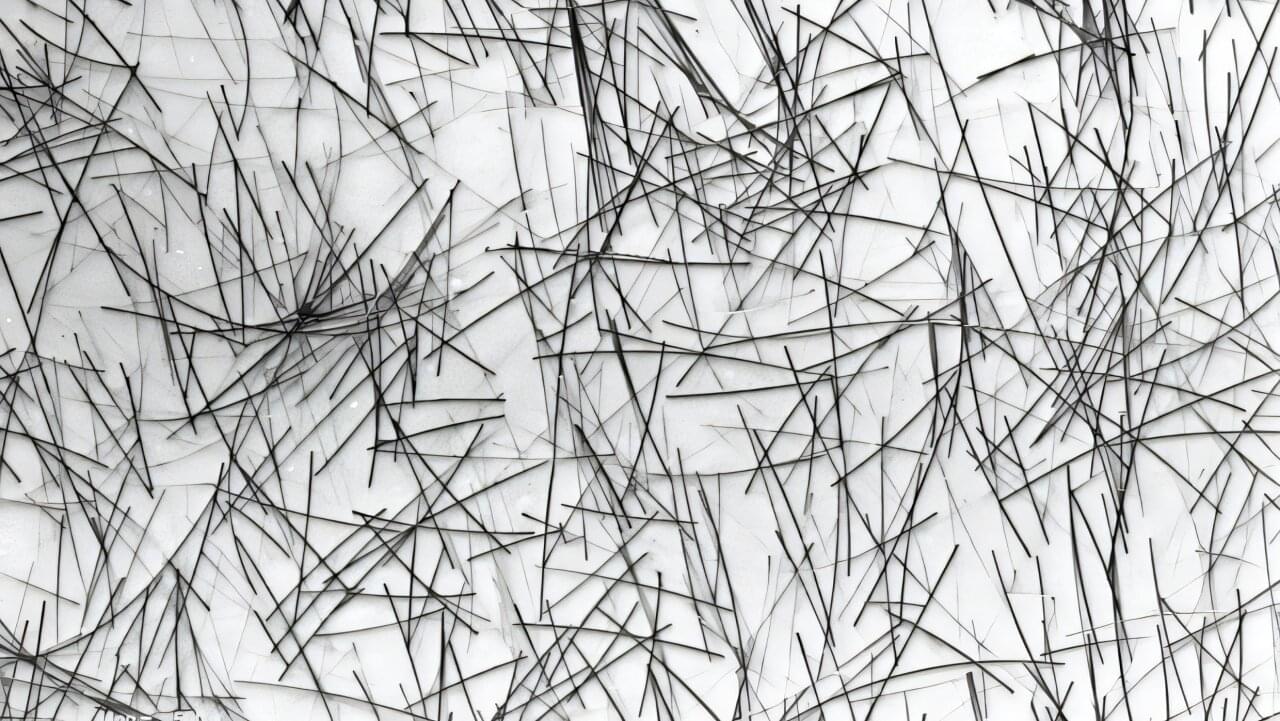
Virginia Tech researchers have created a robotic arm that assists people with mobility issues in complex tasks like preparing a pizza.



Scientific breakthroughs in one disease don’t always shed light on treating other diseases. But that’s been the surprising journey of one Mayo Clinic research team. After identifying a sugar molecule that cancer cells use on their surfaces to hide from the immune system, the researchers have found the same molecule may eventually help in the treatment of type 1 diabetes, once known as juvenile diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes is a chronic autoimmune condition in which the immune system errantly attacks pancreatic beta cells that produce insulin. The disease is caused by genetic and other factors and affects an estimated 1.3 million people in the U.S.
In their studies, the Mayo Clinic researchers took a cancer mechanism and turned it on its head. Cancer cells use a variety of methods to evade immune response, including coating themselves in a sugar molecule known as sialic acid. The researchers found in a preclinical model of type 1 diabetes that it’s possible to dress up beta cells with the same sugar molecule, enabling the immune system to tolerate the cells.

