Improved organoid models uncover potential treatments for endocrine-related conditions and reveal new insights into gastrointestinal diseases.
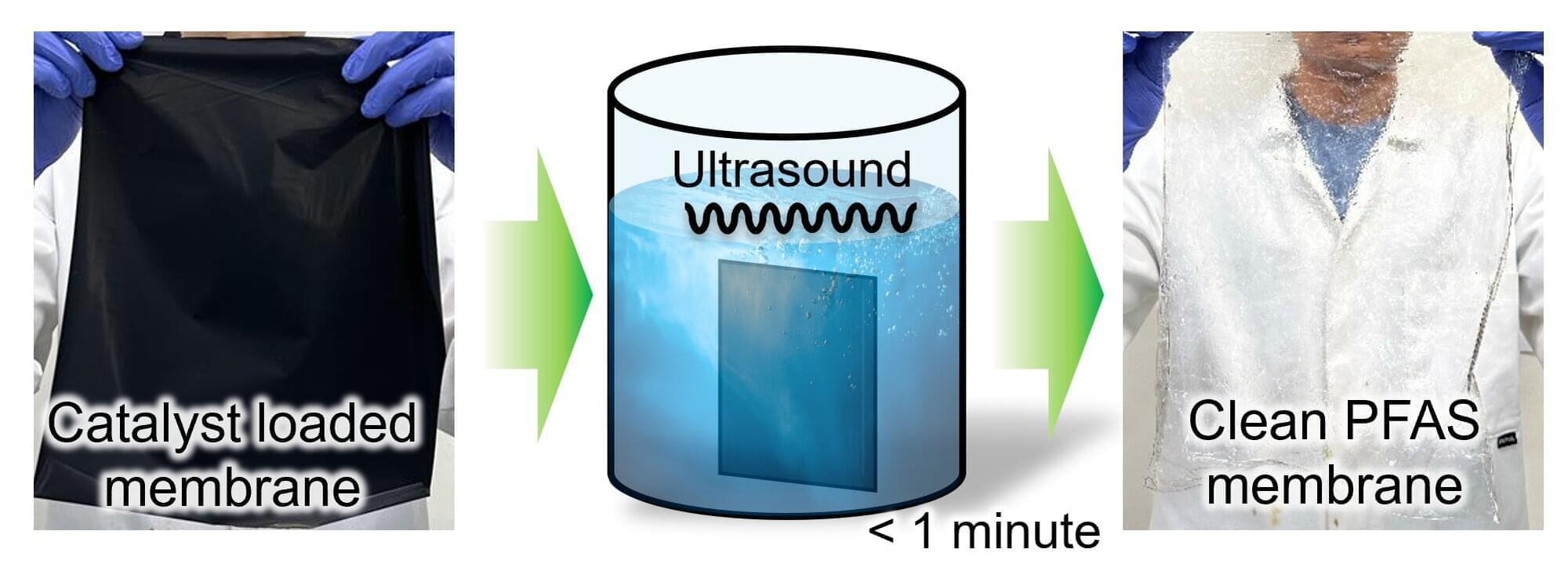
A new technique that uses soundwaves to separate materials for recycling could help prevent potentially harmful chemicals leaching into the environment.
Researchers at the University of Leicester have achieved a major milestone in fuel cell recycling, advancing techniques to efficiently separate valuable catalyst materials and fluorinated polymer membranes (PFAS) from catalyst-coated membranes (CCMs). The articles are published in RSC Sustainability and Ultrasonic Sonochemistry.
This development addresses critical environmental challenges posed by PFAS—often referred to as “forever chemicals”—which are known to contaminate drinking water and have serious health implications. The Royal Society of Chemistry has urged government intervention to reduce PFAS levels in UK water supplies.
