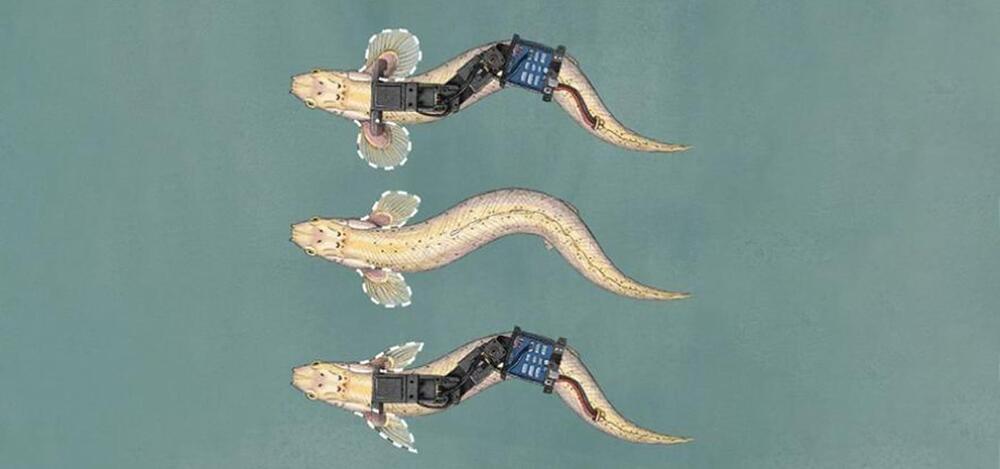
Researchers at the University of Cambridge are close to recreating the movements of the world’s first land animals.

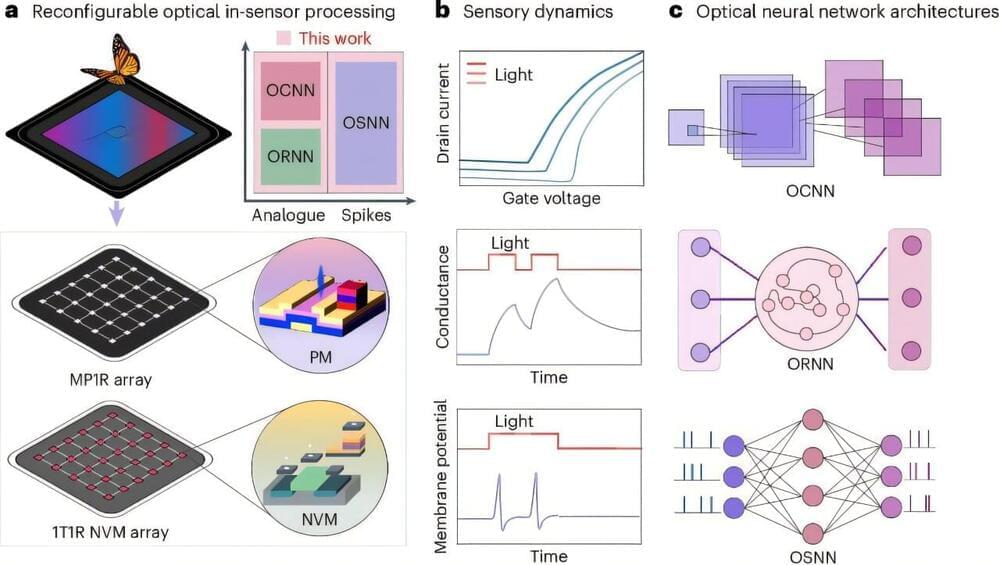
In recent years, engineers have been trying to create hardware systems that better support the high computational demands of machine learning algorithms. These include systems that can perform multiple functions, acting as sensors, memories and computer processors all at once.
Researchers at Peking University recently developed a new reconfigurable neuromorphic computing platform that integrates sensing and computing functions in a single device. This system, outlined in a paper published in Nature Electronics, is comprised of an array of multiple phototransistors with one memristor (MP1R).
“The inspiration for this research stemmed from the limitations of traditional vision computing systems based on the CMOS von Neumann architecture,” Yuchao Yang, senior author of the paper, told Tech Xplore.
Generative artificial intelligence probably won’t change your life in 2025 — at least, not more than it already has, according to Google CEO Sundar Pichai.