Quantum communication is one of the most exciting frontiers in secure data transmission. Now, a groundbreaking discovery by researchers at Kyoto University offers a major leap forward: a single-photon source created using defective tungsten diselenide (WSe2), enhanced under the influence of a magnetic field. The result? A powerful and controllable emitter that could revolutionize quantum information technologies.
The original article can be accessed at: Phys.org.

The DNA of nearly all life on Earth contains many redundancies, and scientists have long wondered whether these redundancies served a purpose or if they were just leftovers from evolutionary processes. Both DNA and RNA contain codons, which are sequences of three nucleotides that either provide information about how to form a protein with a specific amino acid or tell the cell to stop (a stop signal) during protein synthesis.

Males born in summer months reported higher depression symptom scores than males born during other seasons, according to a study from Kwantlen Polytechnic University. Anxiety symptoms showed no association with season of birth for either sex.
Anxiety and depression remain among the most common mental disorders worldwide, with both conditions contributing to long-term disability, physical comorbidities, and substantial economic losses. A range of factors shape mental health across the lifespan, including housing, income, education, and age. Research into early-life exposures remains limited, particularly exposures shaped by environmental seasonality.
During gestation, exposure to temperature shifts, maternal diet, seasonal infections, and variation in daylight may influence neurodevelopment. Birth season has previously been associated with risk for psychiatric conditions including schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and schizoaffective disorder. Studies examining birth season and depression have produced mixed results, often without stratifying by sex.
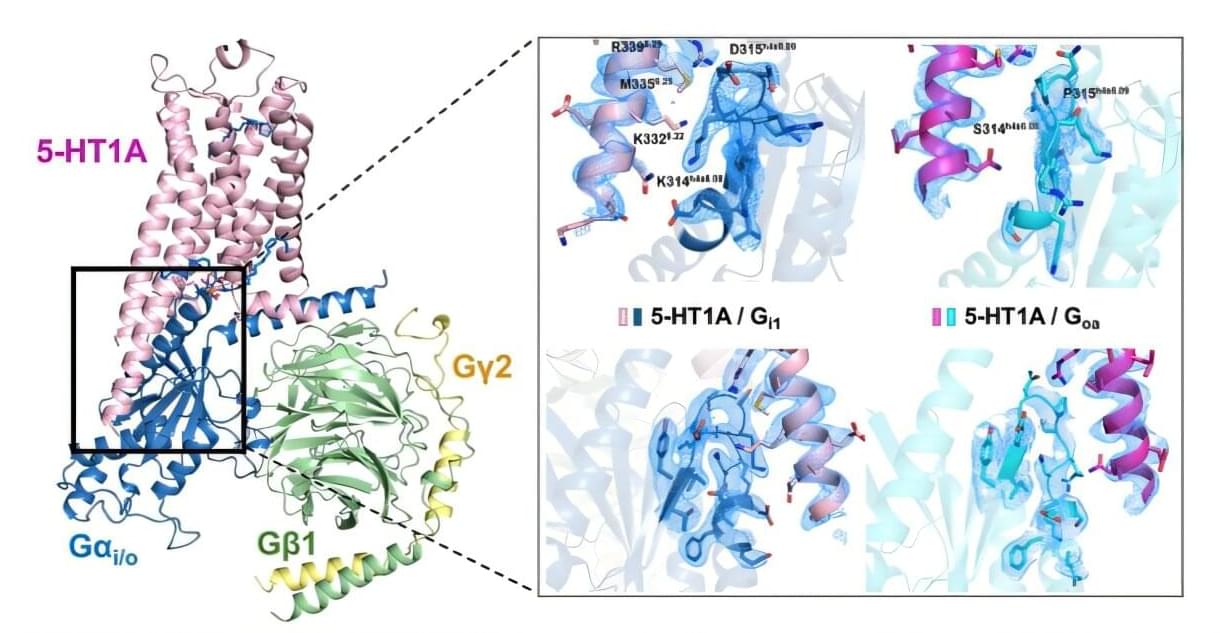
In a discovery that could guide the development of next-generation antidepressants and antipsychotic medications, researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai have developed new insights into how a critical brain receptor works at the molecular level and why that matters for mental health treatments.
