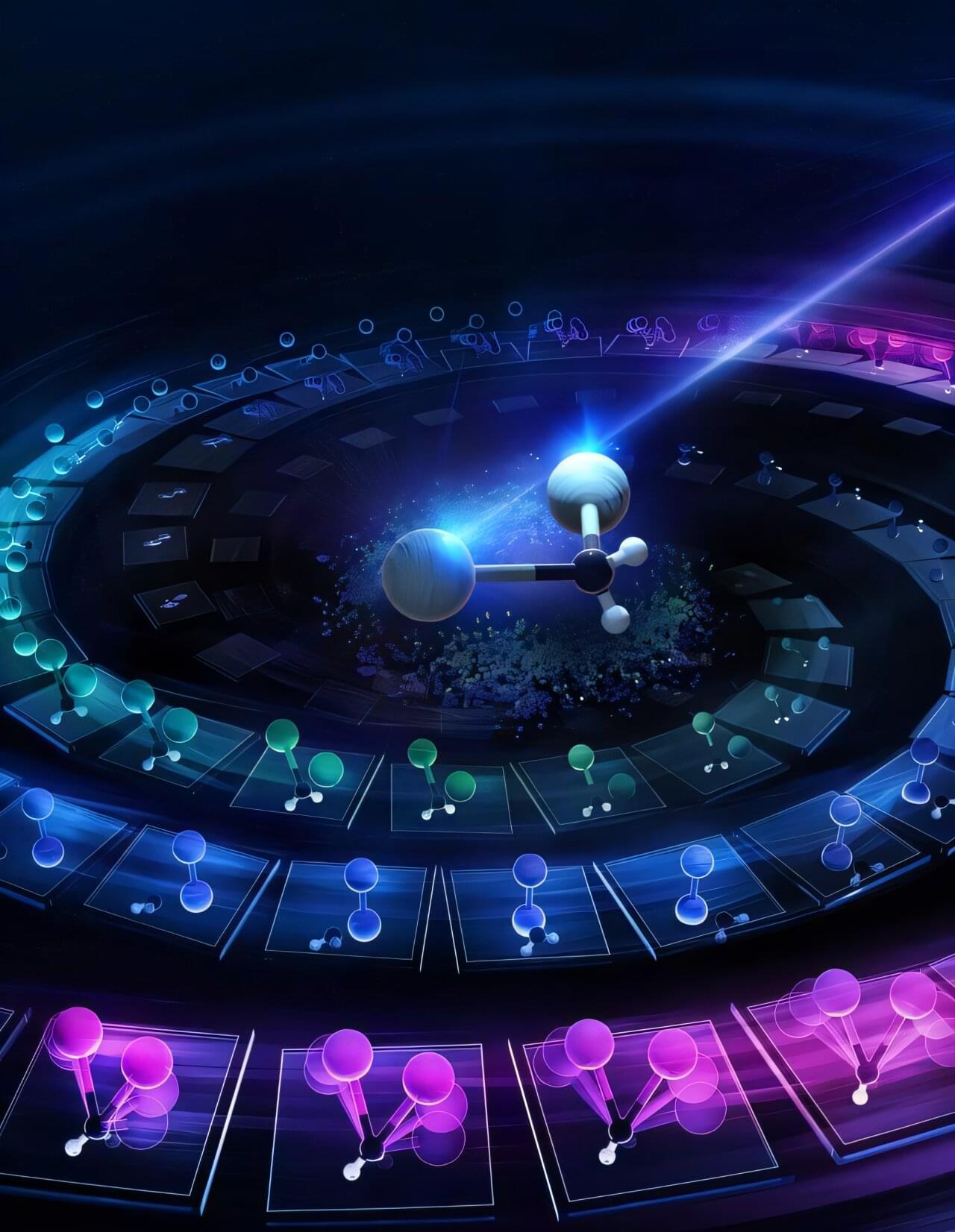
Researchers at European XFEL in Germany have tracked in real time the movement of individual atoms during a chemical reaction in the gas phase. Using extremely short X-ray flashes, they were able to observe the formation of an iodine molecule (I₂) after irradiating diiodomethane (CH₂I₂) molecules by infrared light, which involves breaking two bonds and forming a new one.
At the same time, they were able to distinguish this reaction from two other reaction pathways, namely the separation of a single iodine atom from the diiodomethane, or the excitation of bending vibrations in the bound molecule. The results, published in Nature Communications, provide new insights into fundamental reaction mechanisms that have so far been very difficult to distinguish experimentally.
So-called elimination reactions in which small molecules are formed from a larger molecule are central to many chemical processes—from atmospheric chemistry to catalyst research. However, the detailed mechanism of many reactions, in which several atoms break and re-form their bonds, often remains obscure. The reason: The processes take place in incredibly short times—in femtoseconds, or a few millionths of a billionth of a second.