When OpenAI launched ChatGPT two years ago, generative AI quickly captured the imagination of users around the world. Now, with the industry’s competitive landscape somewhat established — multiple big tech companies, including Google, have competing models — it’ll take time for another technological breakthrough to shock the AI industry into hyper-speed development again, Pichai said at the New York Times’ DealBook Summit last week.
“I think the progress is going to get harder. When I look at [2025], the low-hanging fruit is gone,” said Pichai, adding: “The hill is steeper … You’re definitely going to need deeper breakthroughs as we get to the next stage.”
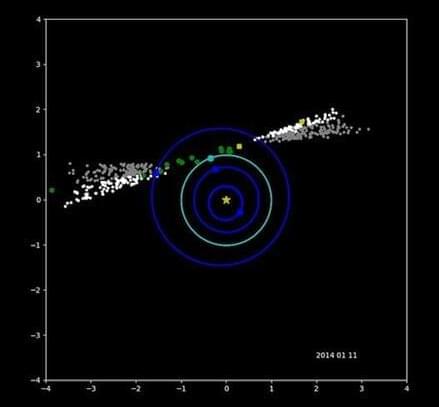
NEOWISE contributed to planetary defense efforts with its research to catalog near-Earth objects. Over the past decade, it helped planetary defenders like us and our colleagues study near-Earth objects.
NEOWISE was a game-changing mission, as it revolutionized how to survey near-Earth objects.
The NEOWISE mission continued to use the spacecraft from NASA’s WISE mission, which ran from late 2009 to 2011 and conducted an all-sky infrared survey to detect not only near-Earth objects but also distant objects such as galaxies.

Artificial intelligence is quickly becoming an integral tool in health care. In our new collection, the editors of NEJM AI provide insight into how the use of AI in clinical practice can improve patient care and outcomes.
Featured in this collection:
GPT versus Resident Physicians — A Benchmark Based on Official Board Scores Artificial Intelligence–Powered Rapid Identification of ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction via Electrocardiogram (ARISE) — A Pragmatic Randomized Controlled Trial Use of GPT-4 to Diagnose Complex Clinical Cases.
Download now.
NEJM AI is a monthly journal from NEJM Group that explores innovative applications of artificial intelligence and machine learning in clinical medicine, serving as a trusted guide to help you navigate the AI revolution.
Access your copy of this valuable collection and discover how AI is transforming and advancing care.
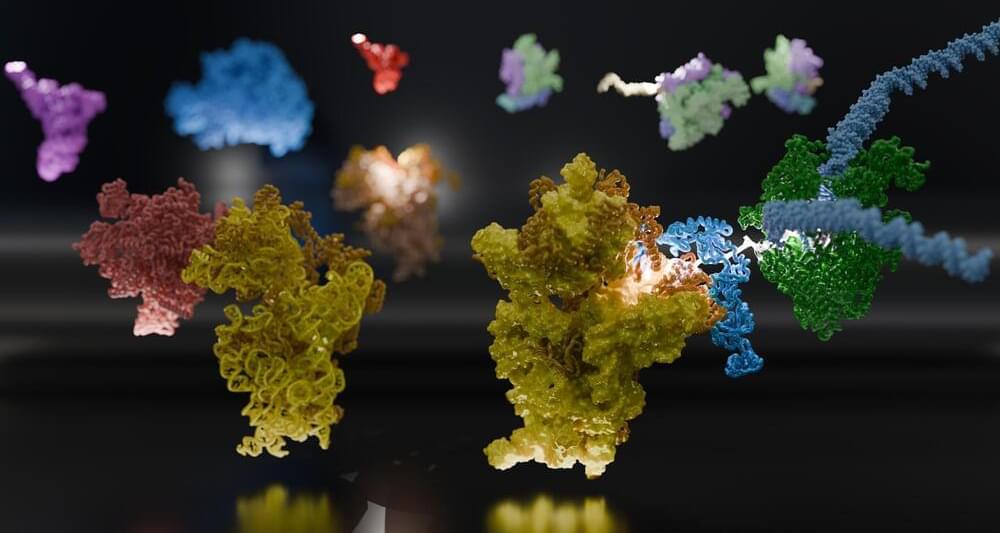
Within a cell, DNA carries the genetic code for building proteins. To build proteins, the cell makes a copy of DNA, called mRNA. Then, another molecule called a ribosome reads the mRNA, translating it into protein. But this step has been a visual mystery; scientists previously did not know how the ribosome attaches to and reads mRNA.