The study, published in the online issue of Science Advances, focuses on the 5-HT1A serotonin receptor, a major player in regulating mood and a common target of both traditional antidepressants and newer therapies such as psychedelics. The paper is titled “Structural determinants of G protein subtype selectivity at the serotonin receptor 5-HT1A.”
Despite its clinical importance, this receptor has remained poorly understood, with many of its molecular and pharmacological properties largely understudied—until now.
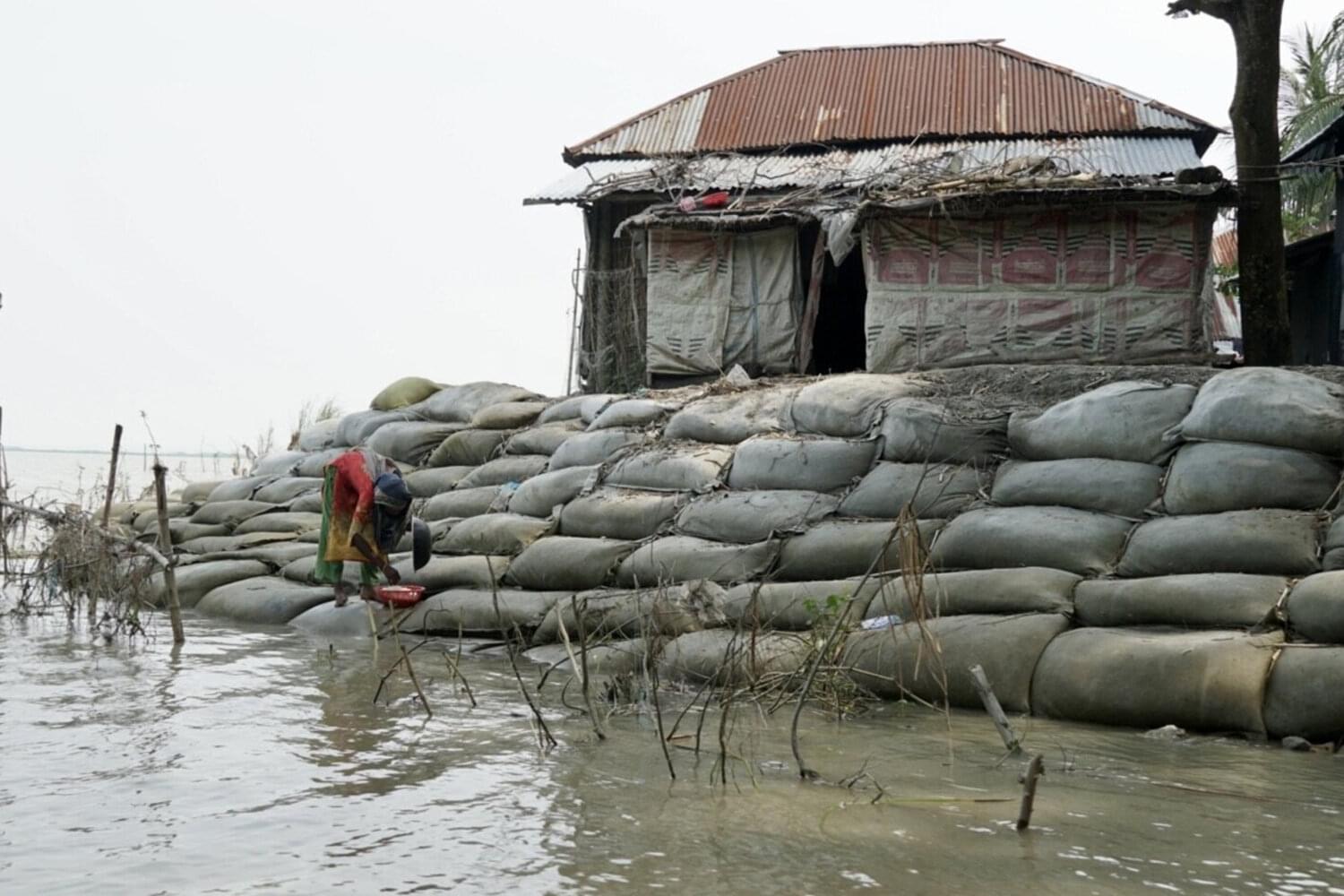

A new Stanford-led study sheds light on “an emerging psychological health crisis” that disproportionately affects girls. Published July 30 in The Lancet Planetary Health, the study is among the first to quantify how repeated climate stressors impact the psychological well-being and future outlook of adolescents in low-resource settings.
