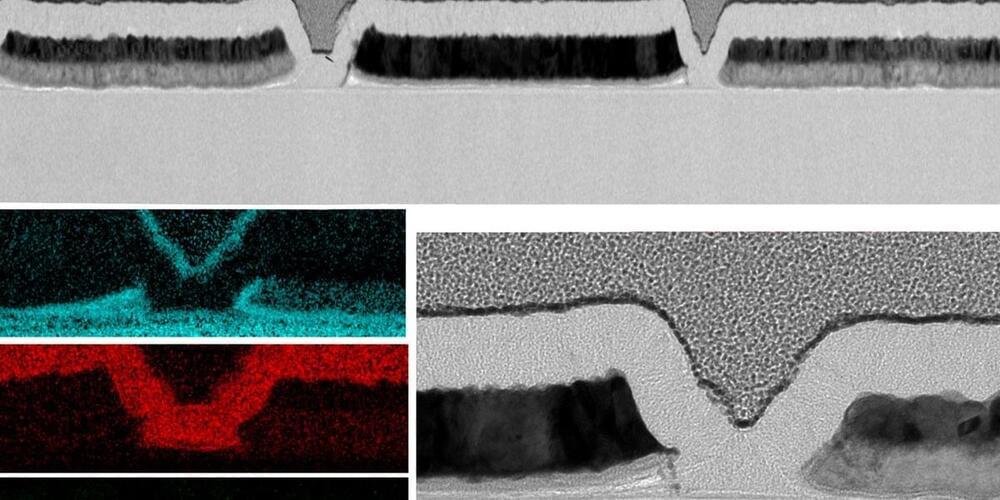
Engineers share progress in the latest CNT transistor designs at IEDM.

The world’s first human trial of a drug that can regenerate teeth will begin in a few months, less than a year on from news of its success in animals. This paves the way for the medicine to be commercially available as early as 2030.
The trial, which will take place at Kyoto University Hospital from September to August 2025, will treat 30 males aged 30–64 who are missing at least one molar. The intravenous treatment will be tested for its efficacy on human dentition, after it successfully grew new teeth in ferret and mouse models with no significant side effects.
“We want to do something to help those who are suffering from tooth loss or absence,” said lead researcher Katsu Takahashi, head of dentistry and oral surgery at Kitano Hospital. “While there has been no treatment to date providing a permanent cure, we feel that people’s expectations for tooth growth are high.”

Brain edema can accompany large ischemic strokes and can increase stroke-related morbidity and mortality. The past few decades have seen no advances in pharmacologic treatment of brain edema. These investigators conducted a manufacturer-funded, randomized, placebo-controlled trial of glibenclamide, a sulfonylurea 1–receptor inhibitor that can decrease brain edema. (Glibenclamide is approved to treat type 2 diabetes.) In a previous study, it was associated with fewer deaths from neurologic causes, but its use in patients with stroke is not widespread.
Eligible patients had large ischemic strokes that could be treated within 10 hours of onset. A large hemispheric infarct in at least the middle cerebral artery territory was defined as either an Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score of 1 to 5 or lesion volumes of 80 mL to 300 mL on computed-tomography perfusion or diffusion-weighted imaging. Glibenclamide (8.6 mg) was given to half the study participants intravenously over 72 hours.
The study was halted early due to underenrollment. Of 535 enrolled patients, 431 were in the intended age range (18–70) and had complete data (mean age, 58; 33% women; median NIH Stroke Scale [NIHSS] score, 19). Treatment began at an average of 9 hours after symptom onset. No favorable shift with glibenclamide occurred on the primary outcome, the 90-day modified Rankin Scale (mRS). Mortality was similar in the two groups (glibenclamide, 32%; placebo, 29%). Hypoglycemia was seen in 6% of glibenclamide recipients and 2% of placebo recipients. Subgroup analysis revealed a signal of potential benefit with glibenclamide in patients with NIHSS scores of 20 or less.
Neural networks are at the core of artificial intelligence (AI), fueling a variety of applications from spotting objects in photos to translating languages. In this article, we’ll dive into what neural networks are, how they work, and why they’re a big deal in our technology-driven world today.
Index · 1: Understanding the Basics ∘ 1.1: What are Neural Networks? ∘ 1.2: Types of Neural Networks
· 2: The Architecture of Neural Networks ∘ 2.1: The Structure of a Neuron ∘ 2.2: Layers ∘ 2.3: The Role of Layers in Learning.
With brains that process information almost like a computer, the sea creatures already use tools and can be social. But they need to make a few changes before they can take over the world.


