Scientists have devised a way to use current gravitational-wave detectors to observe permanent deformations of spacetime caused by certain supernovae.
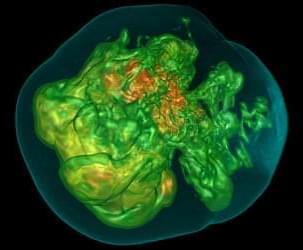



Cell–cell alignment and a background of stationary cells together shape the emergence of cellular clusters in a primary tumor.
In a cancer patient, tumor cells that circulate throughout the body in clusters pose a greater threat of metastasis than those that circulate individually. Those clusters are thought to come together while the cells are still within the primary tumor, but researchers still don’t understand the formation mechanism. Quirine Braat at Eindhoven University of Technology in the Netherlands and her colleagues have now used computer simulations to identify some of the factors at play [1].
The team used a computational lattice model of cells and tissues (the cellular Potts model) to examine a 2D layer of two types of cells—one motile (able to move) and one nonmotile. The tendency of the motile cells to migrate was represented in the model by an external force applied to each one. For a given cell, this force could align strongly or weakly with the forces acting on its neighboring cells.
A trio of archaeologists at the University of Cambridge, in the U.K. conducted a study of hundreds of papers outlining research into hunter–gatherer societies, finding that people in such groups engage in a variety of physical activities. George Brill, Marta Mirazon-Lahr and Mark Dyble published their paper in the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences.
For much of history, male physical and athletic prowess has been considered to be important, while female physical prowess has been mostly overlooked. In this new study, the research team wondered if female physical prowess has also been overlooked in a hunter–gatherer context.