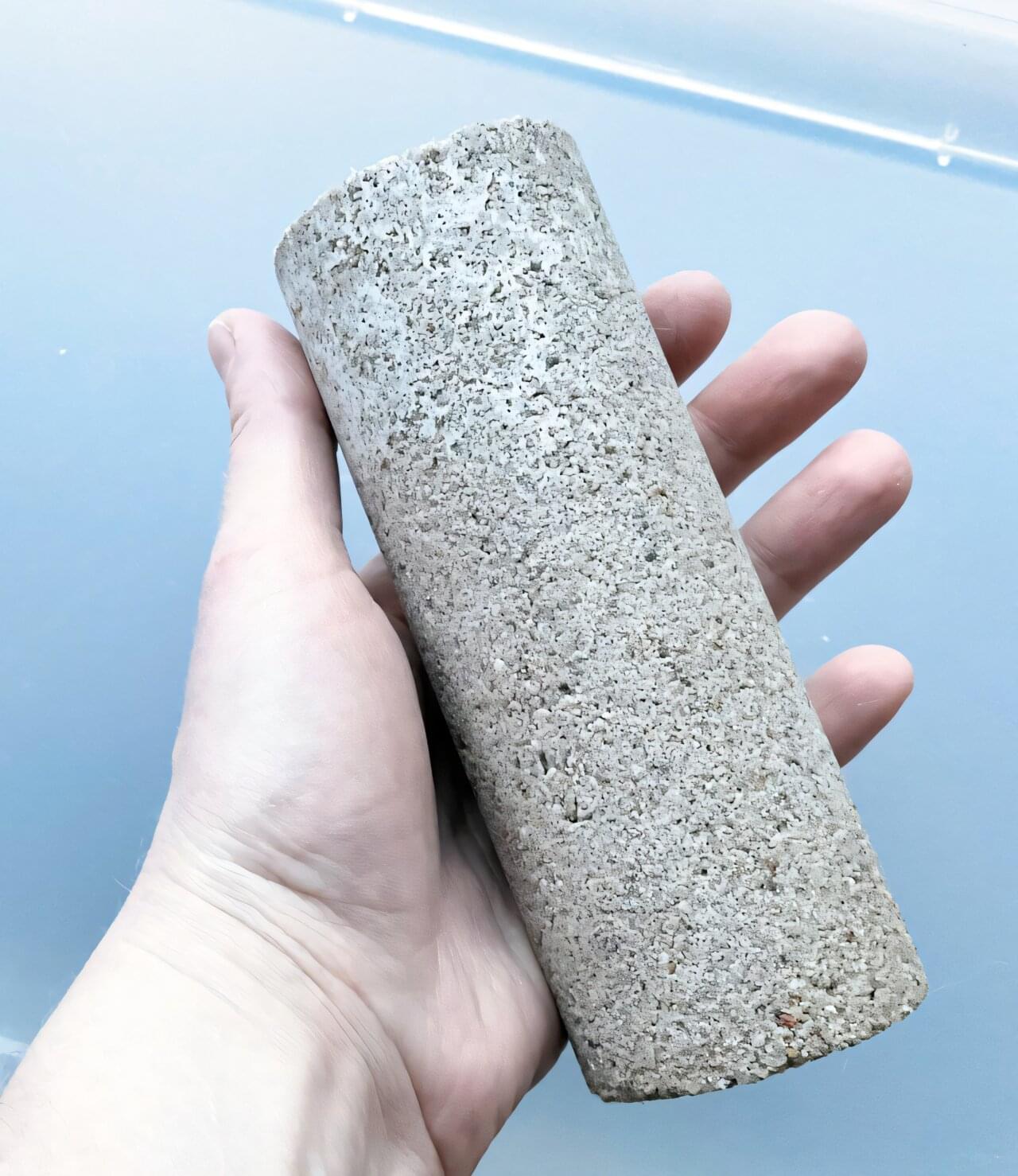
Researchers at the University of Stuttgart have used microbial processes to produce environmentally friendly bio-concrete from urine as part of a “wastewater-bio-concrete-fertilizer” value chain. With the project extension granted by the Baden-Württemberg Ministry of Science, Research, and the Arts, the focus now shifts to product optimization and practical testing.
Concrete is booming. Around 4 billion tons of cement are processed into concrete and used worldwide every year. With serious consequences for the environment.
“Conventional cement is typically fired at temperatures around 1,450 degrees. This consumes a lot of energy and releases large quantities of greenhouse gases,” says Professor Lucio Blandini, Head of the Institute for Lightweight Structures and Conceptual Design (ILEK) at the University of Stuttgart.
