Nature Medicine asks leading researchers to name their top clinical trial for 2025, from gene therapies for prion disease and sickle-cell disease to digital tools for cancer and mental health.


Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/seanmcarroll.
Blog post with audio player, show notes, and transcript: https://www.preposterousuniverse.com/podcast/2024/12/09/298-…the-brain/
The number of neurons in the human brain is comparable to the number of stars in the Milky Way galaxy. Unlike the stars, however, in the case of neurons the real action is in how they are directly connected to each other: receiving signals over synapses via their dendrites, and when appropriately triggered, sending signals down the axon to other neurons (glossing over some complications). So a major step in understanding the brain is to map its wiring diagram, or connectome: the complete map of those connections. For a human brain that’s an intimidatingly complex challenge, but important advances have been made on tinier brains. We talk with Jeff Lichtman, a leader in brain mapping, to gauge the current state of progress and what it implies.
Jeff Lichtman received an MD/PhD from Washington University in St. Louis. He is currently the Jeremy R. Knowles Professor of Molecular and Cellular Biology and Santiago Ramón y Cajal Professor of Arts and Sciences at Harvard University. He is co-inventor of the Brainbow system for imaging neurons. He is a member of the National Academy of Sciences.
Mindscape Podcast playlist: https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLrxfgDEc2NxY_fRExpDXr87tzRbPCaA5x.
Sean Carroll channel: https://www.youtube.com/c/seancarroll.
#podcast #ideas #science #philosophy #culture
Brilliant is a great place to improve your problem solving skills! First 30 days are free and 20% off the annual premium subscription when you use our link ➜ https://brilliant.org/sabine.
This is a brief comment on the recent social media episode in which a young woman attracted a lot of attention by graduating with a thesis on olfactory suppression in English prose. In this video, I try to put these events into context. I find it difficult to wrap my head around the sudden outrage. Let me know what you think about this.
🤓 Check out my new quiz app ➜ http://quizwithit.com/
💌 Support me on Donorbox ➜ https://donorbox.org/swtg.
📝 Transcripts and written news on Substack ➜ https://sciencewtg.substack.com/
👉 Transcript with links to references on Patreon ➜ / sabine.
📩 Free weekly science newsletter ➜ https://sabinehossenfelder.com/newsle…
👂 Audio only podcast ➜ https://open.spotify.com/show/0MkNfXl…
🔗 Join this channel to get access to perks ➜
/ @sabinehossenfelder.
🖼️ On instagram ➜ / sciencewtg.
#science #sciencenews #academia