To find out, they conducted a study focusing on research efforts into hunter–gatherer societies—both those in the past and those still in existence today. In all, they looked at more than 900 papers, focusing most specifically on physical or athletic activities of people of both genders.
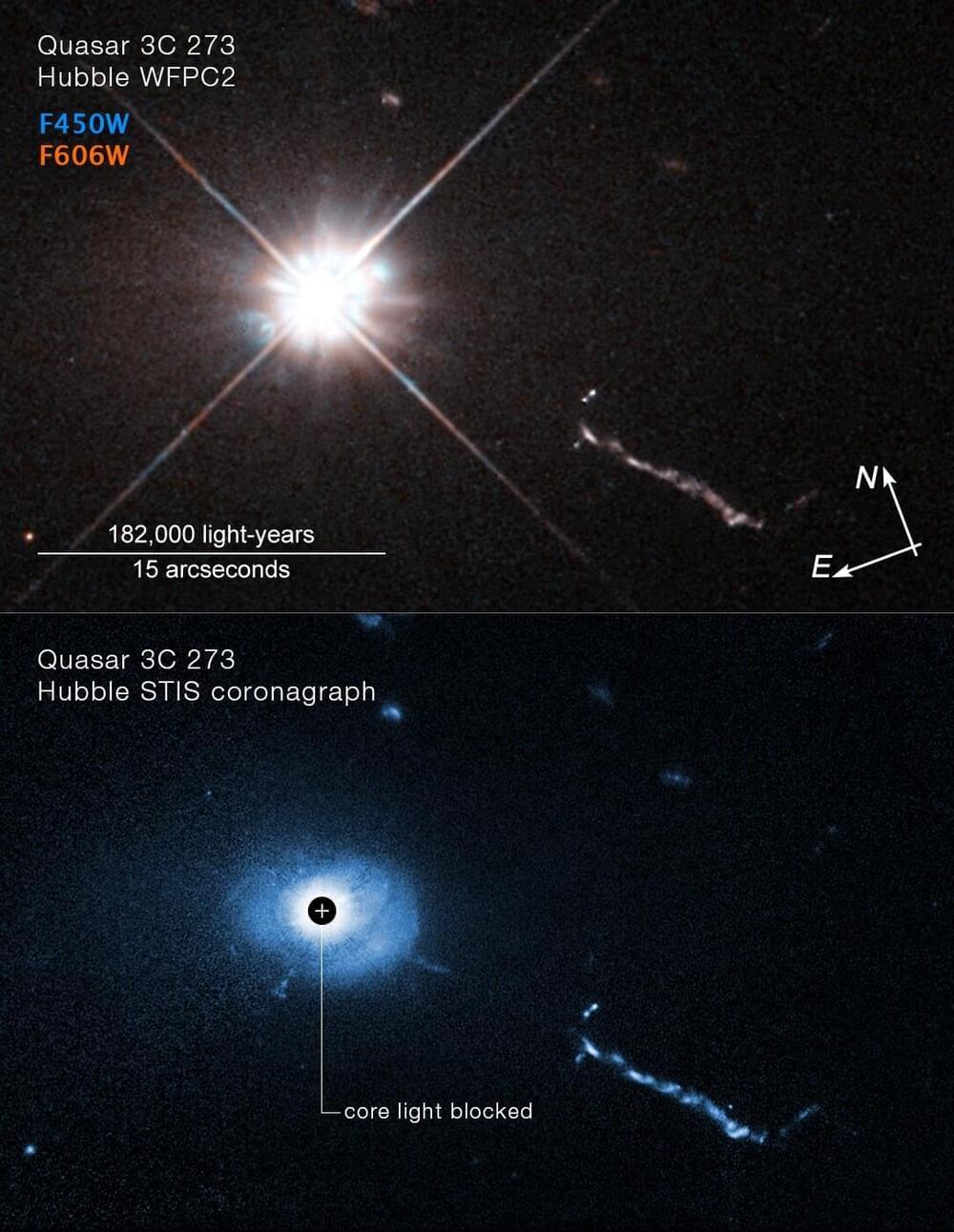

Astronomers have used the unique capabilities of NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope to peer closer than ever into the throat of an energetic monster black hole powering a quasar. A quasar is a galactic center that glows brightly as the black hole consumes material in its immediate surroundings.
The new Hubble views of the environment around the quasar show a lot of “weird things,” according to Bin Ren of the Côte d’Azur Observatory and Université Côte d’Azur in Nice, France. “We’ve got a few blobs of different sizes, and a mysterious L-shaped filamentary structure. This is all within 16,000 light-years of the black hole.”
Some of the objects could be small satellite galaxies around the black hole, and so they could offer the materials that will accrete onto the central super massive black hole, powering the bright lighthouse.
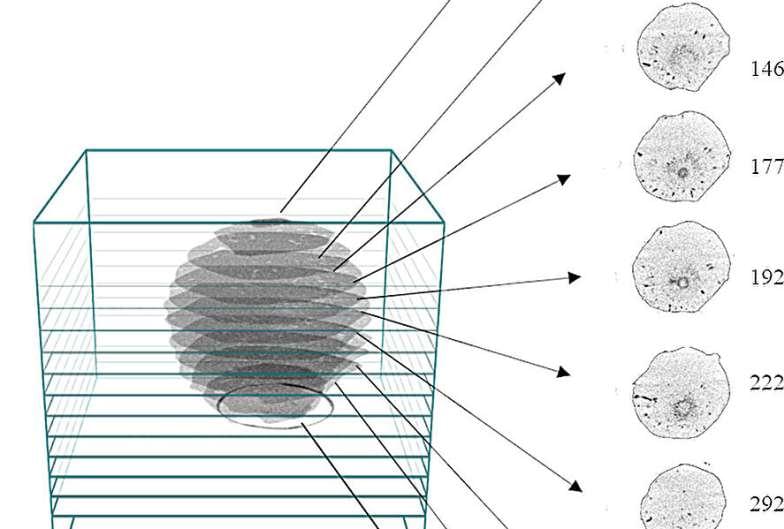
Hailstones are formed during thunderstorms, when raindrops are propelled into very cold parts of a cloud, where they freeze. Once the particles are heavy enough, gravity pulls them back towards Earth. As they plummet, they grow into hailstones, which can cause injury to people and significant damage to homes and cars.
Scientists have been studying how hailstones grow since the 1960s but doing so meant breaking them in the process. To better understand the anatomy and growth of hailstones, researchers in Catalonia have used computed tomography (CT) scans to examine the giant hailstones that hit the north-east of the Iberian Peninsula during an exceptionally strong thunderstorm in the summer of 2022.
