Autism is a neurodevelopmental condition that affects how people’s brains develop and function, impacting behaviour, communication and socialising.
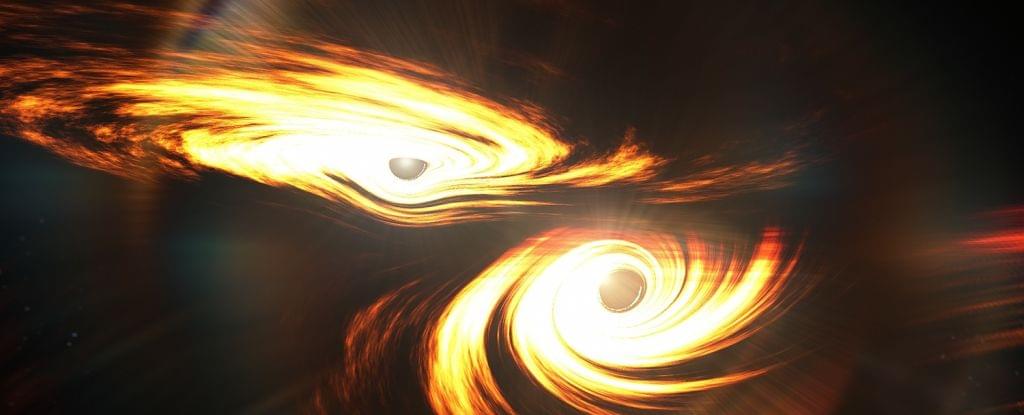



Two black holes have collided in a merger that could revolutionize our understanding of black hole growth.
Named GW 231,123 after the date it was recorded on 23 November 2023, it’s the most massive black hole collision we’ve seen yet, resulting in an object heavier than 225 Suns.
Previously, the most massive black hole collision produced an object 142 times the mass of the Sun.

The artificial intelligence industry is scrambling to reduce its massive energy consumption through better cooling systems, more efficient computer chips, and smarter programming – all while AI usage explodes worldwide.
AI depends entirely on data centers, which could consume three percent of the world’s electricity by 2030, according to the International Energy Agency. That’s double what they use today.
Experts at McKinsey, a US consulting firm, describe a race to build enough data centers to keep up with AI’s rapid growth, while warning that the world is heading toward an electricity shortage.
