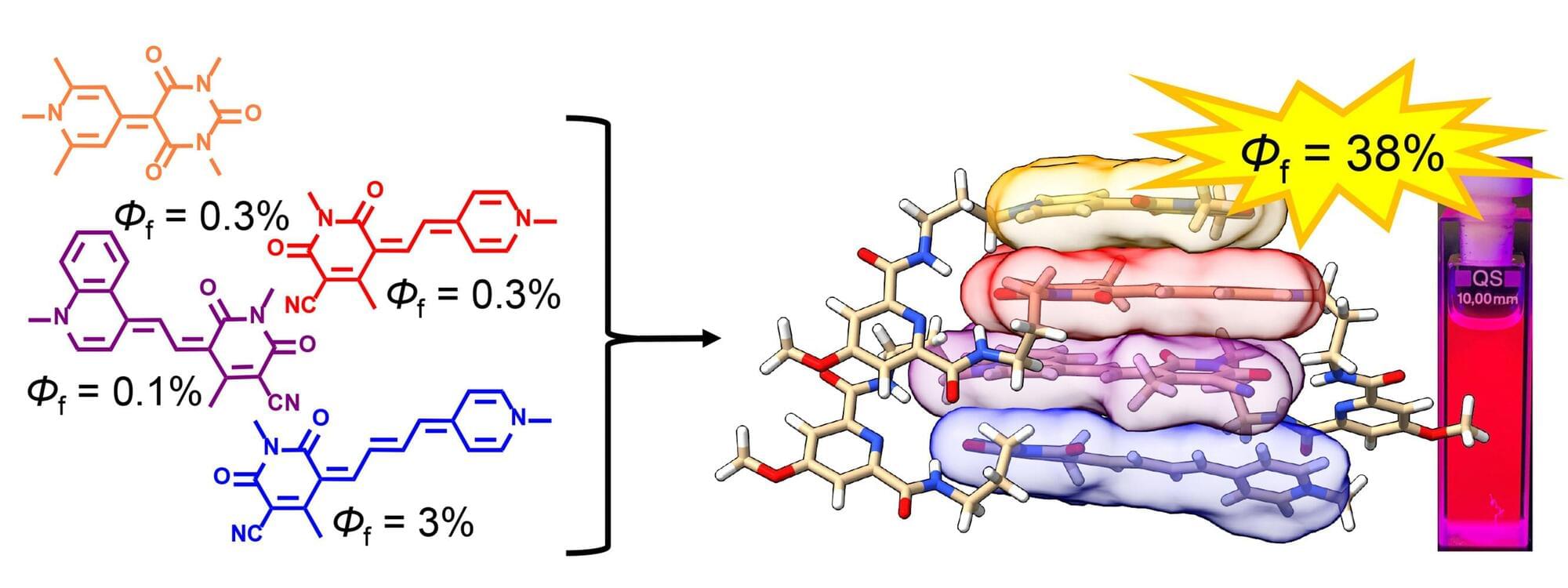
In order to convert sunlight into electricity or other forms of energy as efficiently as possible, the very first step is an efficient light-harvesting system. Ideally, this should be panchromatic, i.e. absorb the entire spectrum of visible light.


Quantum systems hold the promise of tackling some complex problems faster and more efficiently than classical computers. Despite their potential, so far only a limited number of studies have conclusively demonstrated that quantum computers can outperform classical computers on specific tasks. Most of these studies focused on tasks that involve advanced computations, simulations or optimization, which can be difficult for non-experts to grasp.
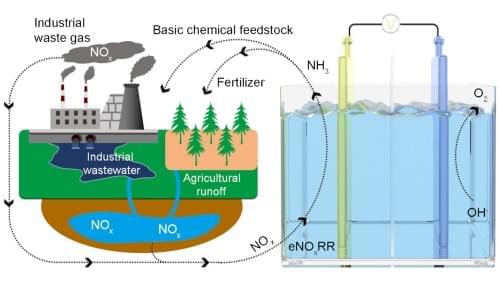
Researchers at the University of Oxford and the University of Sevilla recently demonstrated a quantum advantage over a classical scenario on a cooperation task called the odd-cycle game. Their paper, published in Physical Review Letters, shows that a team with quantum entanglement can win this game more often than a team without.
“There is a lot of talk about quantum advantage and how quantum systems will revolutionize entire industries, but if you look closely, in many cases, there is no mathematical proof that classical methods definitely cannot find solutions as efficiently as quantum algorithms,” Peter Drmota, first author of the paper, told Phys.org.
