A new principle underlying the physics of fragmentation explains why fragment sizes follow a specific, universal distribution.


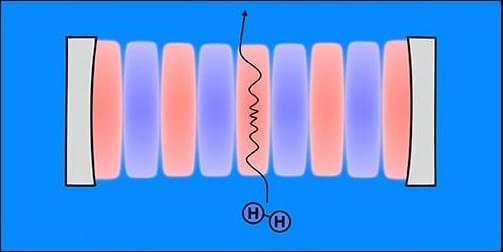
In spaces smaller than a wavelength of light, electric currents jump from point to point and magnetic fields corkscrew through atomic lattices in ways that defy intuition. Scientists have only ever dreamed of observing these marvels directly.
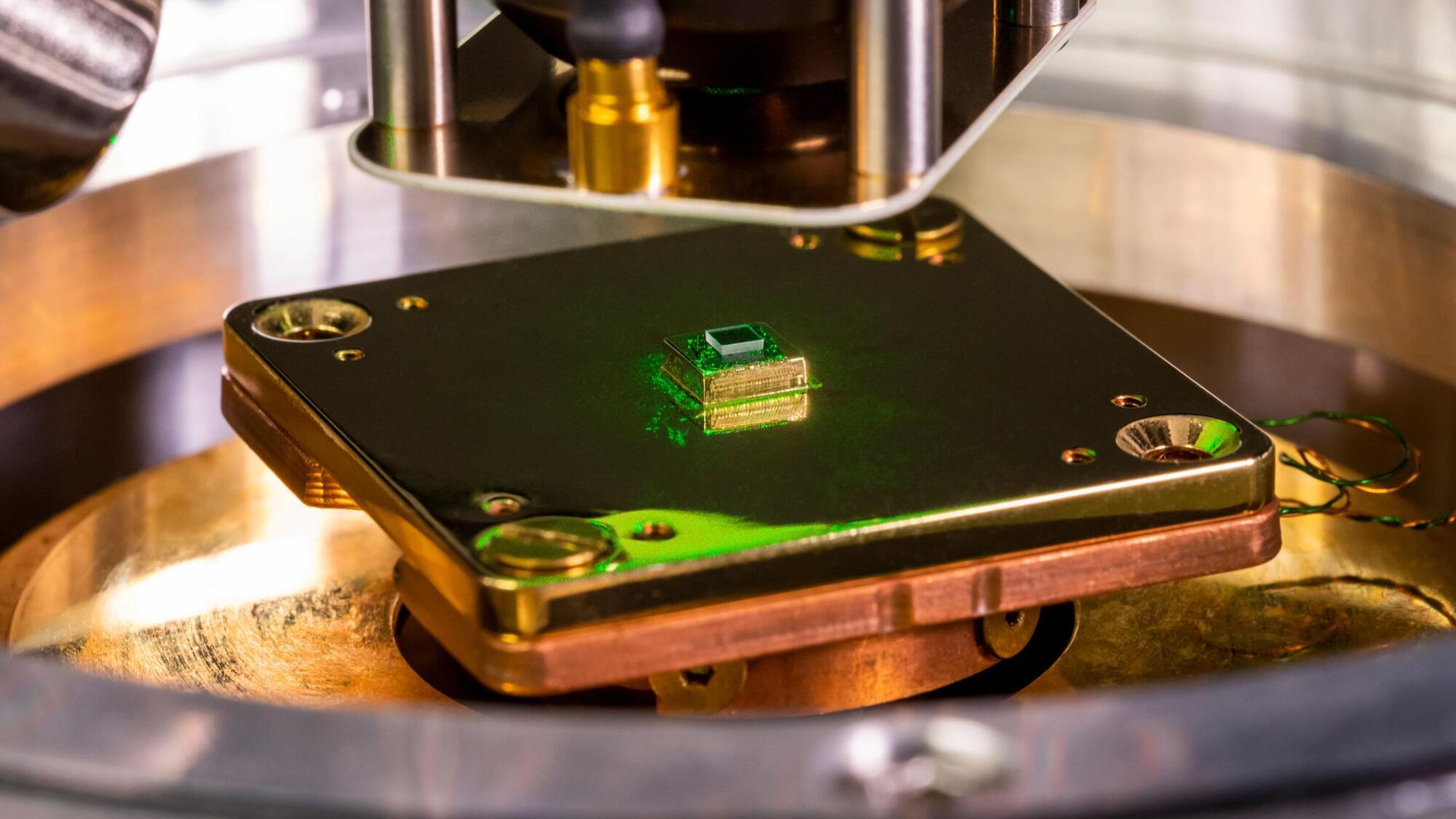
Now Princeton researchers have developed a diamond-based quantum sensor that reveals rich new information about magnetic phenomena at this minute scale. The technique uncovers fluctuations that are beyond the reach of existing instruments and provides key insight into materials such as graphene and superconductors. Superconductors have enabled today’s most advanced medical imaging tools and form the basis of hoped-for technologies like lossless powerlines and levitating trains.
