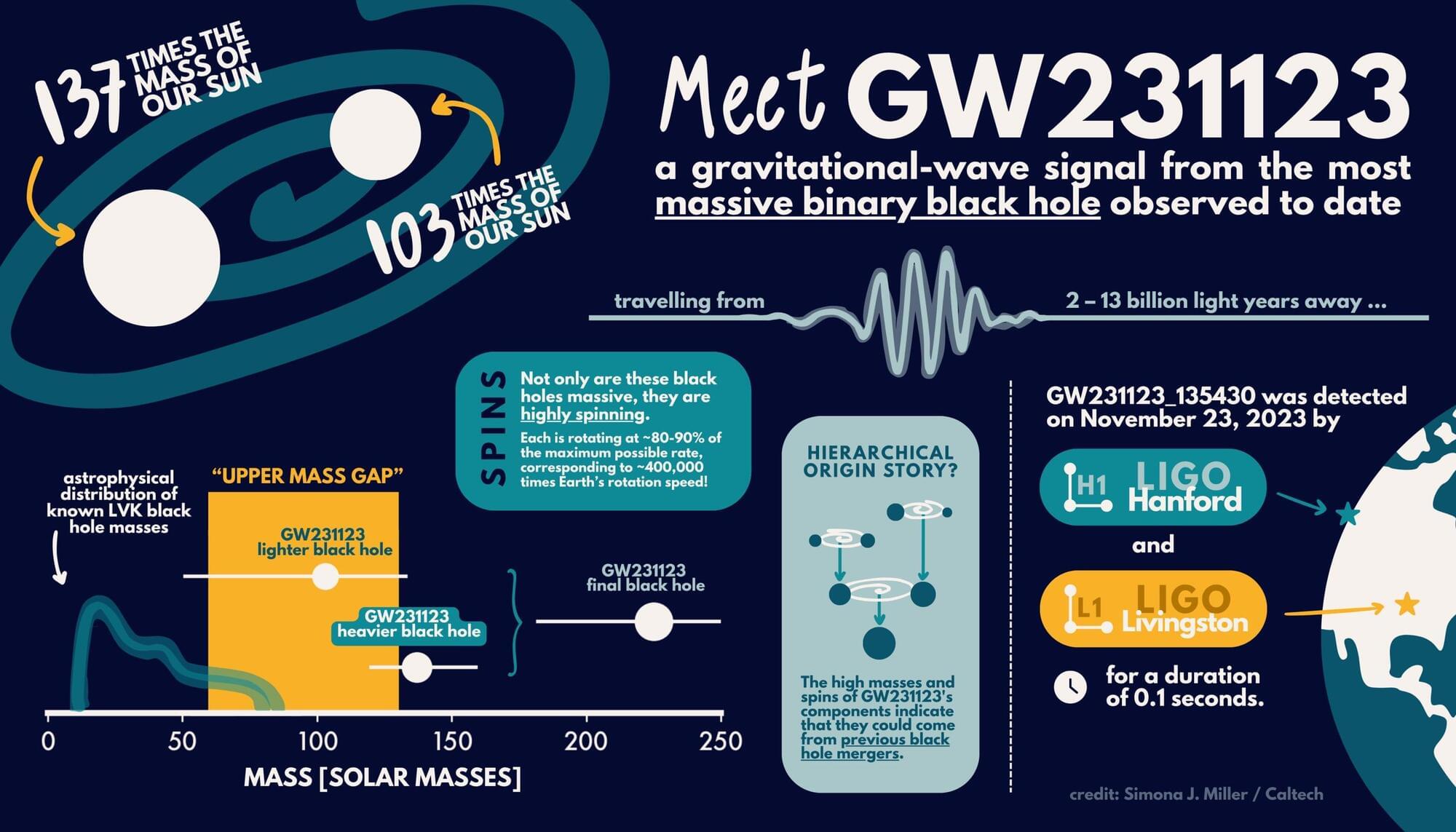
The LIGO-Virgo-KAGRA (LVK) Collaboration has detected the merger of the most massive black holes ever observed with gravitational waves using the LIGO observatories. The powerful merger produced a final black hole approximately 225 times the mass of our sun. The signal, designated GW231123, was detected during the fourth observing run of the LVK network on November 23, 2023.
LIGO, the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-wave Observatory, made history in 2015 when it made the first-ever direct detection of gravitational waves, ripples in space-time. In that case, the waves emanated from a black hole merger that resulted in a final black hole 62 times the mass of our sun. The signal was detected jointly by the twin detectors of LIGO, one located in Livingston, Louisiana, and the other in Hanford, Washington.
Since then, the LIGO team has teamed up with partners at the Virgo detector in Italy and KAGRA (Kamioka Gravitational Wave Detector) in Japan to form the LVK Collaboration. These detectors have collectively observed more than 200 black hole mergers in their fourth run, and about 300 in total since the start of the first run in 2015.