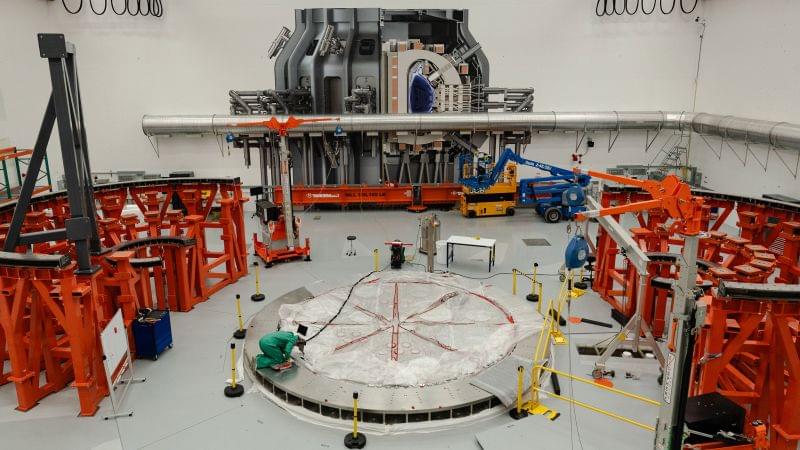
A nuclear fusion power plant prototype is already being built outside Boston. How long until unlimited clean energy is real?
Posted in nuclear energy, particle physics | Leave a Comment on A nuclear fusion power plant prototype is already being built outside Boston. How long until unlimited clean energy is real?
In an unassuming industrial park 30 miles outside Boston, engineers are building a futuristic machine to replicate the energy of the stars. If all goes to plan, it could be the key to producing virtually unlimited, clean electricity in the United States in about a decade.
The donut-shaped machine Commonwealth Fusion Systems is assembling to generate this energy is simultaneously the hottest and coldest place in the entire solar system, according to the scientists who are building it.
It is inside that extreme environment in the so-called tokamak that they smash atoms together in 100-million-degree plasma. The nuclear fusion reaction is surrounded by a magnetic field more than 400,000 times more powerful than the Earth’s and chilled with cryogenic gases close to absolute zero.
AI isn’t just changing how we work and play, but it’s also helping us rethink our underlying reality itself.
Tim Sweeney, CEO of Epic Games, the company behind the wildly popular Fortnite and Unreal Engine, recently delved into a philosophical discussion sparked by the rapid advancements in AI. His musings touch upon the age-old simulation hypothesis, questioning not just the nature of our own reality, but also the reality of our potential creators. What’s particularly intriguing is how Sweeney links the increasing sophistication of AI with the growing plausibility of such thought experiments.
“I don’t know,” Sweeney pondered on the Lex Fridman podcast, “The question of whether we are living in a simulation ourselves always boils down to: if we are living in a simulation, where are *they* living? Because at some point there has to be some base reality.”
Cannabis consumption is associated with lower COVID-19 severity among hospitalized patients: a retrospective cohort analysis
Posted in biotech/medical, sex | Leave a Comment on Cannabis consumption is associated with lower COVID-19 severity among hospitalized patients: a retrospective cohort analysis
While cannabis is known to have immunomodulatory properties, the clinical consequences of its use on outcomes in COVID-19 have not been extensively evaluated. We aimed to assess whether cannabis users hospitalized for COVID-19 had improved outcomes compared to non-users.
We conducted a retrospective analysis of 1831 patients admitted to two medical centers in Southern California with a diagnosis of COVID-19. We evaluated outcomes including NIH COVID-19 Severity Score, need for supplemental oxygen, ICU (intensive care unit) admission, mechanical ventilation, length of hospitalization, and in-hospital death for cannabis users and non-users. Cannabis use was reported in the patient’s social history. Propensity matching was used to account for differences in age, body-mass index, sex, race, tobacco smoking history, and comorbidities known to be risk factors for COVID-19 mortality between cannabis users and non-users.