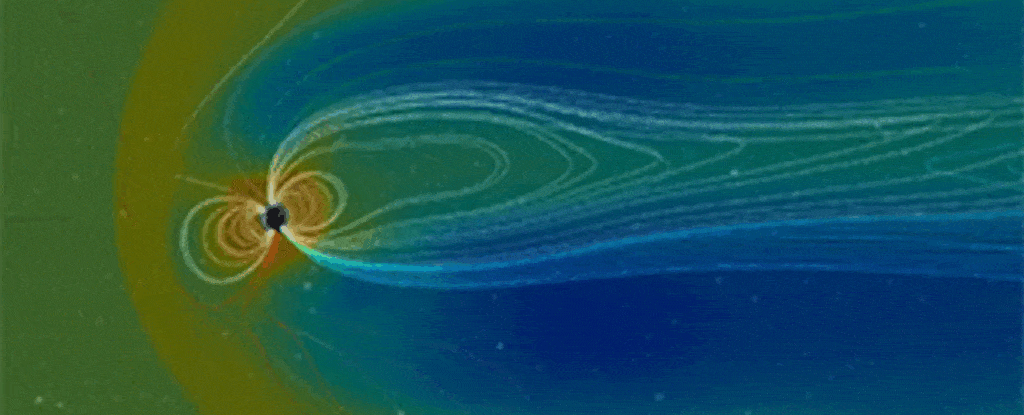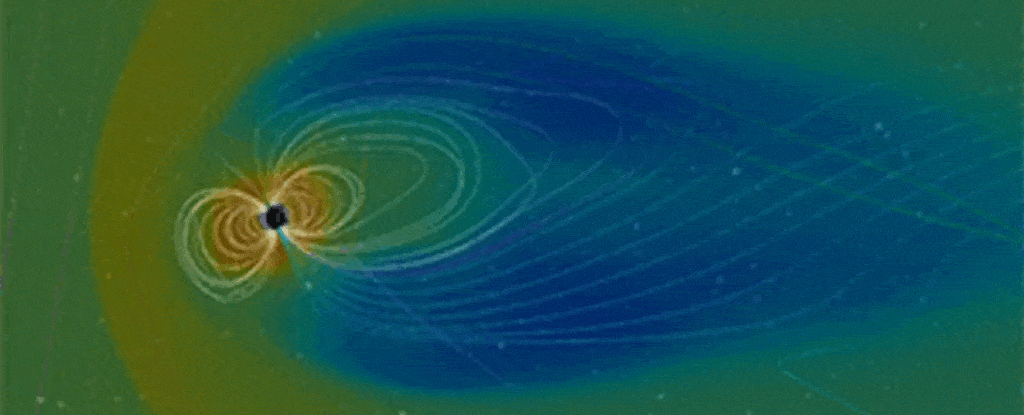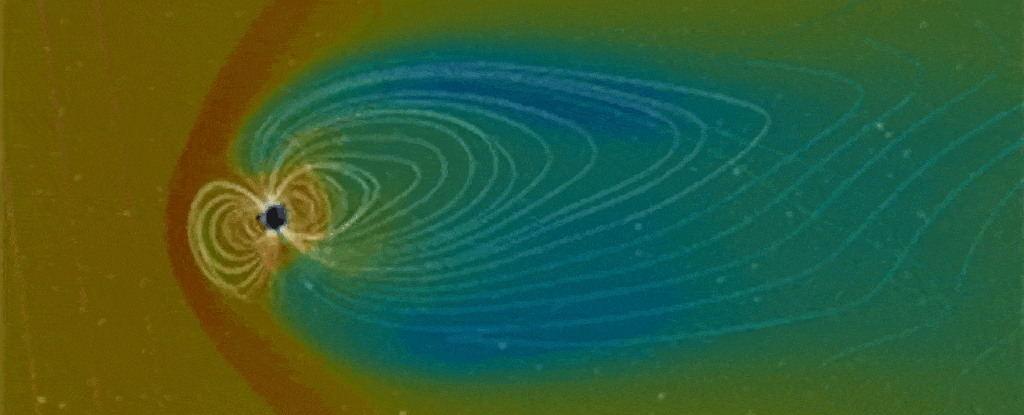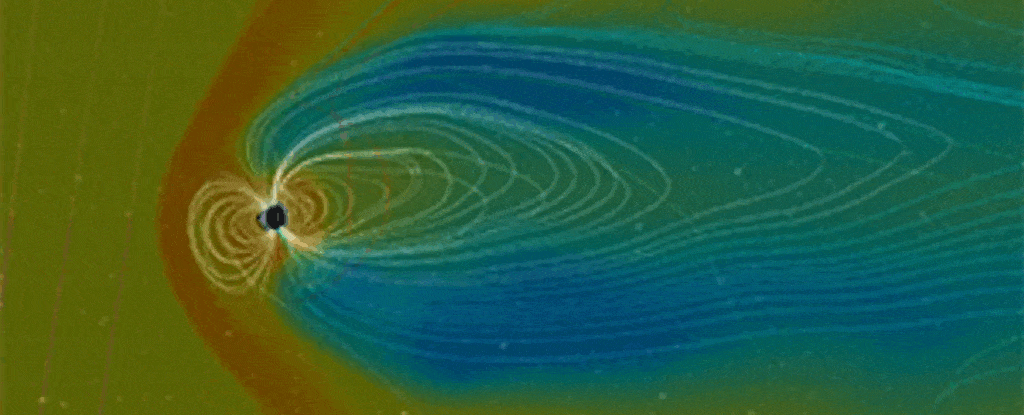
In 2024, researchers transformed readings of an epic upheaval of Earth’s magnetic field flipping 41,000 years ago into an eerie, auditory experience.
Now a team containing some of those same scientists has sonified an even earlier flip, from epochs ago.
The resulting cacophony is an unnerving translation of geological data on the Matuyama-Brunhes reversal, a switching of the planet’s magnetic poles that took place roughly 780,000 years ago.

A team of researchers have made progress in understanding how some of the Universe’s heaviest particles behave under extreme conditions similar to those that existed just after the Big Bang.
A study published in Physics Reports provides new insights into the fundamental forces that shaped our Universe and continues to guide its evolution today.
The research, conducted by an international team from the University of Barcelona, the Indian Institute of Technology, and Texas A&M University, focuses on particles containing heavy quarks, the building blocks of some of the most massive particles in existence.

