:3year 2019
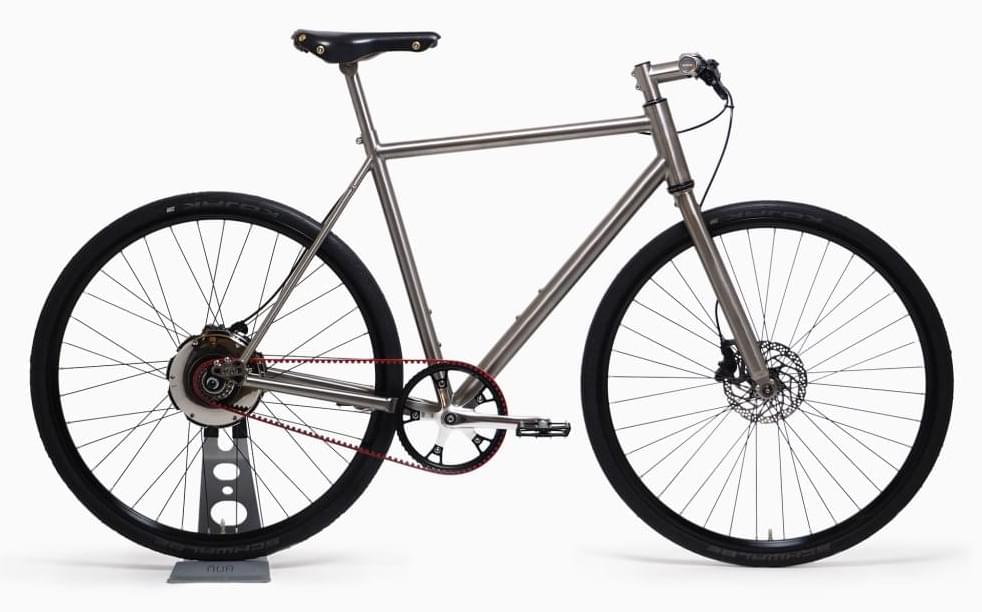
If e-bikes tend to look a little ungainly for your tastes, check out this thing from Barcelona’s Nua Bikes. With the motor, sensors and battery built into a discreet hub unit, the Nua Electrica is barely distinguishable from a regular fixie, and its innovative “self-charging” mode means you can get away without ever charging it.
Weighing in at just 13 kg thanks to a full titanium frame, the Nua Electrica is the stealthiest single-speed e-bike we’ve seen to date. It uses a very cool motor/battery combo unit that we suspect we’ll be seeing a lot more of in the coming months and years.
The Zehus Bike+ is an all-in-one hub unit that weighs just 3 kg (6.6 lb) and fits into any frame with a rear wheel dropout 120 mm (4.7 in) or wider. It contains a 250-watt motor, a 160-watt-hour battery, several sensors, a Bluetooth communications system and all the electronics required to run an e-bike.