Twenty-four stroke patients have already used the complete system, consisting of an exoskeleton for the arm and shoulder in combination with FES as part of the ReHyb research project. Half of them were patients at the Schön Klinik Bad Aibling Harthausen, which is leading the study. The researchers also used a computer game that automatically adapts to the individual player’s capabilities. It trains them to grip and move their arms shortly after a stroke by reacting to colored balls flying toward them at varying speeds on a screen. The task is to catch the balls and match them with color-coded boxes.
At the center of TUM Professor Sandra Hirche’s setup is a digital twin that records the individual requirements of each patient and places them in a control loop. Among other things, the researchers have to determine how well each patient can move their arm and hand. In the event of a stroke, for example, paralysis can be caused by damage to the motor area in the brain responsible for movement. However, it is impossible to predict how severely the signals transmitted from the brain to the muscles in the forearm will be impaired after the stroke. “Individual muscle strands in the forearm can be stimulated to the right extent for hands and fingers to move,” says Prof. Hirche, who holds the Chair of Information-Oriented Control at TUM. In addition to information on muscle activity in the forearm, the researchers need to know how strongly the muscles should be stimulated in conjunction with the exoskeleton assistance.
Growing functional human organs outside the body is a long-sought “holy grail” of organ transplantation medicine that remains elusive. New research from the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) and Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering brings that quest one big step closer to completion.
A team of scientists created a new method to 3D print vascular networks that consist of interconnected blood vessels possessing a distinct “shell” of smooth muscle cells and endothelial cells surrounding a hollow “core” through which fluid can flow, embedded inside a human cardiac tissue. This vascular architecture closely mimics that of naturally occurring blood vessels and represents significant progress toward being able to manufacture implantable human organs. The achievement is published in Advanced Materials .
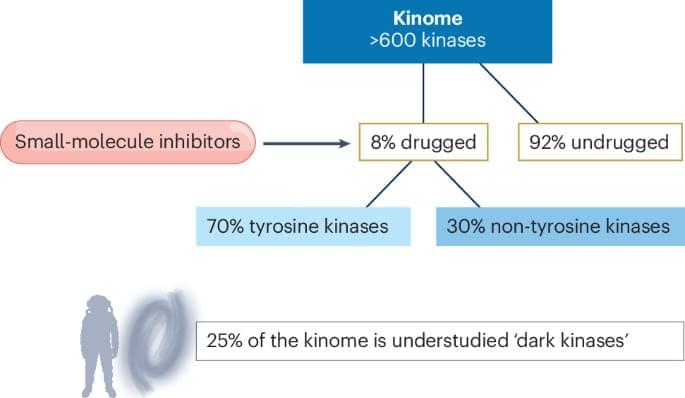
Multiple tumour-agnostic kinase inhibitors have been approved that are clinically effective regardless of tumour location. This Review describes the origins of tumour-agnostic drug development, focusing on small-molecule inhibitors that target kinase pathway aberrations, and discusses the challenges in developing tissue-agnostic agents.
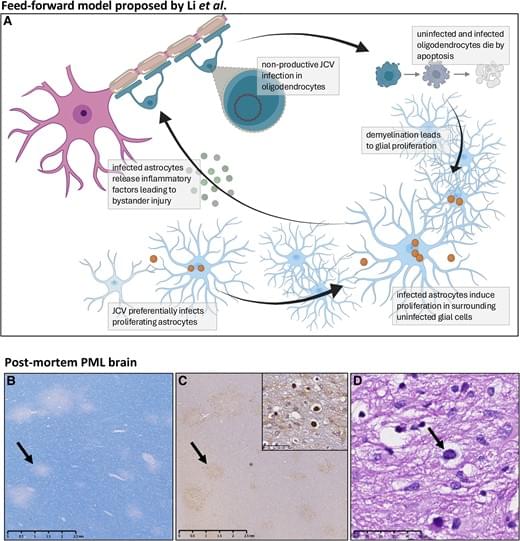
Glial replication and proliferation support JC virus demyelination.
In HIV infected patients, JC virus (JCV) can cause a devastating demyelinating disease of the CNS known as progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML).
JCV replicates in human glial progenitor cells and astrocytes, which undergo viral T-antigen-triggered mitosis, enabling viral replication.
The authors were able to demonstrate that dividing human astrocytes supported JCV propagation to a substantially greater degree than did mitotically quiescent cells.