The underlying diamond-based sensing methods have been under development for half a decade. But in a Nov. 27 paper in Nature, the team reported roughly 40 times greater sensitivity than previous techniques.
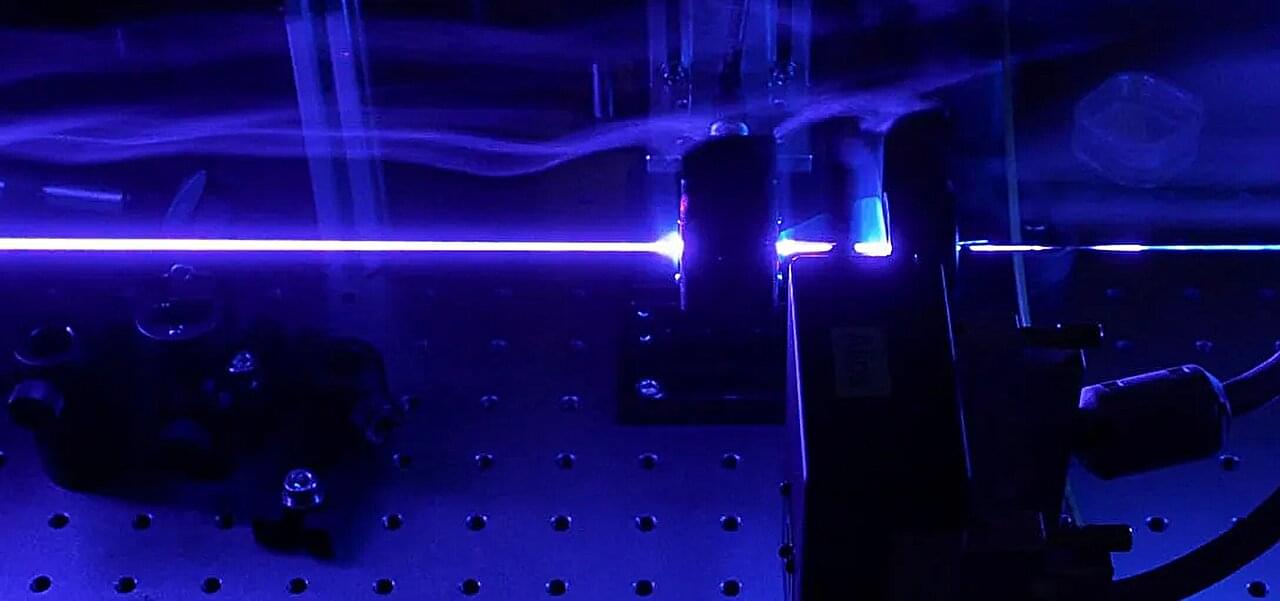

For decades, physicists have dreamed of a quantum internet: a planetary web of ultrasecure communications and super-powered computation built not from electrical signals, but from the ghostly connections between particles of light.
Now, scientists in Edinburgh say they’ve taken a major step toward turning that vision into something real.
Researchers at Heriot-Watt University have unveiled a prototype quantum network that links two smaller networks into one reconfigurable, eight-user system capable of routing and even teleporting entanglement on demand.