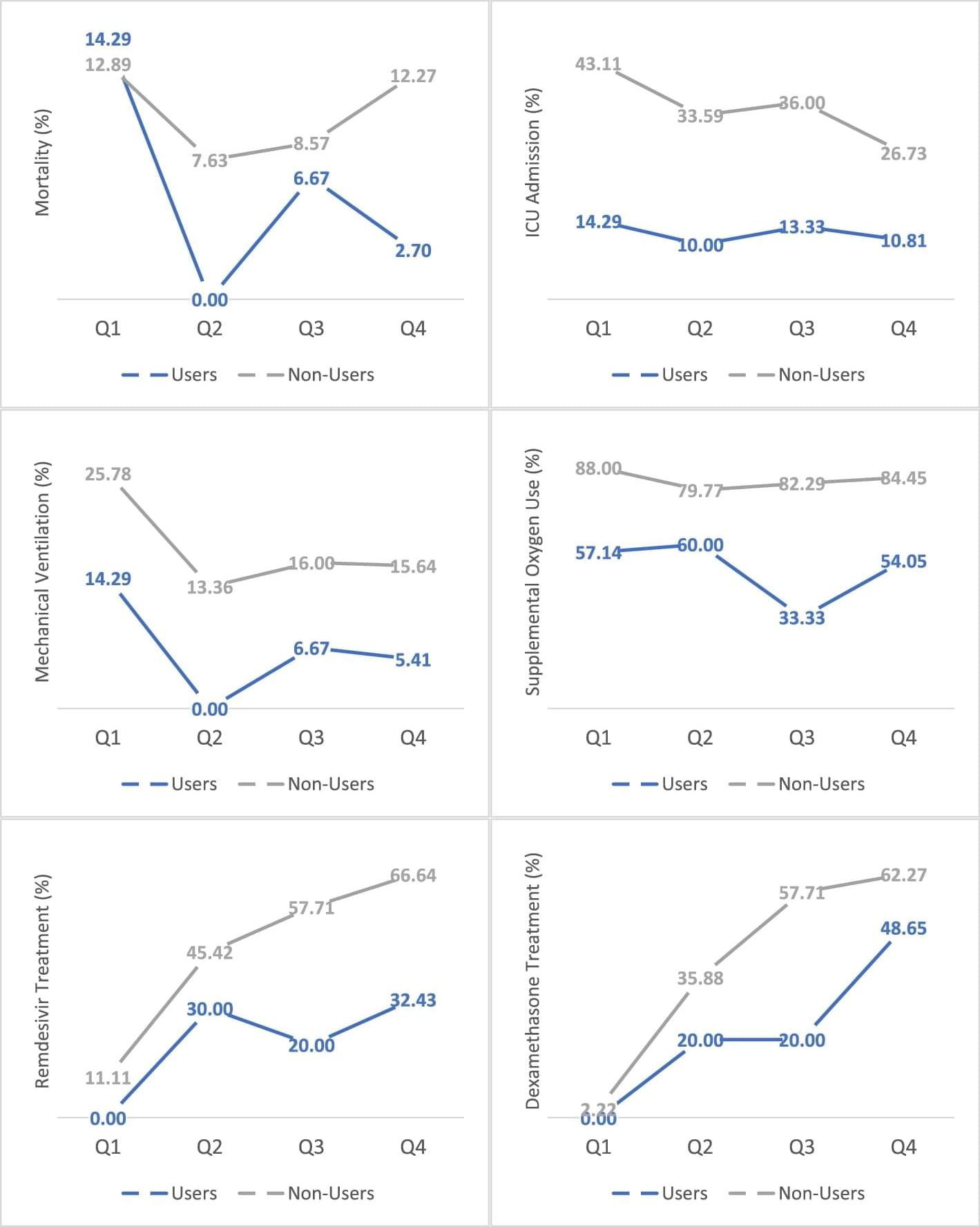
Of 1831 patients admitted with COVID-19, 69 patients reported active cannabis use (4% of the cohort). Active users were younger (44 years vs. 62 years, p < 0.001), less often diabetic (23.2% vs 37.2%, p < 0.021), and more frequently active tobacco smokers (20.3% vs. 4.1%, p < 0.001) compared to non-users. Notably, active users had lower levels of inflammatory markers upon admission than non-users—CRP (C-reactive protein) (3.7 mg/L vs 7.6 mg/L, p < 0.001), ferritin (282 μg/L vs 622 μg/L, p < 0.001), D-dimer (468 ng/mL vs 1,140 ng/mL, p = 0.017), and procalcitonin (0.10 ng/mL vs 0.15 ng/mL, p = 0.001). Based on univariate analysis, cannabis users had significantly better outcomes compared to non-users as reflected in lower NIH scores (5.1 vs 6.0, p < 0.001), shorter hospitalization (4 days vs 6 days, p < 0.001), lower ICU admission rates (12% vs 31%, p < 0.001), and less need for mechanical ventilation (6% vs 17%, p = 0.027).