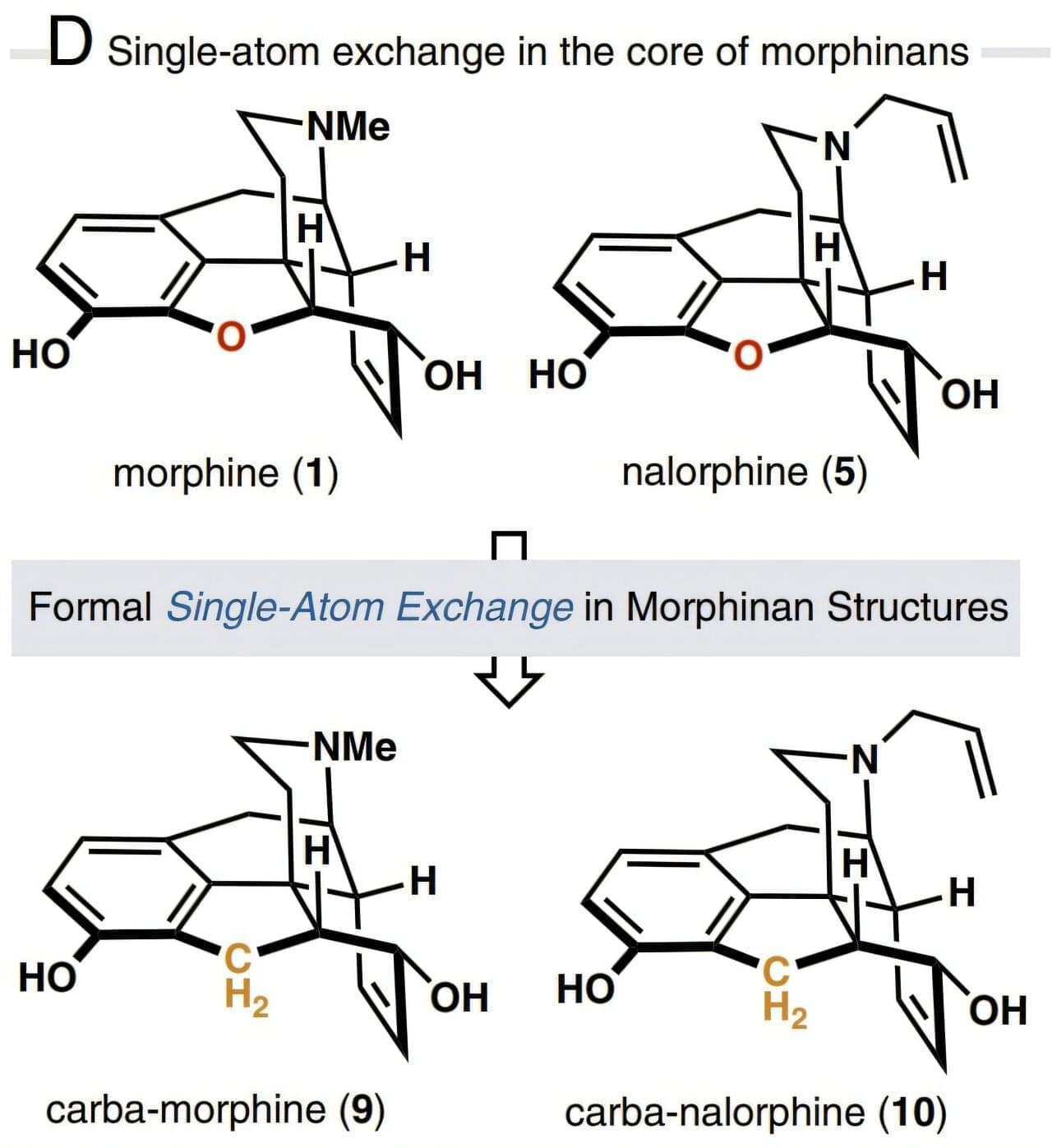
One of the greatest revolutions in the field of pain medication was the isolation of morphine from the opium poppy in the 19th century. Morphine molecules act as painkillers by attaching themselves to the µ-opioid receptor (MOR) in the central nervous system and blocking the brain from sending pain signals to the rest of the body. This potent opioid analgesic also has side effects such as constipation, respiratory depression, and even serious addiction problems.