As an emerging new class, metal nanoparticles and especially silver nanoparticles hold great potential in the field of cancer biology. Due to cancer-specific targeting, the consequently attenuated side-effects and the massive anti-cancer features render nanoparticle therapeutics desirable platforms for clinically relevant drug development. In this review, we highlight those characteristics of silver nanoparticle-based therapeutic concepts that are unique, exploitable, and achievable, as well as those that represent the critical hurdle in their advancement to clinical utilization. The collection of findings presented here will describe the features that distinguish silver nanoparticles from other anti-cancer agents and display the realistic opportunities and implications in oncotherapeutic innovations to find out whether cancer therapy by silver nanoparticles is fiction or reality.
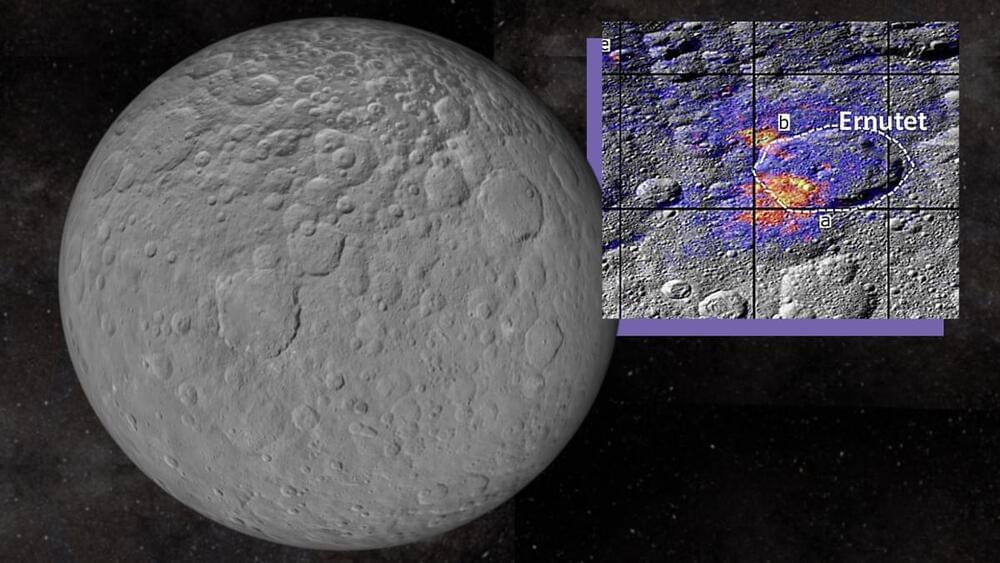
These findings dispute the former theory, suggesting the organic materials come from within the dwarf planet or are “endogenous.”
“The significance of this discovery lies in the fact that, if these are endogenous materials, it would confirm the existence of internal energy sources that could support biological processes,” team leader and Instituto de Astrofísica de Andalucía researcher Juan Luis Rizos said in a statement.
To investigate the organic compounds found on Ceres, the team used a new approach that examined the dwarf planet’s surface and the distribution of organic matter at the highest possible resolution.

“Everything about this discovery was surprising.”
The team’s research was published on Thursday (Dec. 12) in the journal Science.
This year, the sun has been particularly turbulent, blasting Earth with usually strong solar storms and ramping up auroral displays as a reminder of how violent our star can be. While scientists have been able to study this behavior and collect invaluable data, this represents the sun’s behavior over a tiny fraction of its 4.6 billion-year life so far.
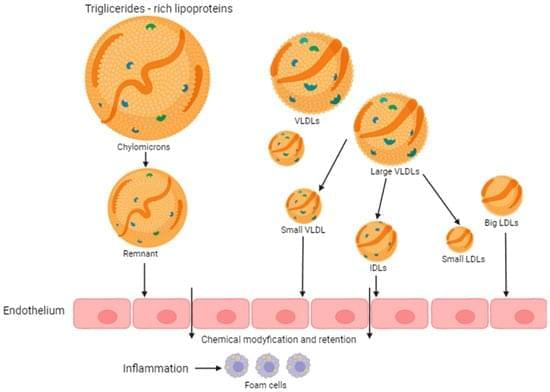
Lipids, together with lipoprotein particles, are the cause of atherosclerosis, which is a pathology of the cardiovascular system. In addition, it affects inflammatory processes and affects the vessels and heart. In pharmaceutical answer to this, statins are considered a first-stage treatment method to block cholesterol synthesis. Many times, additional drugs are also used with this method to lower lipid concentrations in order to achieve certain values of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol. Recent advances in photodynamic therapy (PDT) as a new cancer treatment have gained the therapy much attention as a minimally invasive and highly selective method. Photodynamic therapy has been proven more effective than chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and immunotherapy alone in numerous studies.

It could lead to vaccines that could be simply rubbed onto the skin like creams.
Some bacteria, like harmless Staphylococcus epidermidis, have adapted to thrive on human skin.
Immunologists have often overlooked the role of skin bacteria in our health. However, recent research suggests that this seemingly ordinary bacterium triggers a powerful immune response in our bodies.
The researchers wanted to know if a mouse, which doesn’t naturally have S. epidermidis on its skin, would produce antibodies against this bacteria if it were introduced.