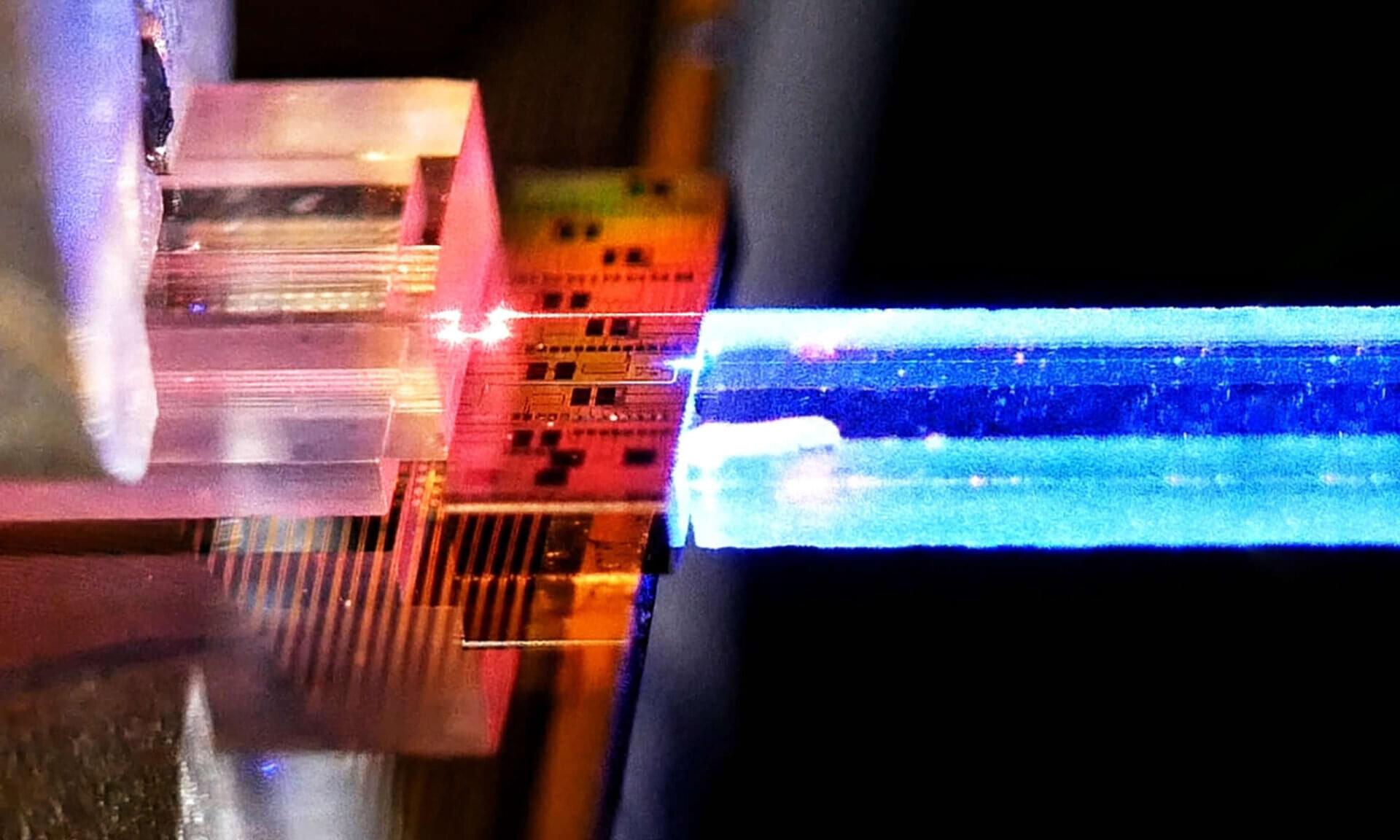
Researchers at the University of Rochester and Rochester Institute of Technology recently connected their campuses with an experimental quantum communications network using two optical fibers. In a new paper published in Optica Quantum, scientists describe the Rochester Quantum Network (RoQNET), which uses single photons to transmit information about 11 miles along fiber-optic lines at room temperature using optical wavelengths.