A new study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences has found that a single heavy atom replacement in the morphine core structure can transform its pharmacological behavior, resulting in reduced respiratory depression and no evidence of reward behavior—a key component of addiction tendencies—even at high doses.
Based on the insight that core-atom changes to the opioid drug molecule may exhibit biological effects distinct from the parent compound, the researchers developed a 15-step total synthesis of a morphine derivative where an oxygen atom in the E-ring is replaced with a methylene (CH2) group and called the new derivative carbamorphine.
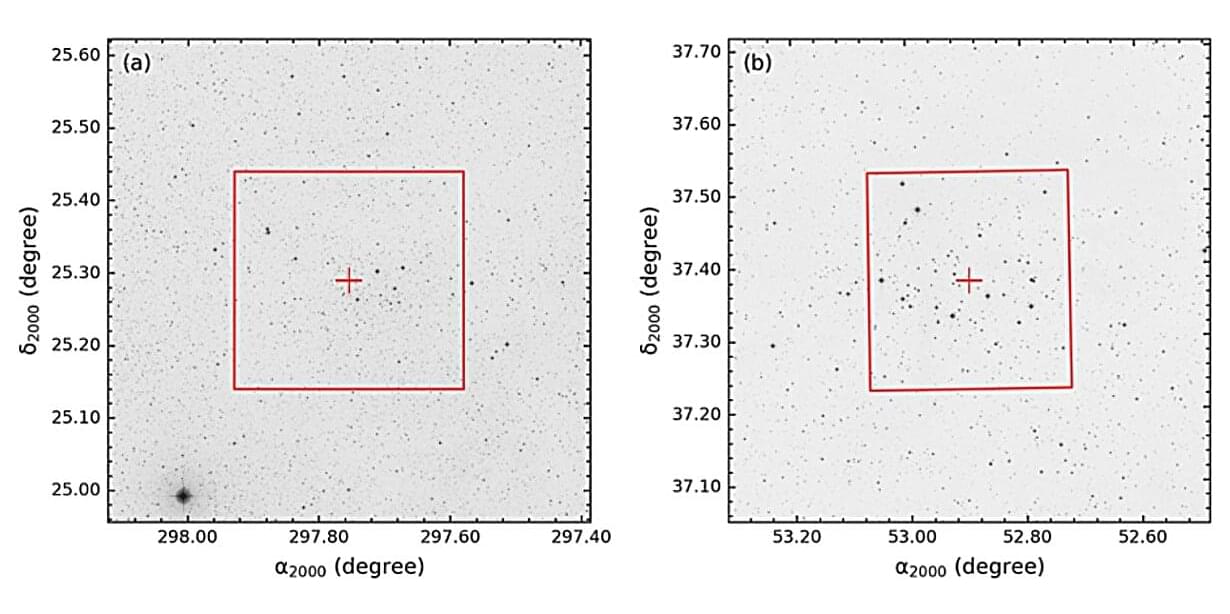
Using the TUBITAK National Observatory and ESA’s Gaia satellite, astronomers from the Istanbul University in Turkey and elsewhere have conducted comprehensive observations of two open clusters, namely: Czernik 41 and NGC 1342. Results of the observational campaign, published July 7 on the arXiv preprint server, deliver important insights into the properties of these clusters.
Open clusters (OCs) are groups of stars formed from the same giant molecular cloud and loosely gravitationally bound to each other. Astronomers are interested in inspecting OCs in detail as such studies could be crucial for improving our understanding of the formation and evolution of our galaxy.
That is why a group of researchers led by Istanbul University’s Burçin Tanık Öztürk decided to take a closer look at two well-known OCs—Czernik 41, discovered in 1966, and NGC 1,342, dubbed the Stingray Cluster, which was identified by William Herschel in 1799. For this purpose, they employed the T100 telescope at the TUBITAK National Observatory in Turkey and analyzed the data from the Gaia satellite.

University of Leeds psychologists report that stress appraisal and perceived stress act as key conduits linking childhood trauma to adult depression, anxiety, defeat, and entrapment.
Childhood trauma affects nearly one third of young people in the United Kingdom. Early experiences of abuse or neglect have been associated with depression, anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder, and substance use later in life.
Exposure to multiple types of trauma has been linked to higher rates of suicidal thoughts and suicide attempts. Females who experience childhood sexual abuse can face substantially elevated risks of attempting suicide compared to peers without such histories.