They also show that JCV infection greatly accentuated by cuprizone-induced demyelination and its associated mobilization of glial progenitor cells and triggered the death of both uninfected and infected glia, reflecting significant bystander death. https://sciencemission.com/JCV-infection-models
This scientific commentary refers to ‘JC virus spread is potentiated by glial replication and demyelination-linked glial proliferation’ by Li et al. (https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awae252).
Howard Bloom, Dr. Ben Goertzel, and Dr. Mihaela Ulieru examine how principles of emergent intelligence in natural systems can inform artificial general intelligence (AGI) development.
Join us at the Beneficial AGI Summit & Unconference 2025 (May 26–28 in Istanbul) to learn more about these topics and collaborate on addressing the critical challenges of developing beneficial AGI. Register now to watch online or attend in-person: https://bgisummit.io/
/ 22517.global_brain.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Howard_… • A Cultural Legend Tackles the Benefic… 00:00 Intro 01:20 Howard Bloom’s Online Journey and the Global Brain 04:33 Ben Goertzel’s Perspective on the Global Brain 09:07 The Evolution of Intelligence and AI 12:42 Challenges and Philosophies in AI Development 17:56 Human Values and AI: A Complex Relationship 24:18 The Role of Compassion in AI and Human Evolution 29:31 Tribalism and Ethical Reasoning in AI 30:16 Emergence of AI Values 31:26 Self-Organization and Compassion in AI 32:21 Ethical Theories and AI Attractors 34:33 Future Economy and AI Impact 34:48 AI and Human Economy Transformation 35:44 Cosmic Ambitions and AI 37:15 Competition Among AIs 38:00 Vision of Beneficial AGI 38:20 Path to Human-Level AGI 42:32 Emergence and Cooperation in AI 46:17 Singularity and Human Nature 50:09 Punctuated Equilibrium in AI Development 52:27 Engineering the Future of Intelligence 54:22 Closing Thoughts on AI and the Future #AGI #AI #BGI — SingularityNET was founded by Dr. Ben Goertzel with the mission of creating a decentralized, democratic, inclusive and beneficial Artificial General Intelligence (AGI). According to Dr. Goertzel, AGI should be independent of any central entity, open to anyone and not restricted to the narrow goals of a single corporation or even a single country. The SingularityNET team includes seasoned engineers, scientists, researchers, entrepreneurs, and marketers. The core platform and AI teams are further complemented by specialized teams devoted to application areas such as finance, robotics, biomedical AI, media, arts and entertainment. Website: https://singularitynet.io X: https://twitter.com/SingularityNET Linkedin:
/ singularitynet Instagram:
/ singularitynet.io Discord:
/ discord Telegram: https://t.me/singularitynet WhatsApp: https://whatsapp.com/channel/0029VaM8… Warpcast: https://warpcast.com/singularitynet Bluesky: https://bsky.app/profile/singularityn… Github: https://github.com/singnet.
• A Cultural Legend Tackles the Benefic…
00:00 Intro.
01:20 Howard Bloom’s Online Journey and the Global Brain.
04:33 Ben Goertzel’s Perspective on the Global Brain.
09:07 The Evolution of Intelligence and AI
12:42 Challenges and Philosophies in AI Development.
17:56 Human Values and AI: A Complex Relationship.
24:18 The Role of Compassion in AI and Human Evolution.
29:31 Tribalism and Ethical Reasoning in AI
30:16 Emergence of AI Values.
31:26 Self-Organization and Compassion in AI
32:21 Ethical Theories and AI Attractors.
34:33 Future Economy and AI Impact.
34:48 AI and Human Economy Transformation.
35:44 Cosmic Ambitions and AI
37:15 Competition Among AIs.
38:00 Vision of Beneficial AGI
38:20 Path to Human-Level AGI
42:32 Emergence and Cooperation in AI
46:17 Singularity and Human Nature.
50:09 Punctuated Equilibrium in AI Development.
52:27 Engineering the Future of Intelligence.
54:22 Closing Thoughts on AI and the Future.
#AGI #AI #BGI
SingularityNET was founded by Dr. Ben Goertzel with the mission of creating a decentralized, democratic, inclusive and beneficial Artificial General Intelligence (AGI). According to Dr. Goertzel, AGI should be independent of any central entity, open to anyone and not restricted to the narrow goals of a single corporation or even a single country. The SingularityNET team includes seasoned engineers, scientists, researchers, entrepreneurs, and marketers. The core platform and AI teams are further complemented by specialized teams devoted to application areas such as finance, robotics, biomedical AI, media, arts and entertainment.