“We show that the CT scanning technique enables the observation of the internal structure of the hailstones without breaking the samples,” said Carme Farnell Barqué, a researcher at the Meteorological Service of Catalonia and lead author of the study published in Frontiers in Environmental Science.
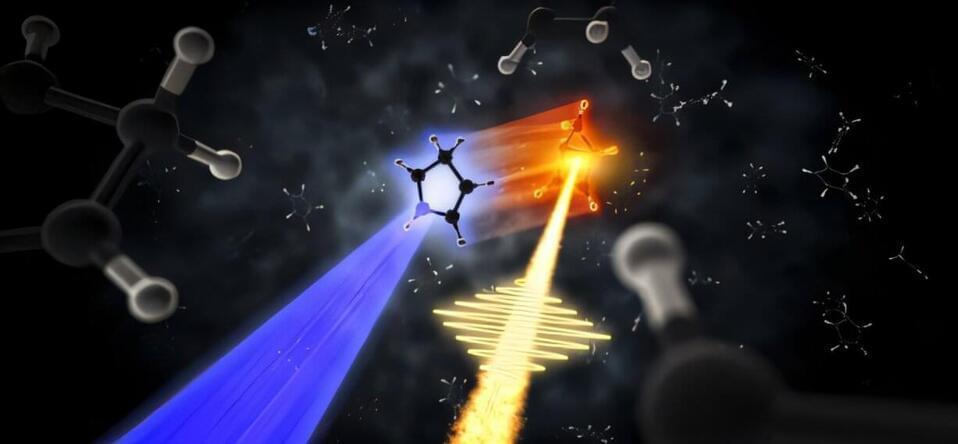
When molecules interact with ultraviolet (UV) light, they can change shape quickly, producing strain—stress in a molecule’s chemical structure due to an increase in the molecule’s internal energy. These processes typically take just tens of picoseconds (one millionth of a millionth of a second). Advanced capabilities at X-ray free electron laser (XFEL) facilities now enable scientists to create images of these ultrafast structural changes.
In work appearing in The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, researchers found structural evidence of a strained bicyclic molecule (a molecule consisting of two joined rings) that emerges from the chemical reaction that occurs when a cyclopentadiene molecule absorbs UV light. Cyclopentadiene is a good sample chemical for studying a range of reactions, and these findings have broad implications for chemistry.
Highly strained molecules have a variety of interesting applications in solar energy and pharmaceuticals. However, strain doesn’t typically occur naturally—energy must be added to a molecular system to create the strain. Identifying processes that produce molecules with strained rings is a challenge of broad interest in physical chemistry.
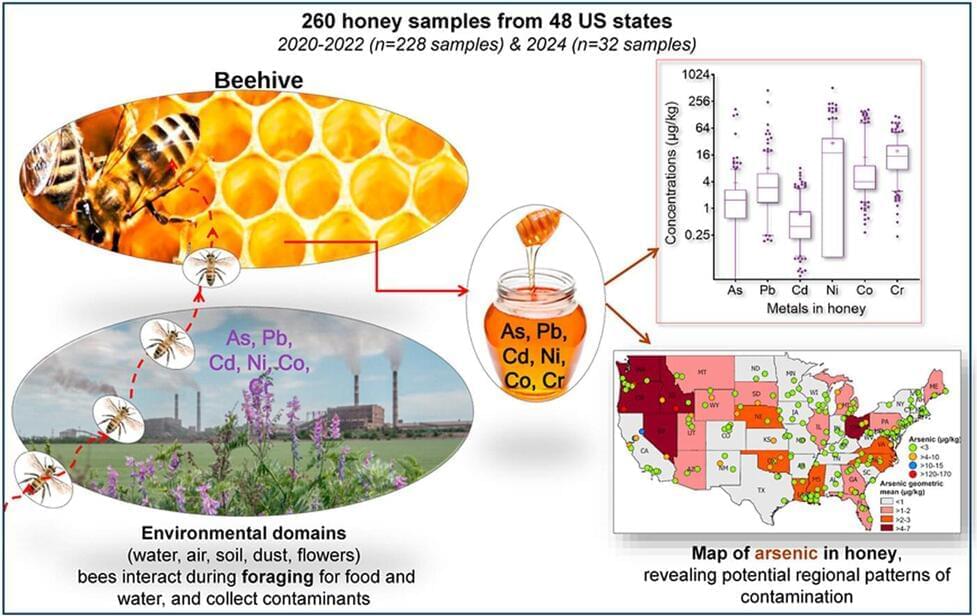
Inside every jar of honey is a taste of the local environment, its sticky sweet flavor enhanced by whichever nearby flowers bees have decided to sample. But a new study from Tulane University has found that honey can also offer a glimpse of nearby pollution.