Quantum communications networks have the potential to massively improve the security with which information is transmitted, making messages impossible to clone or intercept without detection. Quantum communication works with quantum bits, or qubits, that can be physically created using atoms, superconductors, and even in defects in materials like diamond. However, photons—individual particles of light—are the best type of qubit for long distance quantum communications.
Photons are appealing for quantum communication in part because they could theoretically be transmitted over existing fiber-optic telecommunications lines that already crisscross the globe. In the future, many types of qubits will likely be utilized because qubit sources, like quantum dots or trapped ions, each have their own advantages for specific applications in quantum computing or different types of quantum sensing.
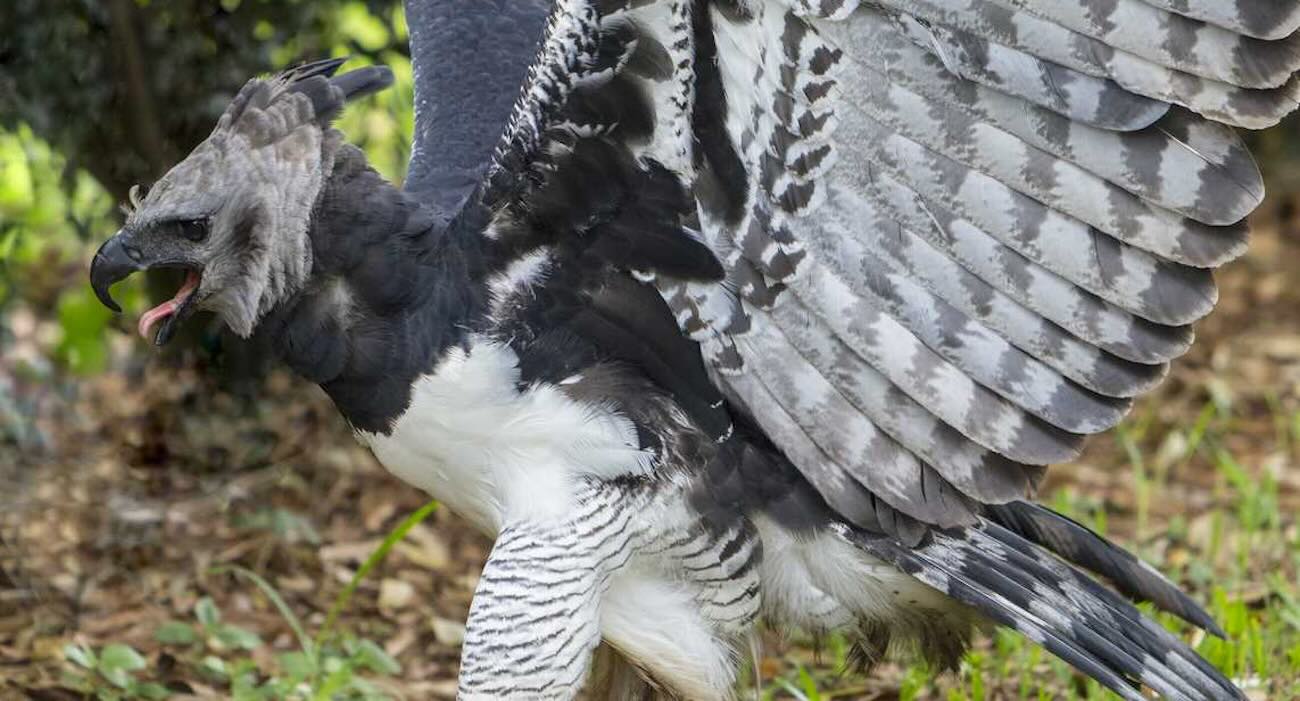
A harpy eagle, South America’s largest bird of prey, has been sighted in a rainforest in southern Mexico, where it was believed to be locally extinct.
Named for the crone-bird hybrid of Greek mythology, the appearance of this large and majestic raptor is worthy of the association. Adult females are much larger than their male counterparts, weighing in at close to 40 pounds, and measuring more than 6 feet from wing tip to wing tip.
Despite a significantly slower and lower birthrate than other eagle species, the harpy eagle numbers in the tens of thousands across South America. In Central America however, they’re virtually extinct.