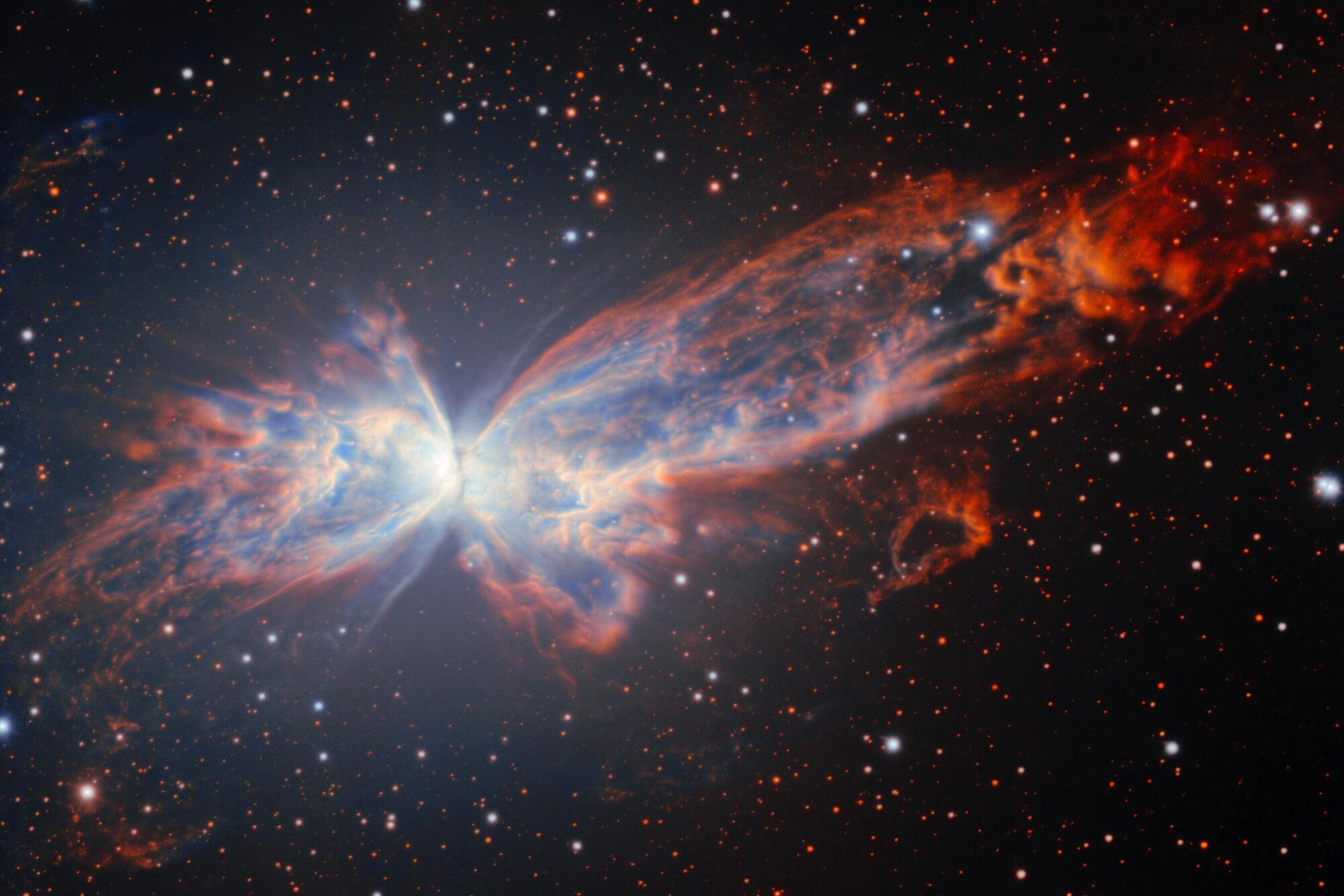

A telescope in Chile has captured a stunning new picture of a grand and graceful cosmic butterfly.
The National Science Foundation’s NoirLab released the picture Wednesday.
Snapped last month by the Gemini South telescope, the aptly named Butterfly Nebula is 2,500 to 3,800 light-years away in the constellation Scorpius. A single light-year is 6 trillion miles.
The same brain cells linked to disorientation in Alzheimer’s disease have been preserved—and even slightly increased—across millions of years of evolution.
A new University of Michigan study suggests these neurons are vital to evolutionary survival. Nature has guarded and amplified them through countless generations, helping mammals instinctively know where they are in their environments. The research is published in The Journal of Neuroscience.