Now, a team of international scientists, including University of Michigan researchers, has used advanced microscopy to image how ribosomes recruit to mRNA while it’s being transcribed by an enzyme called RNA polymerase (RNAP). Their results, which examine the process in bacteria, are published in the journal Science.
“Understanding how the ribosome captures or ‘recruits’ the mRNA is a prerequisite for everything that comes after, such as understanding how it can even begin to interpret the information encoded in the mRNA,” said Albert Weixlbaumer, a researcher from Institut de génétique et de biologie moléculaire et cellulaire in France who co-led the study.
Abstract. Pharmacological inhibition of the mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway with rapamycin can extend lifespan in several organisms. Although this includes the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans, effects in this species are relatively weak and sometimes difficult to reproduce. Here we test effects of drug dosage and timing of delivery to establish the upper limits of its capacity to extend life, and investigate drug effects on age-related pathology and causes of mortality. Liposome-mediated rapamycin treatment throughout adulthood showed a dose-dependent effect, causing a maximal 21.9% increase in mean lifespan, but shortening of lifespan at the highest dose, suggesting drug toxicity. Rapamycin treatment of larvae delayed development, weakly reduced fertility and modestly extended lifespan. By contrast, treatment initiated later in life robustly increased lifespan, even from Day 16 (or ~70 years in human terms). The rapalog temsirolimus extended lifespan similarly to rapamycin, but effects of everolimus were weaker. As in mouse, rapamycin had mixed effects on age-related pathologies, inhibiting one (uterine tumor growth) but not several others, suggesting a segmental antigeroid effect. These findings should usefully inform future experimental studies with rapamycin and rapalogs in C. elegans.
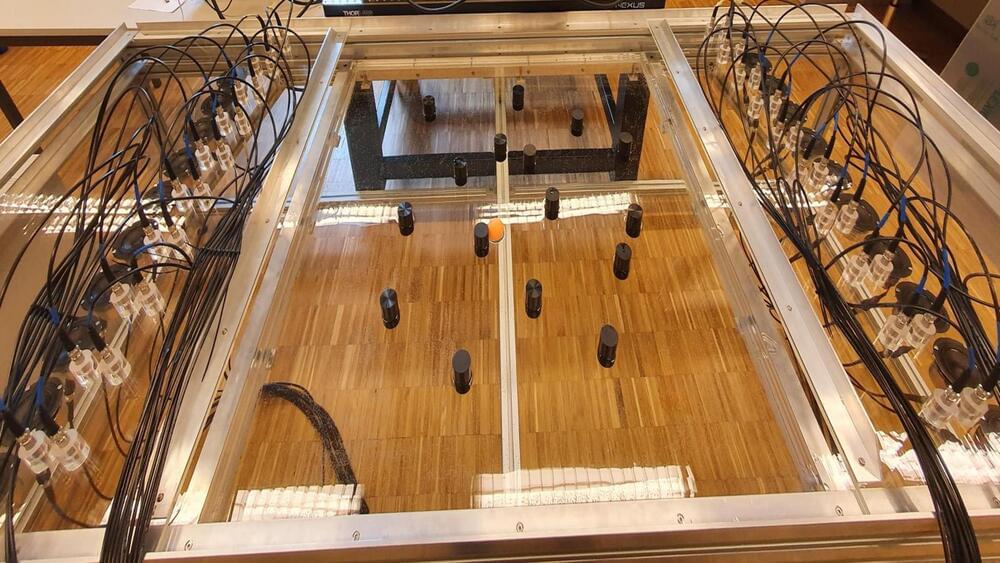

The new sound-based method moves objects regardless of surroundings or properties.
Researchers have successfully manipulated the movement of objects using sound. They directed floating objects around obstacles in an aquatic environment, unveiling new possibilities for noninvasive, targeted drug delivery and other biomedical applications.
Researchers from EPFL’s School of Engineering employed optics-inspired techniques to achieve this object manipulation.
“Optical tweezers work by creating a light ‘hotspot’ to trap particles, like a ball falling into a hole. But if there are other objects in the vicinity, this hole is difficult to create and move around,” said Romain Fleury, head of the Laboratory of Wave Engineering in EPFL’s School of Engineering.