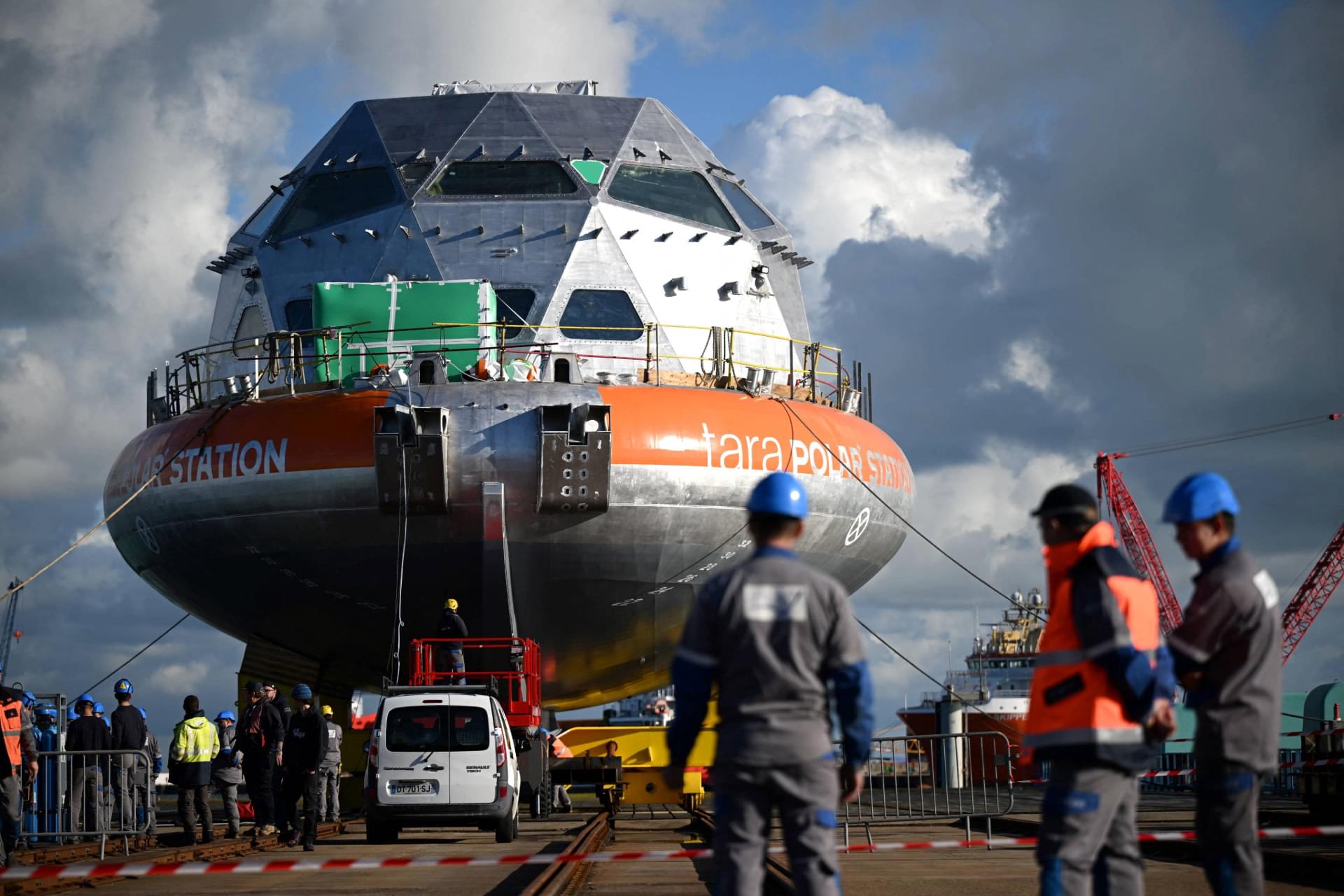
In what’s being called “an unprecedented scientific and human adventure at the North Pole,” the $23 million Tara Polar Station will be the home of a team of 18 people made up of scientists, artists, physicians, journalists, and sailors.
The mission of this drifting science station is to gather data and perform research during the period from November to February, a part of the year that lacks observations because of the dangers inherent in a region of the world that is warming faster than anywhere else.
“We have basically no information,” Tara Ocean Foundation’s Chris Bowler told New Scientist. “Which is alarming, considering it is such a fragile place and it is changing so rapidly.”