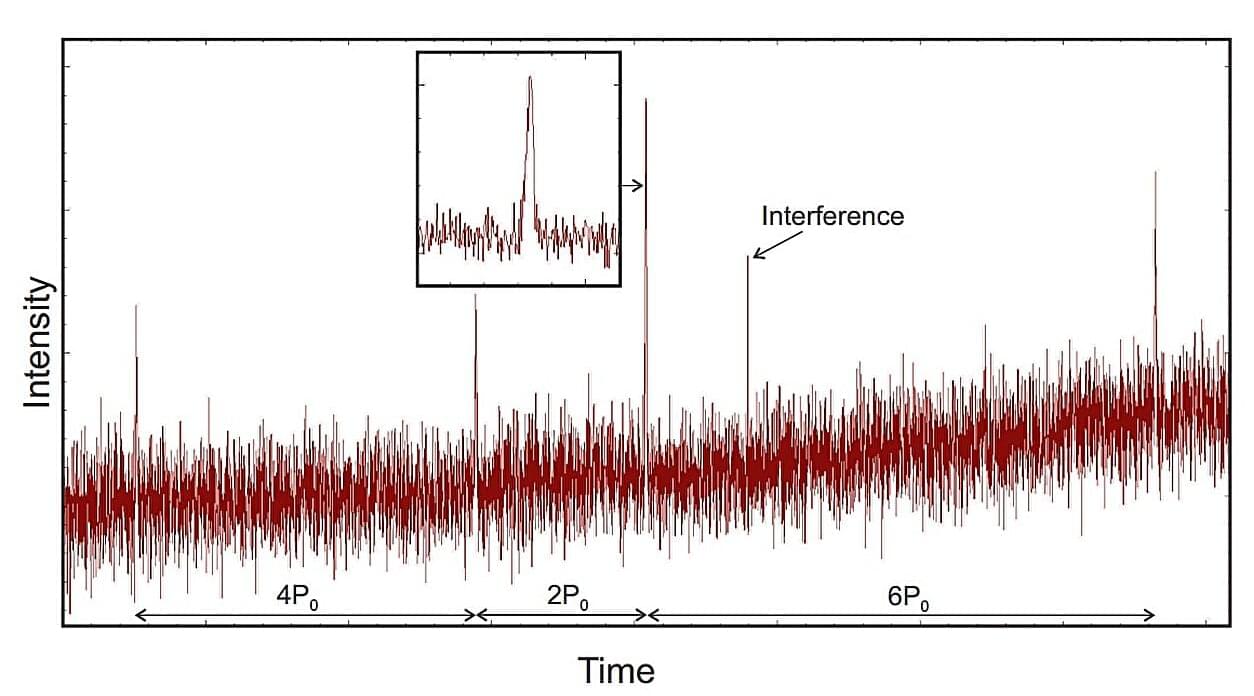
Using the Large Phased Array (LPA) and the Five-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical radio Telescope (FAST), astronomers from Russia and China have observed a nearby pulsar designated PSR J1951+2837. The new observations, presented Nov. 18 on the pre-print server arXiv, deliver important insights into the nature of this pulsar.
Pulsars are highly magnetized, rotating neutron stars emitting a beam of electromagnetic radiation. They are usually detected in the form of short bursts of radio emission; however, some of them are also observed via optical, X-ray and gamma-ray telescopes.