Researchers from Stanford’s schools of Medicine, Law, and Sustainability partnered with health experts in Bangladesh to survey more than 1,000 teenagers and conduct focus groups across two regions with starkly different flood exposure.
“What we found really lifts the voices of frontline adolescents —a group whose perspectives and health outcomes are so rarely investigated and communicated,” said lead author Liza Goldberg, an incoming Earth system science Ph.D. student in the Stanford Doerr School of Sustainability.
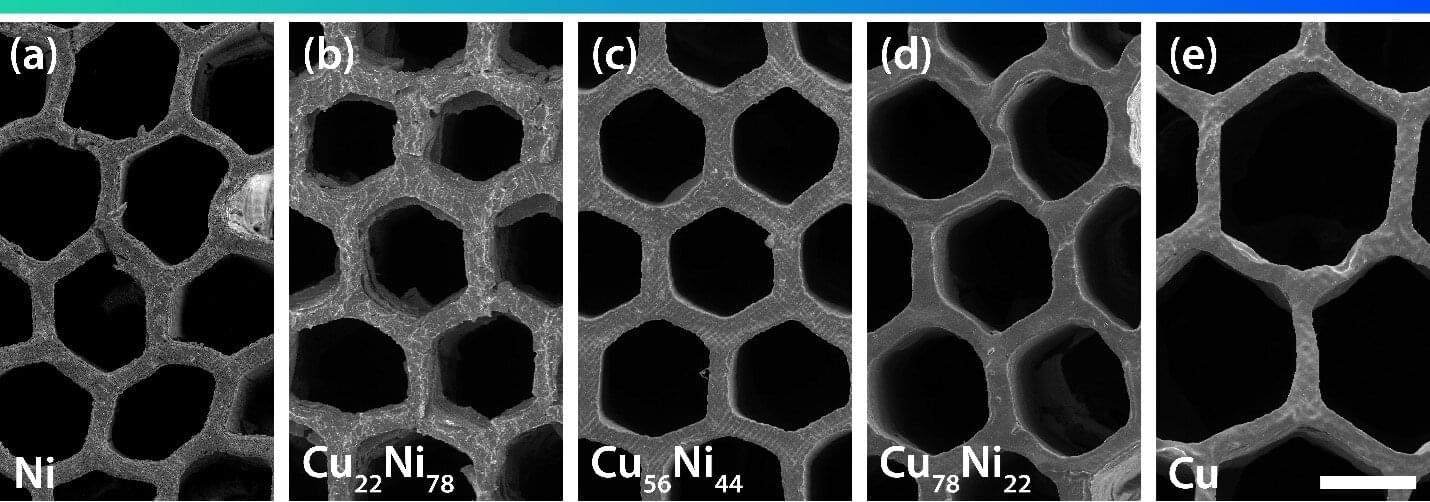
Caltech scientists have developed a method to create metallic objects of a precisely specified shape and composition, giving them unprecedented control of the metallic mixtures, or alloys, they create and the enhanced properties those creations will display. Want a stent that is biocompatible and mechanically robust? How about strong but lightweight satellite components that can operate in space for decades?
