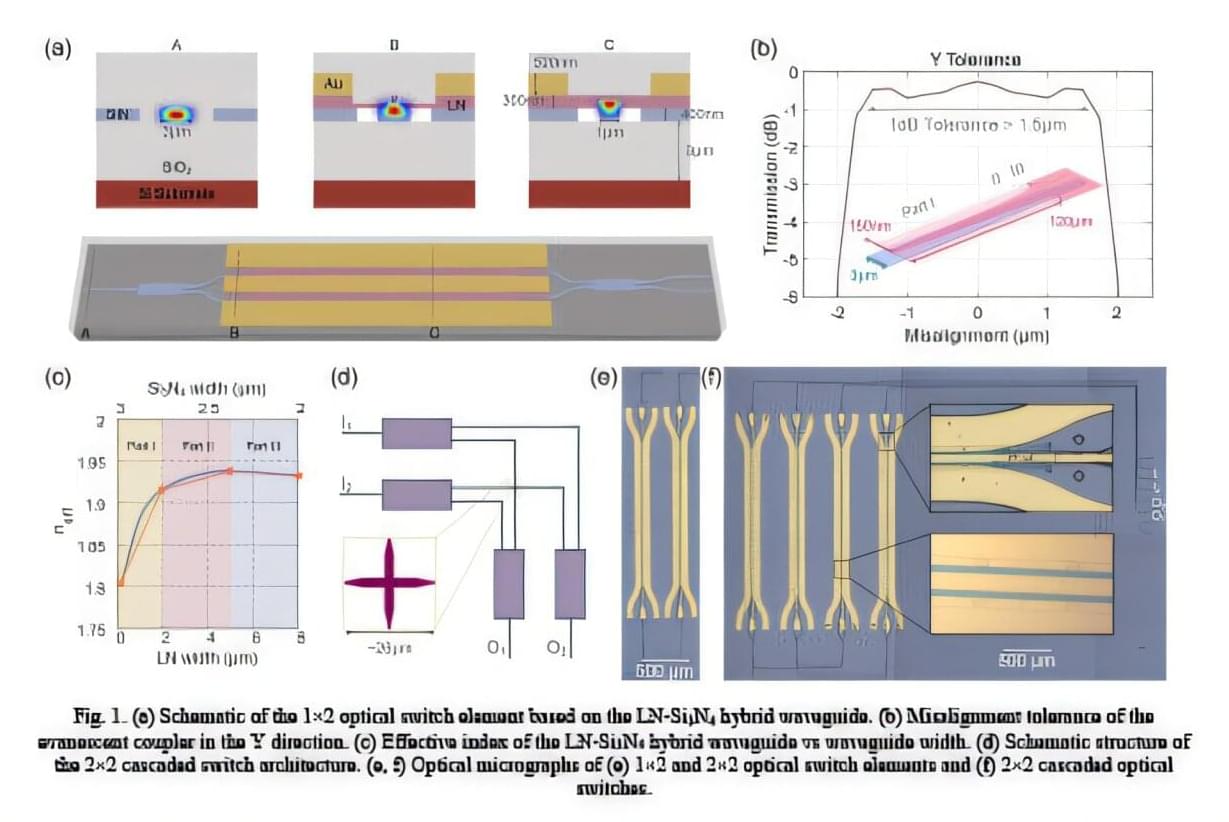
Researchers have developed a high-speed electro-optic switch that is energy-efficient, has low crosstalk and works across a broad bandwidth. Made using a scalable, chip-friendly process, this switch could enhance data capacity in optical networks and data centers by improving signal routing and switching.
Jinwei Su from the Shanghai Jiao Tong University in China will present this research at Optical Fiber Communications Conference and Exhibition (OFC), the global event for optical communications and networking, which will take place 30 March–3 April 2025 at the Moscone Center in San Francisco.
As artificial intelligence and cloud computing rapidly advance, the demand for high-capacity data exchange continues to rise. Optical switching, with its broad bandwidth and low latency, is emerging as one of the most promising solutions to address this challenge. To achieve nanosecond-scale optical switching, the researchers fabricated a 2×2 cascaded electro-optic switch by micro-transfer printing pre-etched thin-film lithium niobate (TFLN) onto silicon nitride.