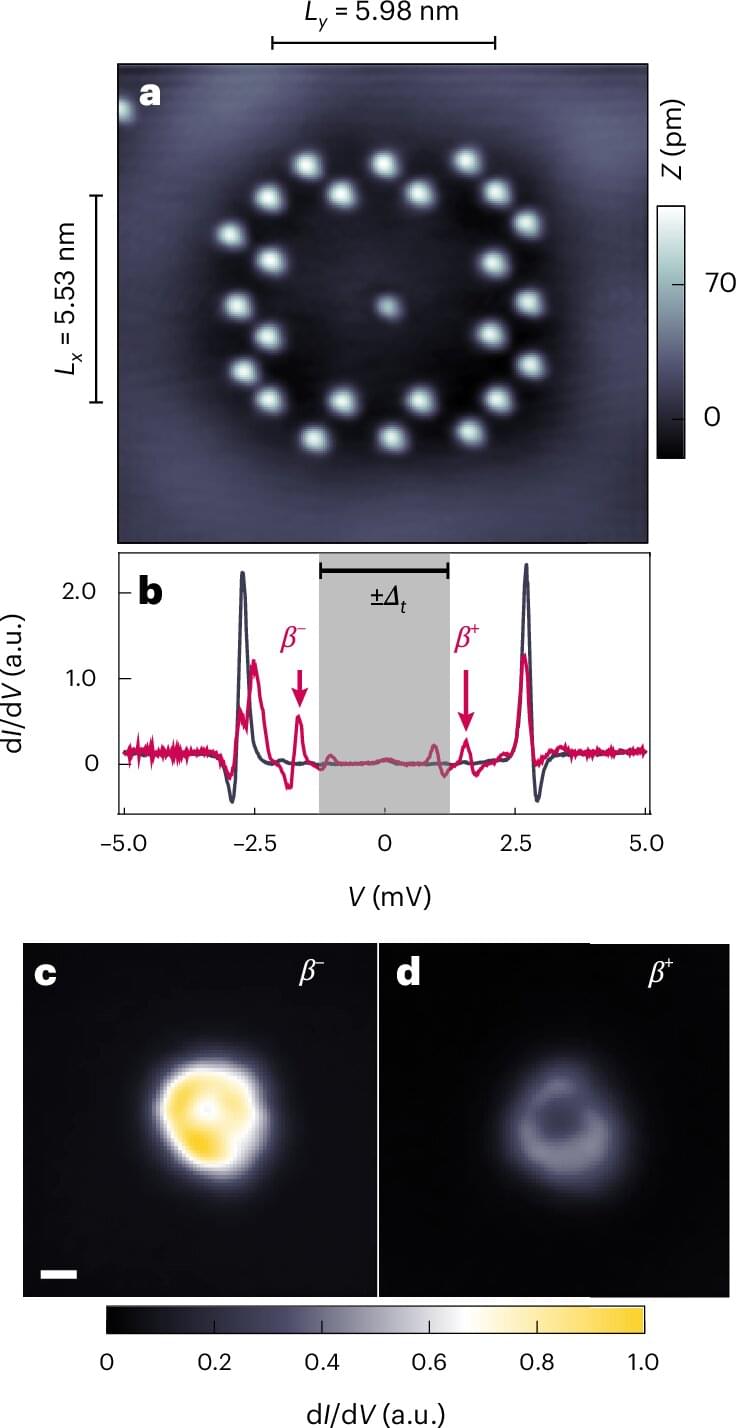
Hybrid materials made of magnets and superconductors give rise to fascinating quantum phenomena, which are so sensitive that it is crucial to measure them with minimal interference. Researchers at the University of Hamburg and the University of Illinois Chicago have now demonstrated, both experimentally and theoretically, how these quantum phenomena can be detected and controlled over longer distances using special techniques with a scanning tunneling microscope.
Their findings, which could be important for topological quantum computers, were published in the journal Nature Physics.
When a magnetic atom is located in a superconductor, so-called Yu-Shiba-Rusinov quasiparticles are created. Normally, they can only be measured with a high detection probability directly at the location of the atom using the tip of a scanning tunneling microscope.
Organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) power the high-end screens of our digital world, from TVs and phones to laptops and game consoles.
If those displays could stretch to cover any 3D or irregular surfaces, the doors would be open for technologies like wearable electronics, medical implants and humanoid robots that integrate better with or mimic the soft human body.
“Displays are the intuitive application, but a stretchable OLED can also be used as the light source for monitoring, detection and diagnosis devices for diabetes, cancers, heart conditions and other major health problems,” said Wei Liu, a former postdoctoral researcher in the lab of University of Chicago Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering (UChicago PME) Assoc. Prof. Sihong Wang.
Researchers at the Department of Mechanical Engineering, Seoul National University, have applied the principle of interlacing to an origami-inspired structure and developed a “Foldable-and-Rollable corruGated Structure (FoRoGated-Structure)” that can be smoothly folded and rolled up for compact storage while maintaining very high strength when deployed. The study was published in the journal Science Robotics on November 26.
The team was led by Professor Kyu-Jin Cho—Director of the Human-Centered Soft Robotics Research Center and a founding member of the SNU Robotics Institute (SNU RI).