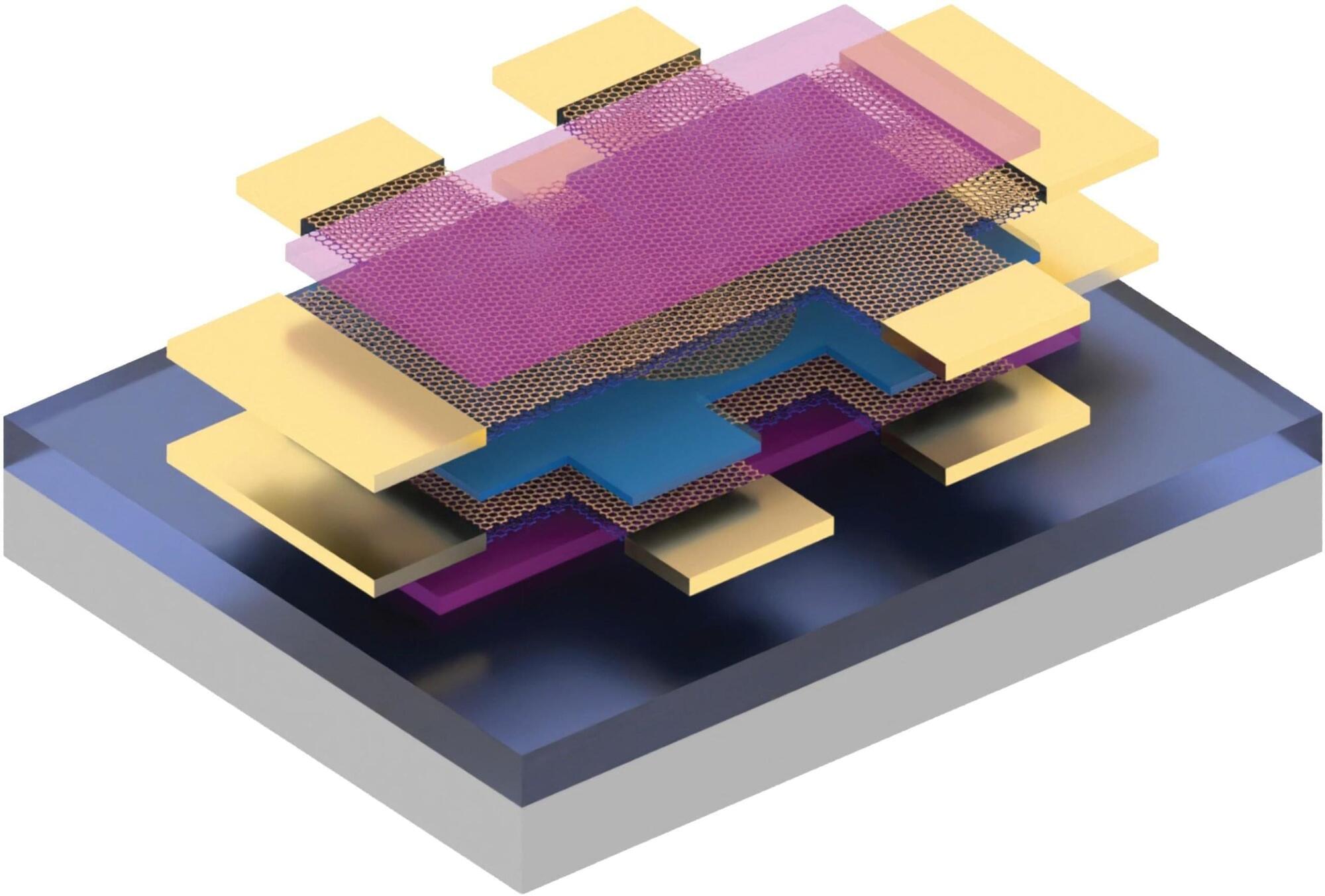
MIT researchers uncovered clear evidence of unconventional superconductivity in magic-angle twisted trilayer graphene.
Their new measurement system revealed a sharp, V-shaped superconducting gap — proof of a new pairing mechanism unlike that in traditional superconductors. This breakthrough sheds light on quantum behaviors in ultra-thin materials and could accelerate the quest for room-temperature superconductivity.
Superconductors: Nature’s Perfect Conductors.