Synchronization abounds in nature: from the flashing lights of fireflies to the movement of fish wriggling through the ocean, biological systems are often in rhythmic movement with each other. The mechanics of how this synchronization happens are complex.
For instance, in the vasculature of the brain, blood vessels oscillate, expanding and contracting as needed. When there is neural activity, the arterioles expand to increase blood flow, oxygen and nutrients. These oscillations are self-sustained, but the arterioles also work in concert with each other. How this happens is not well understood.
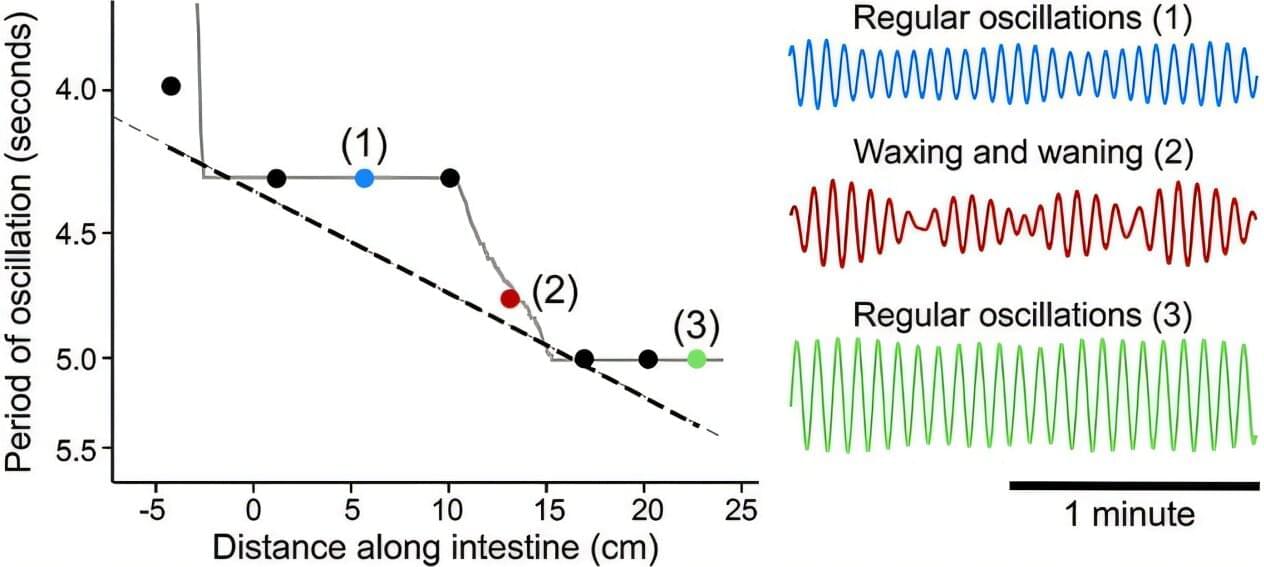
To uncover the answer, researchers at the University of California San Diego looked to another part of the body: the gut. Here they found that oscillators operating at similar frequencies lock onto each other in succession, creating a staircase effect. Their work appears in Physical Review Letters.