The study, published in Environmental Pollution, tested 260 honey samples from 48 states for traces of six toxic metals: arsenic, lead, cadmium, nickel, chromium and cobalt. None of the honeys showed unsafe levels of toxic metals—based on a serving size of one tablespoon per day—and concentrations in the United States were lower than global averages.
However, researchers found regional differences in toxic metal distribution: the highest arsenic levels were found in honeys from a cluster of states in the Pacific Northwest (Oregon, Idaho, Washington and Nevada); the Southeast tested highest for cobalt levels, including Louisiana and Mississippi; and two of the three highest lead levels were found in the Carolinas.

A joint research team led by Yuuki Kubo and Shiji Tsuneyuki of the University of Tokyo has developed a new computational method that can efficiently determine the crystal structures of multiphase materials, powders that contain more than one type of crystal structures. The method can predict the structure directly from powder X-ray diffraction patterns, the patterns of X-rays passing through crystals roughly the same size as instant coffee particles.
Unlike conventional methods, this approach does not require the use of “lattice constants” and can be applied to existing experimental data that could not be analyzed until now. Thus, the new method is a crucial asset for discovering new material phases and developing new materials. The findings are published in The Journal of Chemical Physics.
Many materials can have several crystal structures, “phases,” even in the same solid state. Determining the underlying crystal structures of materials is essential for understanding their properties and formulating strategies to develop new materials. However, conventional methods make calculations using the “lattice constant,” a property of the crystal being investigated.
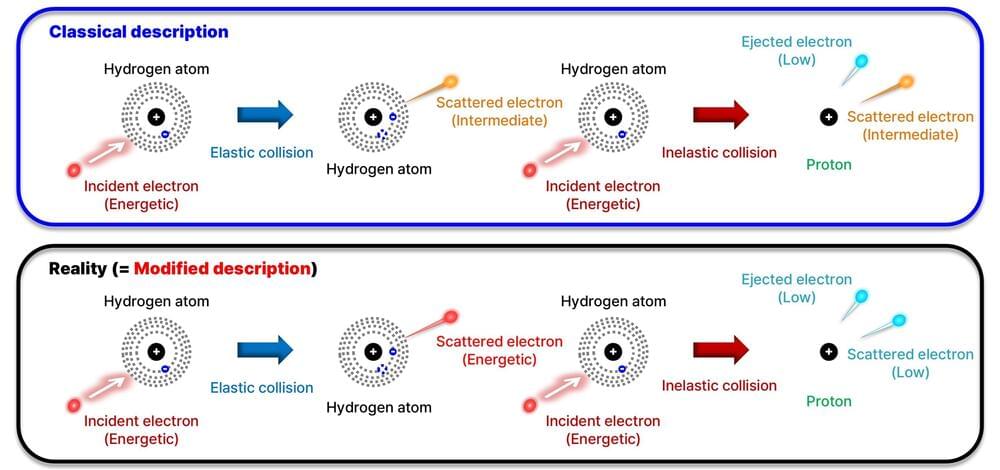
A research team has clarified the mechanism behind the generation of runaway electrons during the startup phase of a tokamak fusion reactor. The paper, “Binary Nature of Collisions Facilitates Runaway Electron Generation in Weakly Ionized Plasmas,” was published in the journal Physical Review Letters.
Nuclear fusion energy refers to a power generation method that harnesses the energy of an artificial sun created on Earth, using resources extracted from seawater. To achieve this, technology capable of confining high-temperature plasma exceeding 100 million degrees for extended periods in a fusion reactor is essential.
A tokamak is an artificial sun system in the shape of a torus, with no beginning or end, where magnetic fields are applied to confine particles.