That means digging all the trenching and building out all the electrical distribution equipment on site, if not all the chargers, with a microgrid that’s capable of working as well in the future with 12 MW of power as it does with just 4 MW.
“I think this is the same challenge that all of these large sites are facing—it takes an extremely long time to get the power from the utility. Meanwhile, you don’t need it immediately. So how do you create this sort of staged future-proof solution where you’re not having to open the roads multiple times? You want one construction phase and you want that site to support the future demand,” Putignano said.
For fleets that need their own private charging infrastructure, there are other things to think about, too. Energy management solutions are as important here—microgrids as well as battery storage and battery-buffered chargers will play an important role, for example. But not every energy management solution is charger-agnostic, and the collapse of charger manufacturers like Juicebox and Tritium highlight the perils of being stuck in a walled garden belonging to a dead company.
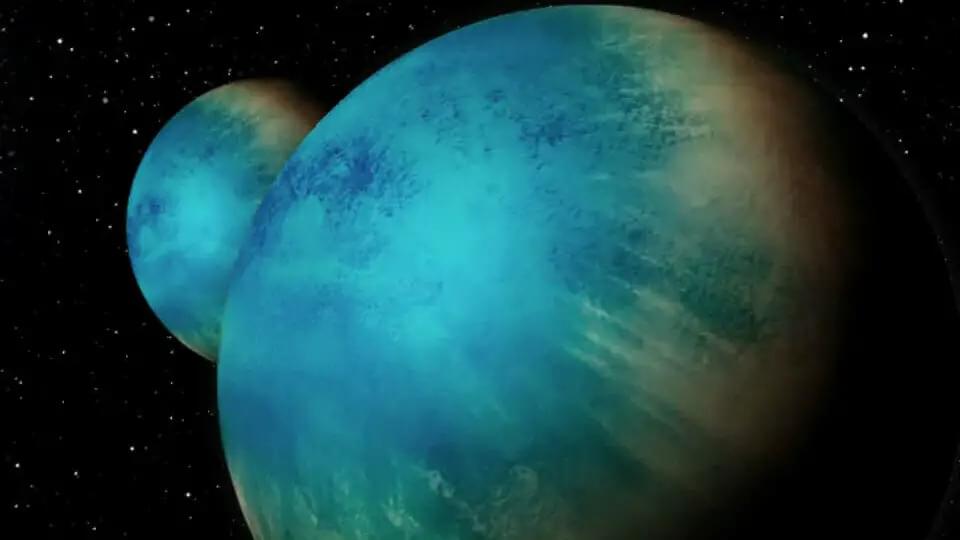


Hubble Finds Two Exoplanets Covered in Oceans 1,000 Miles Deep, Possibly Hiding Exotic Forms of Life.
Using data from the Hubble telescope, scientists have discovered two exoplanets, Kepler-138c and Kepler-138d, which appear to be “water worlds” with oceans potentially as deep as 1,000 miles. These planets, located 218 light-years away, are unlike any in our solar system, with low densities suggesting that they are primarily composed of water. Though they may not have surface oceans like Earth, the atmosphere on these planets could be made of steam, with high-pressure liquid water existing beneath. This breakthrough raises new questions about the habitability of exoplanets.
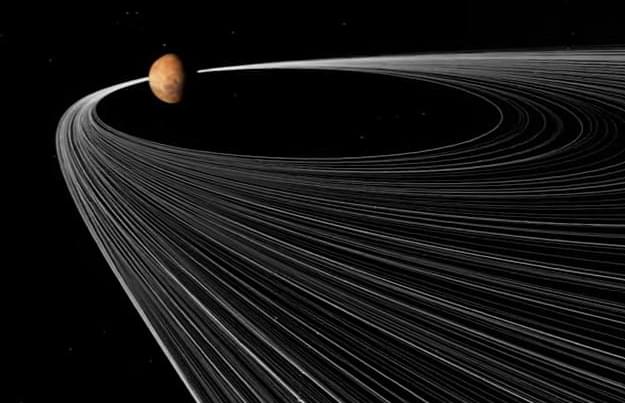

A NASA study using a series of supercomputer simulations reveals a potential new solution to a longstanding Martian mystery: How did Mars get its moons? The first step, the findings say, may have involved the destruction of an asteroid.
The research team, led by Jacob Kegerreis, a postdoctoral research scientist at NASA’s Ames Research Center in California’s Silicon Valley, found that an asteroid passing near Mars could have been disrupted—a nice way of saying “ripped apart”—by the red planet’s strong gravitational pull.
The paper is published in the journal Icarus.